What is the inheritance pattern of the observed trait indicated by the pedigree below?
What is the inheritance pattern of the observed trait indicated by the pedigree below?
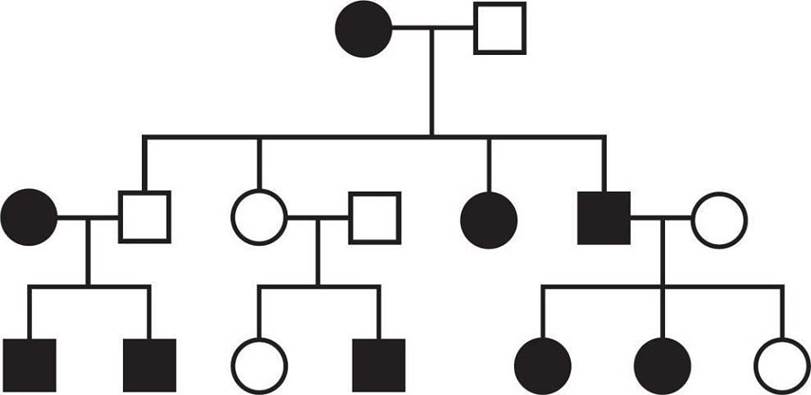
A . Autosomal recessive
B . Autosomal dominant
C . X-linked recessive
D . X-linked
E . Cannot be determined
Answer: A
Explanation:
Pedigrees show the distribution of a single observable trait, or phenotype, across a family tree. In classical genetics, each phenotype is determined by a combination of two alleles contributed by two copies of the same (but not necessarily identical) chromosome. One allele is generally dominant, meaning it is expressed if it is present at all. In contrast, the other allele is recessive, meaning it is only expressed in the absence of a dominant allele, which generally means two copies need to be inherited to display the recessive phenotype. The exceptions are those alleles found on the X chromosome in males; males’ sex chromosomes include only one X (and one Y), so each trait coded for on the X chromosome is determined by only one allele instead of a combination of two alleles. This means it’s statistically more likely for males to inherit recessive X-linked traits since only one copy of the recessive alleles needs to be inherited to display the recessive phenotypes, as opposed to the usual two.
The fastest way to determine which inheritance pattern is shown by a pedigree, then, is to use the Kaplan shortcut: Identify whether two matching parents have an opposite offspring. If two affected parents have an unaffected offspring, both parents must have been heterozygous (having one of each allele), and the trait must be dominant: Rr × Rr C> rr. If two unaffected parents have an affected offspring, both parents must have one again been heterozygous, but in that situation, the trait being tracked must have been the recessive one: Rr × Rr C> rr. In the pedigree provided in this question, generational skipping occurs in the middle portion: Generation 2 has two unaffected parents, but generation 3 has an affected offspring. This indicates a recessive trait. Since a roughly equal number of males and females are affected (5 : 4 ratio), this is an autosomal trait.
Latest PCAT Dumps Valid Version with 282 Q&As
Latest And Valid Q&A | Instant Download | Once Fail, Full Refund

