PECB ISO-9001 Lead Auditor QMS ISO 9001:2015 Lead Auditor Online Training
PECB ISO-9001 Lead Auditor Online Training
The questions for ISO-9001 Lead Auditor were last updated at Feb 21,2025.
- Exam Code: ISO-9001 Lead Auditor
- Exam Name: QMS ISO 9001:2015 Lead Auditor
- Certification Provider: PECB
- Latest update: Feb 21,2025
In the context of a third-party audit, select the issue which is not expected to be included in the audit plan.
- A . Number of sites to be audited
- B . Risk to achieving audit objectives
- C . Expectations of the organisation’s management
- D . Scope of the audit
In a third-party audit to ISO 9001, select two options of when the organisation is required to act in response to reported findings.
- A . A recommendation is given in the report.
- B . A finding of good practice is reported.
- C . An opportunity for improvement is raised.
- D . A major non-conformity is raised.
- E . A finding of conformity is reported.
- F . A minor non-conformity is raised.
DRAG DROP
The following are stages of an audit, put them in the order they would be conducted.
The first and last stages have been done for you
To complete the sequence click on the bank section you want to complete so it is highlighted in red and then click on the applicable text from the options below.

Audit criteria are a set of requirements used as a reference against which objective evidence is compared.
Which two of the following are not potential audit criteria?
- A . ISO management system standards
- B . Verbal statements by the general manager
- C . Verbal agreements with interested parties
- D . Health and safety notices
- E . Written agreements with interested parties
- F . Commercial advertisements
- G . Organisation’s documented information
- H . Claims made on the organisation’s website
- I . Commitment to follow principles issued by an NGO
- J . Environmental aspects register
Which of the following two documents does an auditor need to prepare and complete prior to the on-site audit?
- A . Audit Report
- B . Audit Plan
- C . Procedures
- D . Checklist / Prompts
- E . Risk Matrices
- F . Findings
You will lead a third-party audit next Monday on ABC, an organisation that provides services for cleaning windows from the outside of tall buildings. They work on demand, and usually have 4-5 orders per week. All documented information on these activities is kept at the central office.
On Friday evening, before the audit, you are informed by mail that customers cancelled all orders for the next week; therefore, the auditors will not have the chance to see them working at the customer’s premises, but the field supervisors will be available at the ABC offices.
You have prepared the audit plan and the checklist. Choose the best action you would take:
- A . Start the audit on Monday at ABC’s as planned, interviewing the functions that regularly work at the central office, and plan visits to ABC customers wherever they may be working during the following week.
- B . Ask the Certification Body you work for how to proceed with the audit.
- C . Start the audit on Monday as planned, interviewing the functions that regularly work at the central office, and visit another customer’s premises they cleaned the week before.
- D . Complete the audit but ask the quality manager to clean some windows at the ABC’s office, simulating the process they carry out at customers’ premises.
Select which one of the following statements is true.
- A . The team leader shall be an auditor that is qualified in the scheme.
- B . An audit team can include non-qualified auditors.
- C . A technical expert can replace a qualified auditor on an audit team.
- D . Audits leading to auditor qualification are undertaken annually.
Select one option that must be considered when determining the scope of a QMS to ISO 9001.
- A . Business improvement
- B . Performance of business processes
- C . External issues of the organisation’s context
- D . Competence of top management
DRAG DROP
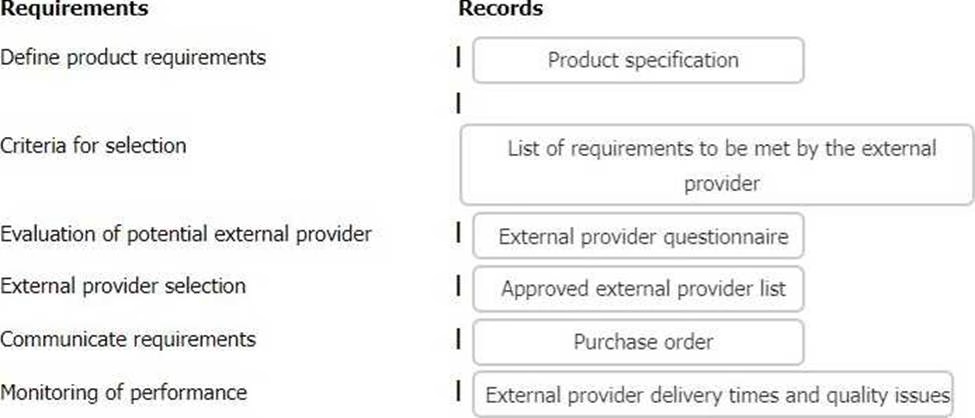
The following list gives examples of records that may be evidence of how an organisation has fulfilled the requirements of clause 8.4 of ISO 9001. Match the records to the appropriate requirement of clause 8.4.
To complete the table click on the blank section you want to complete so it is highlighted in red and then click on the appropriate record from the option listed. Alternatively, drag and drop the appropriate record to the requirement of clause 8.4 that applies.

An audit team leader arrives at a printing organisation to carry out a Stage 2 audit for a certification body. At a meeting with the Quality Manager, she is told that they have won their biggest contract from a computer manufacturer to print and compile computer documentation packages. They have leased the unit next door for space reasons but have never worked in this sector before. The Quality Manager wants the ISO 9001 certificate to cover the new contract.
During the audit, a team member finds that a number of print jobs have been rejected by several clients over a number of months due to spelling errors in the print run. The Print Manager blames the new employees they had to take on because of a big contract. The auditor raises a nonconformance against clause 10.2.1.b of ISO 9001.
Which one of the evidence statements would support this finding?
- A . There was no record that the organisation evaluated the effectiveness of the training given to new
employees. - B . There was no evidence that a check of spelling took place before the release of printing to the client.
- C . The actions taken to deal with customer complaints did not prevent recurrence of the problem.
- D . The organisation did not provide the correct resources to prevent nonconformity.
Latest ISO-9001 Lead Auditor Dumps Valid Version with 110 Q&As
Latest And Valid Q&A | Instant Download | Once Fail, Full Refund