What is the nature and behavior of the Virtual IP for the VSX pair if clients are connected to the access switch using VSX as the default gateway?
Refer to the exhibit.
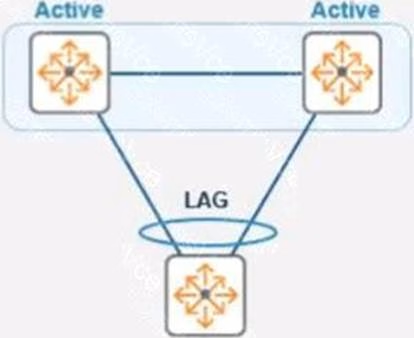
In the given topology, a pair of Aruba CX 8325 switches are in a VSX stack using the active gateway.
What is the nature and behavior of the Virtual IP for the VSX pair if clients are connected to the access switch using VSX as the default gateway?
A . Virtual IP is active on the primary VSX switch
B . Virtual floating IP will failover in case of a failure
C . Virtual IP is active on both CX switches
D . Virtual IP uses SVI IP address synced with VSX
Answer: A
Explanation:
Virtual Switching Extension (VSX) is a feature that allows two Aruba CX switches to operate as a single logical device with a single control plane and data plane. VSX provides high availability, scalability, and simplified management for campus and data center networks3. In VSX, one switch is designated as the primary switch and the other as the secondary switch. The primary switch owns and responds to ARP Address Resolution Protocol. ARP is a communication protocol used for discovering the link layer address, such as a MAC address, associated with a given internet layer address, typically an IPv4 address. This mapping is a critical function in the Internet protocol suite. requests for the virtual IP address of the VSX pair4. The virtual IP address is used as the default gateway for clients connected to the access switch. If the primary switch fails, the secondary switch takes over the virtual IP address and continues to forward traffic for the clients5.
References:
3 https://www.arubanetworks.com/techdocs/AOS-CX_10_04/UG/Content/cx-ug/vsx/vsx-overview.htm
4 https://www.arubanetworks.com/techdocs/AOS-CX_10_04/UG/Content/cx-ug/vsx/vsx-ip-addressing.htm
5 https://www.arubanetworks.com/techdocs/AOS-CX_10_04/UG/Content/cx-ug/vsx/vsx-failover.htm
Latest HPE6-A85 Dumps Valid Version with 60 Q&As
Latest And Valid Q&A | Instant Download | Once Fail, Full Refund

