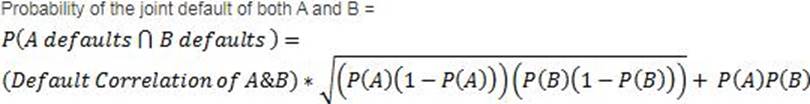PRMIA 8008 Exam III: Risk Management Frameworks . Operational Risk . Credit Risk . Counterparty Risk . Market Risk . ALM . FTP – 2015 Edition Online Training
PRMIA 8008 Online Training
The questions for 8008 were last updated at Dec 12,2025.
- Exam Code: 8008
- Exam Name: Exam III: Risk Management Frameworks . Operational Risk . Credit Risk . Counterparty Risk . Market Risk . ALM . FTP - 2015 Edition
- Certification Provider: PRMIA
- Latest update: Dec 12,2025
Which of the following credit risk models focuses on default alone and ignores credit migration when assessing credit risk?
- A . CreditPortfolio View
- B . The contingent claims approach
- C . The CreditMetrics approach
- D . The actuarial approach
There are two bonds in a portfolio, each with a market value of $50m. The probability of default of the two bonds are 0.03 and 0.08 respectively, over a one year horizon.
If the probability of the two bonds defaulting simultaneously is 1.4%, what is the default correlation between the two?
- A . 0%
- B . 100%
- C . 40%
- D . 25%
Which of the following best describes a ‘break clause?
- A . A break clause gives either party to a transaction the right to terminate the transaction at market price at future date(s)
- B . A break clause determines the process by which amounts due on early termination will be determined
- C . A break clause describes rights and obligations when the derivative contract is broken
- D . A break clause sets out the conditions under which the transaction will be terminated upon non-compliance with the ISDA MA
Under the CreditPortfolio View approach to credit risk modeling, which of the following best describes the conditional transition matrix:
- A . The conditional transition matrix is the unconditional transition matrix adjusted for the state of the economy and other macro economic factors being modeled
- B . The conditional transition matrix is the transition matrix adjusted for the risk horizon being different from that of the transition matrix
- C . The conditional transition matrix is the unconditional transition matrix adjusted for probabilities of defaults
- D . The conditional transition matrix is the transition matrix adjusted for the distribution of the firms’ asset returns
Which of the following are elements of ‘group risk’:
I. Market risk
II. Intra-group exposures
III. Reputational contagion
IV. Complex group structures
- A . II, III and IV
- B . II and III
- C . I and IV
- D . I and II
A bank extends a loan of $1m to a home buyer to buy a house currently worth $1.5m, with the house serving as the collateral. The volatility of returns (assumed normally distributed) on house prices in that neighborhood is assessed at 10% annually. The expected probability of default of the home buyer is 5%.
What is the probability that the bank will recover less than the principal advanced on this loan; assuming the probability of the home buyer’s default is independent of the value of the house?
- A . More than 1%
- B . Less than 1%
- C . More than 5%
- D . 0
When the volatility of the yield for a bond increases, which of the following statements is true:
- A . The VaR for the bond decreases and its value increases
- B . The VaR for the bond increases and its value decreases
- C . The VaR for the bond decreases and its value is unaffected
- D . The VaR for the bond increases and its value stays the same
Altman’s Z-score does not consider which of the following ratios:
- A . Market capitalization to debt
- B . Sales to total assets
- C . Net income to total assets
- D . Working capital to total assets
Which of the following methods cannot be used to calculate Liquidity at Risk?
- A . Monte Carlo simulation
- B . Analytical or parametric approaches
- C . Historical simulation
- D . Scenario analysis
For a corporate issuer, which of the following can be used to calculate market implied default probabilities?
I. CDS spreads
II. Bond prices
III. Credit rating issued by S&P
IV. Altman’s scoring model
- A . III and IV
- B . I and II
- C . I, II and III
- D . II and III
Latest 8008 Dumps Valid Version with 362 Q&As
Latest And Valid Q&A | Instant Download | Once Fail, Full Refund