Test Prep PCAT Pharmacy College Admission Test Online Training
Test Prep PCAT Online Training
The questions for PCAT were last updated at Mar 03,2026.
- Exam Code: PCAT
- Exam Name: Pharmacy College Admission Test
- Certification Provider: Test Prep
- Latest update: Mar 03,2026
In photosynthesis, high-energy electrons move through electron transport chains to produce ATP and NADPH.
Which of the following provides the energy to create high energy electrons?
- A . O2
- B . Light
- C . Water
- D . NADP+
- E . NADH
B
Explanation:
Electrons trapped by the chlorophyll P680 molecule in photosystem II are energized by light. They are then transferred to electron acceptors in an electron transport chain.
Cyanide is a poison that binds to the active site of the enzyme cytochrome c and prevents its activity. Cyanide is a(n):
- A . Prosthetic group
- B . Cofactor
- C . Reverse regulator
- D . Coenzyme
- E . Inhibitor
E
Explanation:
Enzyme inhibitors attach to an enzyme and block substrates from entering the active site, thereby preventing enzyme activity. As stated in the question, cyanide is a poison that irreversibly binds to an enzyme and blocks its active site, thus fitting the definition of an enzyme inhibitor.
The synaptonemal complex is present in which of the following phases of the cell cycle?
- A . Telophase of meiosis I
- B . Metaphase of meiosis II
- C . Metaphase of meiosis I
- D . Metaphase of mitosis
- E . Telophase of meiosis II
A
Explanation:
The synaptonemal complex is the point of contact between homologous chromatids. It is formed when nonsister chromatids exchange genetic material through crossing over. Once meiosis I has completed, crossovers have resolved and the synaptonemal complex no longer exists. Rather, sister chromatids are held together at their centromeres prior to separation in anaphase II.
Leaves have parallel veins: A. Monocots
B. Nonvascular plants
C. Gymnosperms
D. Dicots
E. Angiosperms
Explanation:
Monocots differ from dicots in that they have one cotyledon, or embryonic leaf in their embryos. They also have parallel veination, fibrous roots, petals in multiples of three, and a random arrangement of vascular bundles in their stems.
In ferns, the joining of egg and sperm produces a zygote, which will grow into the:
- A . Gametophyte
- B . Sporophyte
- C . Seedling
- D . Sporangium
- E . Spore
B
Explanation:
In ferns, the mature diploid plant is called a sporophyte. Sporophytes undergo meiosis to produce spores, which develop into gametophytes, which produce gametes.
The structure in which microspores are produced:
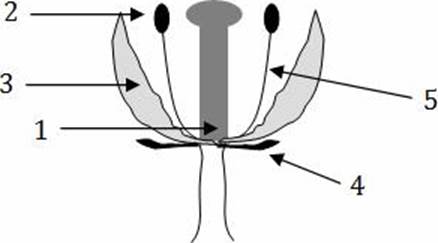
- A . 3
- B . 1
- C . 5
- D . 4
- E . 2
E
Explanation:
Anthers produce microspores (the male gametophytes of flowering plants), which undergo meiosis to produce pollen grains.
The structures composed solely of diploid cells:
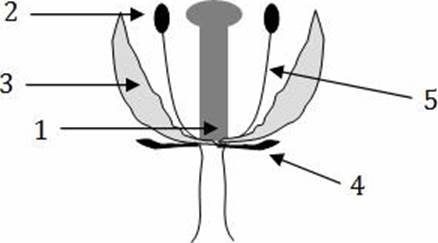
- A . 1, 2, and 3
- B . 3, 4, and 5
- C . 1, 4, and 5
- D . 2, 3, and 4
- E . 1, 2, and 4
B
Explanation:
In flowering plants, the anthers house the male gametophytes (which produce sperm) and the pistils house the female gametophytes (which produce eggs). Eggs and sperm are haploid. All other tissues are solely diploid.
Which of the following processes is an example of positive feedback?
- A . High blood glucose levels stimulate insulin release, which makes muscle and liver cells take in glucose
- B . Low blood oxygen levels stimulate erythropoietin production which increases red blood cell production by bone marrow
- C . High CO2 blood levels stimulate respiration which decreases blood CO2 levels
- D . Low blood calcium levels stimulate parathyroid hormone release from the parathyroid gland. Parathyroid hormone stimulates calcium release from bones.
- E . Increased nursing stimulates increased milk production in mammary glands
E
Explanation:
In a positive feedback loop, an action intensifies a chain of events that, in turn, intensify the conditions that caused the action beyond normal limits. Nursing stimulates lactation, which promotes nursing. Contractions during childbirth, psychological hysteria, and sexual orgasm are all examples of positive feedback.
In which of the following stages of embryo development are the three primary germ layers first present?
- A . Blastula
- B . Zygote
- C . Gastrula
- D . Coelomate
- E . Morula
C
Explanation:
The gastrula is formed from the blastocyst, which contains a bilayered embryonic disc. One layer of this disc’s inner cell mass further subdivides into the epiblast and the hypoblast, resulting in the three primary germ layers (endoderm, mesoderm, ectoderm).
In the food chain below, vultures represent grass C> cow C> wolf C> vulture:
- A . Scavengers
- B . Primary carnivores
- C . Detritivores
- D . Secondary consumers
- E . Herbivores
A
Explanation:
Vultures eat carrion, or dead animals, so they are considered scavengers. Detritivores are heterotrophs that eat decomposing organic matter such as leaf litter. They are usually small.
Latest PCAT Dumps Valid Version with 282 Q&As
Latest And Valid Q&A | Instant Download | Once Fail, Full Refund

