You are currently looking at a table that contains data from an e-commerce platform, each row contains a list of items(Item number) that were present in the cart, when the customer makes a change to the cart the entire information is saved as a separate list and appended to an existing list for the duration of the customer session, to identify all the items customer bought you have to make a unique list of items, you were asked to create a unique item’s list that was added to the cart by the user, fill in the blanks of below query by choosing the appropriate higher-order function?
You are currently looking at a table that contains data from an e-commerce platform, each row contains a list of items(Item number) that were present in the cart, when the customer makes a change to the cart the entire information is saved as a separate list and appended to an existing list for the duration of the customer session, to identify all the items customer bought you have to make a unique list of items, you were asked to create a unique item’s list that was added to the cart by the user, fill in the blanks of below query by choosing the appropriate higher-order function?
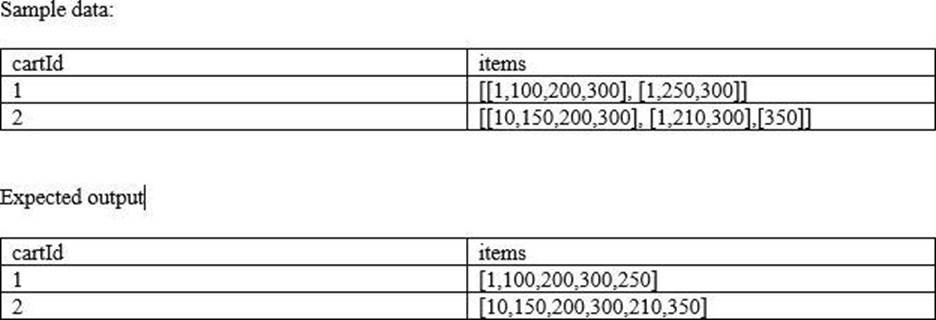
Note: See below sample data and expected output.
Schema: cartId INT, items Array<INT>
Fill in the blanks:
Fill in the blanks:
SELECT cartId, _(_(items)) FROM carts
A . ARRAY_UNION, ARRAY_DISCINT
B. ARRAY_DISTINCT, ARRAY_UNION
C. ARRAY_DISTINCT, FLATTEN
D. FLATTEN, ARRAY_DISTINCT
E. ARRAY_DISTINCT, ARRAY_FLATTEN
Answer: C
Explanation:
FLATTEN -> Transforms an array of arrays into a single array.
ARRAY_DISTINCT -> The function returns an array of the same type as the input argument where all duplicate values have been removed.

Table
Description automatically generated
Latest Databricks Certified Professional Data Engineer Dumps Valid Version with 222 Q&As
Latest And Valid Q&A | Instant Download | Once Fail, Full Refund

