PECB ISO-IEC-27001 Lead Auditor PECB Certified ISO/IEC 27001 Lead Auditor exam Online Training
PECB ISO-IEC-27001 Lead Auditor Online Training
The questions for ISO-IEC-27001 Lead Auditor were last updated at Feb 21,2025.
- Exam Code: ISO-IEC-27001 Lead Auditor
- Exam Name: PECB Certified ISO/IEC 27001 Lead Auditor exam
- Certification Provider: PECB
- Latest update: Feb 21,2025
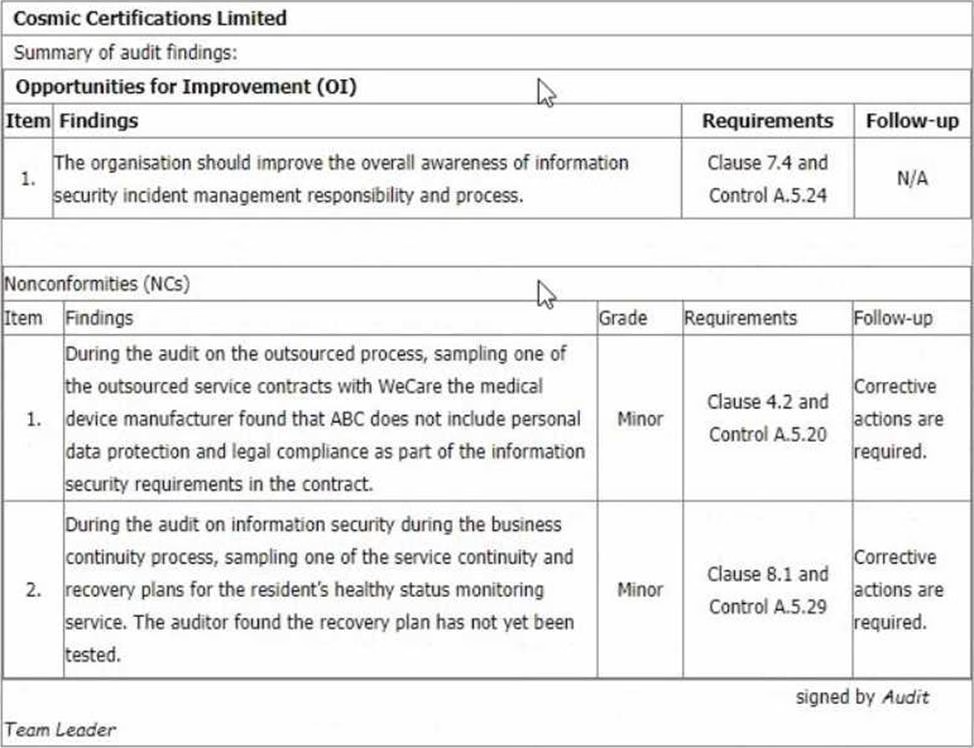
You are performing an ISMS initial certification audit at a residential nursing home that provides healthcare services. The next step in your audit plan is to conduct the closing meeting.
During the final audit team meeting, as an audit team leader, you agree to report 2 minor nonconformities and 1 opportunity for improvement as below:
Select one option of the recommendation to the audit programme manager you are going to advise to the auditee at the closing meeting.
- A . Recommend certification immediately
- B . Recommend that a full scope re-audit is required within 6 months
- C . Recommend that an unannounced audit is carried out at a future date
- D . Recommend certification after your approval of the proposed corrective action plan Recommend that the findings can be closed out at a surveillance audit in 1 year
- E . Recommend that a partial audit is required within 3 months
You are an ISMS audit team leader tasked with conducting a follow-up audit at a client’s data centre. Following two days on-site you conclude that of the original 12 minor and 1 major nonconformities that prompted the follow-up audit, only 1 minor nonconformity still remains outstanding. Select four options for the actions you could take.
- A . Book another follow-up audit on-site to review the one outstanding minor nonconformity once it has been cleared
- B . Recommend that the outstanding minor nonconformity is dealt with at the next surveillance audit
- C . Advise the auditee that you will arrange an online audit to deal with the outstanding nonconformity
- D . Note the progress made but hold the audit open until all corrective action has been cleared
- E . Agree with the auditee/audit client how the remaining nonconformity will be cleared, by when, and how its clearance will be verified
- F . Advise the individual managing the audit programme of any decision taken regarding the outstanding nonconformity
- G . Recommend suspension of the organisation’s certification as they have failed to implement the agreed corrections and corrective actions within the agreed timescale
- H . Close the follow-up audit as the organisation has demonstrated it is committed to clearing the nonconformities raised
You are an experienced ISMS audit team leader guiding an auditor in training. Your team has just completed a third-party surveillance audit of a mobile telecom provider. The auditor in training asks you how you intend to prepare for the Closing meeting.
Which four of the following are appropriate responses?
- A . I will advise the auditee that the purpose of the closing meeting is for the audit team to communicate our findings. It is not an opportunity for the auditee to challenge the findings
- B . I will instruct my audit team to wait outside the auditee’s offices so we can leave as quickly as possible after the closing meeting. This saves our time and the client’s time too
- C . It is not necessary to prepare for the closing meeting. Once you have carried out as many audits as
I have you already know what needs to be discussed - D . I will schedule a closing meeting with the auditee’s representatives at which the audit conclusions will be presented
- E . I will contact head office to ensure our invoice has been paid, If not, I will cancel the closing meeting and temporarily withhold the audit report
- F . I will discuss any follow-up required with my audit team
- G . I will review and, as appropriate, approve my teams audit conclusions
- H . I will review the audit evidence and the audit findings with the rest of the team
You are an experienced ISMS audit team leader guiding an auditor in training. You are testing her understanding of follow-up audits by asking her a series of questions to which the answer is either "true* or ‘false’.
Which four of the following questions should the answer be true"’
- A . A follow-up audit may be carried out where nonconformities are major
- B . A follow-up audit may be carried out where nonconformities are minor
- C . The outcomes of a follow-up audit should be reported to top management and the audit team leader who carried out the audit where the nonconformities were initially identified
- D . The outcome of a follow-up audit could lower a major nonconformity to minor status
- E . The outcome of a follow-up audit could be a recommendabon to suspend the client’s certification
- F . The outcomes of a follow-up audit should be reported to the individual managing the audit programme and the audit client
- G . A follow-up audit is required in all instances where nonconformities have been identified
- H . A follow-up audit is required only in instances where a major nonconformity has been identified
DRAG DROP
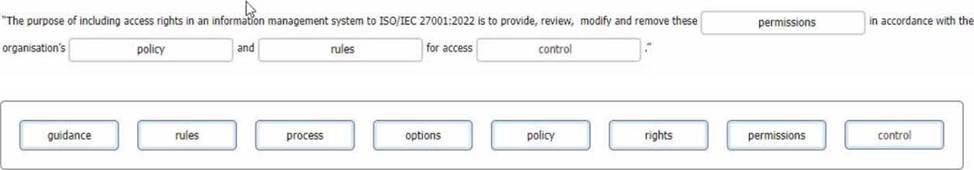
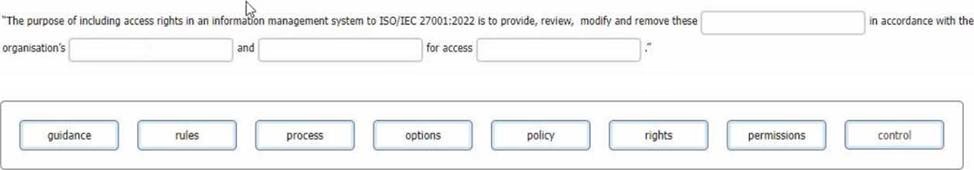
As the ISMS audit team leader, you are conducting a second-party audit of an international logistics company on behalf of an online retailer. During the audit, one of your team members reports a nonconformity relating to control 5.18 (Access rights) of Appendix A of ISO/IEC 27001:2022. She found evidence that removing the server access protocols of 20 people who left in the last 3 months took up to 1 week whereas the policy required removing access within 24 hours of their departure.
Complete the sentence with the best word(s), dick on the blank section you want to complete so that it is highlighted in red, and then click on the applicable text from the options below. Alternatively, you may drag and drop the option to the appropriate blank section.
You are conducting an ISMS audit in the despatch department of an international logistics organisation that provides shipping services to large organisations including local hospitals and government offices. Parcels typically contain pharmaceutical products, biological samples, and documents such as passports and driving licences. You note that the company records show a very large number of returned items with causes including mis-addressed labels and, in 15% of company cases, two or more labels for different addresses for the one package. You are interviewing the Shipping Manager (SM).
You: Are items checked before being dispatched?
SH: Any obviously damaged items are removed by the duty staff before being dispatched, but the small profit margin makes it uneconomic to implement a formal checking process. You: What action is taken when items are returned?
SM: Most of these contracts are relatively low value, therefore it has been decided that it is easier and more convenient to simply reprint the label and re-send individual parcels than it is to implement an investigation.
You raise a nonconformity. Referencing the scenario, which six of the following Appendix A controls would you expect the auditee to have implemented when you conduct the follow-up audit?
- A . 5.11 Return of assets
- B . 8.12 Data leakage protection
- C . 5.3 Segregation of duties
- D . 6.3 Information security awareness, education, and training
- E . 7.10 Storage media
- F . 8.3 Information access restriction
- G . 5.6 Contact with special interest groups
- H . 6.4 Disciplinary process
- I . 7.4 Physical security monitoring
- J . 5.13 Labelling of information
- K . 5.32 Intellectual property rights
You are conducting an ISMS audit in the despatch department of an international logistics organisation that provides shipping services to large organisations including local hospitals and government offices. Parcels typically contain pharmaceutical products, biological samples, and documents such as passports and driving licences. You note that the company records show a very large number of returned items with causes including misaddressed labels and, in 15% of cases, two or more labels for different addresses for the one package. You are interviewing the Shipping Manager (SM).
You: Are items checked before being dispatched?
SM: Any obviously damaged items are removed by the duty staff before being dispatched, but the small profit margin makes it uneconomic to implement a formal checking process.
You: What action is taken when items are returned?
SM: Most of these contracts are relatively low value, therefore it has been decided that it is easier and more convenient to simply reprint the label and re-send individual parcels than it is to implement an investigation.
You raise a nonconformity against ISO 27001:2022 based on the lack of control of the labelling process.
At the closing meeting, the Shipping Manager issues an apology to you that his comments may have been misunderstood. He says that he did not realise that there is a background IT process that automatically checks that the right label goes onto the right parcel otherwise the parcel is ejected at labelling. He asks that you withdraw your nonconformity.
Select three options of the correct responses that you as the audit team leader would make to the request of the Shipping Manager.
- A . Advise the Shipping Manager that his request will be included in the audit report
- B . Advise management that the new information provided will be discussed when the auditors have more time
- C . Inform the Shipping Manager that the nonconformity is minor and should be quickly corrected
- D . Ask the audit team members to state what they think should happen
- E . Inform him of your understanding and withdraw the nonconformity
- F . Thank the Shipping Manager for his honesty but advise that withdrawing the nonconformity is not the right way to proceed
- G . Advise the Shipping Manager that the nonconformity must stand since the evidence obtained for it was dear
- H . Indicate that the nonconformity is evidence of a deeper system failure that needs to be rectified
Which two of the following statements are true?
- A . The benefits of implementing an ISMS primarily result from a reduction in information security risks
- B . The benefit of certifying an ISMS is to obtain contracts from governmental institutions
- C . The purpose of an ISMS is to apply a risk management process for preserving information security
- D . The purpose of an ISMS is to demonstrate compliance with regulatory requirements
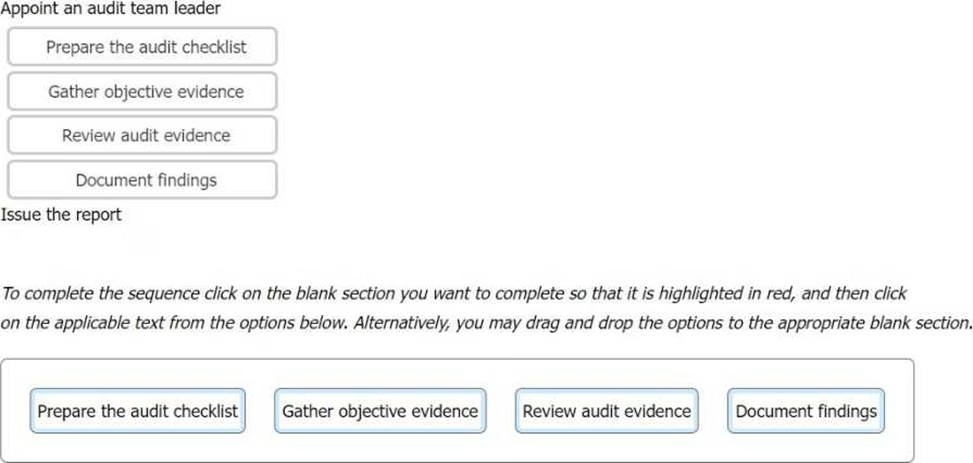
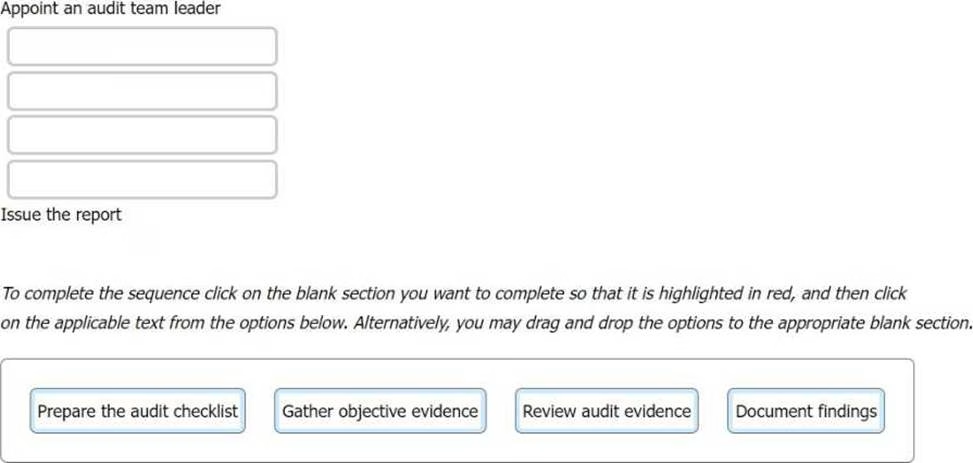
DRAG DROP
The following options are key actions involved in a first-party audit.
Order the stages to show the sequence in which the actions should take place.
Which two of the following phrases would apply to "plan" in relation to the Plan-Do-Check-Act cycle for a business process?
- A . Retaining documentation
- B . Retaining documentation
- C . Organising changes
- D . Setting objectives
- E . Training staff
- F . Providing ICT assets
Latest ISO-IEC-27001 Lead Auditor Dumps Valid Version with 100 Q&As
Latest And Valid Q&A | Instant Download | Once Fail, Full Refund