PRMIA 8008 Exam III: Risk Management Frameworks . Operational Risk . Credit Risk . Counterparty Risk . Market Risk . ALM . FTP – 2015 Edition Online Training
PRMIA 8008 Online Training
The questions for 8008 were last updated at Jan 02,2026.
- Exam Code: 8008
- Exam Name: Exam III: Risk Management Frameworks . Operational Risk . Credit Risk . Counterparty Risk . Market Risk . ALM . FTP - 2015 Edition
- Certification Provider: PRMIA
- Latest update: Jan 02,2026
The daily VaR of an investor’s commodity position is $10m. The annual VaR, assuming daily returns are independent, is ~$158m (using the square root of time rule).
Which of the following statements are correct?
I. If daily returns are not independent and show mean-reversion, the actual annual VaR will be higher than $158m.
II. If daily returns are not independent and show mean-reversion, the actual annual VaR will be lower than $158m.
III. If daily returns are not independent and exhibit trending (autocorrelation), the actual annual VaR will be higher than $158m.
IV. If daily returns are not independent and exhibit trending (autocorrelation), the actual annual VaR will be lower than $158m.
- A . I and IV
- B . I and III
- C . II and III
- D . II and IV
Which of the following is a most complete measure of the liquidity gap facing a firm?
- A . Residual liquidity gap
- B . Liquidity at Risk
- C . Marginal liquidity gap
- D . Cumulative liquidity gap
Which of the following statements is a correct description of the phrase present value of a basis point?
- A . It refers to the present value impact of 1 basis point move in an interest rate on a fixed income security
- B . It refers to the discounted present value of 1/100th of 1% of a future cash flow
- C . It is another name for duration
- D . It is the principal component representation of the duration of a bond
Calculate the 99% 1-day Value at Risk of a portfolio worth $10m with expected returns of 10% annually and volatility of 20%.
- A . 290218
- B . 2326000
- C . 126491
- D . 294218
If E denotes the expected value of a loan portfolio at the end on one year and U the value of the portfolio in the worst case scenario at the 99% confidence level, which of the following expressions correctly describes economic capital required in respect of credit risk?
- A . E – U
- B . U/E
- C . U
- D . E
Which of the following are valid objectives of a reverse stress test:
I. Ensure that a firm can survive for long enough after risks have materialized for it to either regain market confidence, restructure or be sold, or be closed down in an orderly manner,
II. Discover the vulnerabilities of the current business plan,
III. Better integrate business and capital planning,
IV. Create a ‘zero-failure’ environment at the systemic level in the financial sector
- A . I and IV
- B . I, II and III
- C . II and III
- D . All of the above
The VaR of a portfolio at the 99% confidence level is $250,000 when mean return is assumed to be zero. If the assumption of zero returns is changed to an assumption of returns of $10,000, what is the revised VaR?
- A . 240000
- B . 226740
- C . 273260
- D . 260000
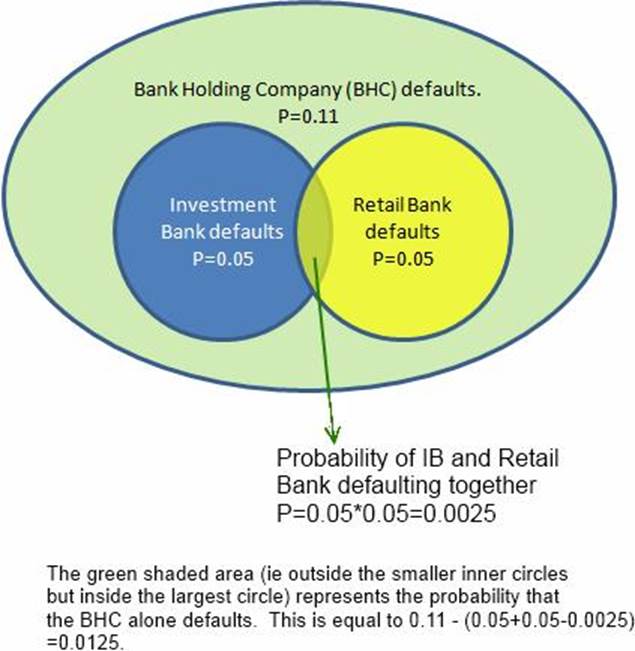
A Bank Holding Company (BHC) is invested in an investment bank and a retail bank. The BHC defaults for certain if either the investment bank or the retail bank defaults. However, the BHC can also default on its own without either the investment bank or the retail bank defaulting. The investment bank and the retail bank’s defaults are independent of each other, with a probability of default of 0.05 each. The BHC’s probability of default is 0.11.
What is the probability of default of both the BHC and the investment bank? What is the probability of the BHC’s default provided both the investment bank and the retail bank survive?
- A . 0.0475 and 0.10
- B . 0.11 and 0
- C . 0.08 and 0.0475
- D . 0.05 and 0.0125
When pricing credit risk for an exposure, which of the following is a better measure than the others:
- A . Expected Exposure (EE)
- B . Notional amount
- C . Potential Future Exposure (PFE)
- D . Mark-to-market
Which of the following statements are true:
I. The sum of unexpected losses for individual loans in a portfolio is equal to the total unexpected loss for the portfolio.
II. The sum of unexpected losses for individual loans in a portfolio is less than the total unexpected loss for the portfolio.
III. The sum of unexpected losses for individual loans in a portfolio is greater than the total unexpected loss for the portfolio.
IV. The unexpected loss for the portfolio is driven by the unexpected losses of the individual loans in the portfolio and the default correlation between these loans.
- A . I and II
- B . I, II and III
- C . III and IV
- D . II and IV
Latest 8008 Dumps Valid Version with 362 Q&As
Latest And Valid Q&A | Instant Download | Once Fail, Full Refund