What API policy would LEAST likely be applied to a Process API?
- A . Custom circuit breaker
- B . Client ID enforcement
- C . Rate limiting
- D . JSON threat protection
D
Explanation:
Reference: https://docs.mulesoft.com/api-manager/2.x/policy-mule3-provided-policies
What is a key performance indicator (KPI) that measures the success of a typical C4E that is immediately apparent in responses from the Anypoint Platform APIs?
- A . The number of production outage incidents reported in the last 24 hours
- B . The number of API implementations that have a publicly accessible HTTP endpoint and are being managed by Anypoint Platform
- C . The fraction of API implementations deployed manually relative to those deployed using a CI/CD tool
- D . The number of API specifications in RAML or OAS format published to Anypoint Exchange
D
Explanation:
Reference: https://help.mulesoft.com/s/question/0D52T00004mXSTUSA4/how-should-a-companymeasure-c4e-success
An organization is implementing a Quote of the Day API that caches today’s quote.
What scenario can use the CloudHub Object Store via the Object Store connector to persist the cache’s state?
- A . When there are three CloudHub deployments of the API implementation to three separate CloudHub regions that must share the cache state.
- B . When there are two CloudHub deployments of the API implementation by two Anypoint Platform business groups to the same CloudHub region that must share the cache state.
- C . When there is one deployment of the API implementation to CloudHub and another deployment to a customer-hosted Mule runtime that must share the cache state.
- D . When there is one CloudHub deployment of the API implementation to three CloudHub workers that must share the cache state.
What condition requires using a CloudHub Dedicated Load Balancer?
- A . When cross-region load balancing is required between separate deployments of the same Mule application
- B . When custom DNS names are required for API implementations deployed to customer-hosted Mule runtimes
- C . When API invocations across multiple CloudHub workers must be load balanced
- D . When server-side load-balanced TLS mutual authentication is required between API implementations and API clients
What do the API invocation metrics provided by Anypoint Platform provide?
- A . ROI metrics from APIs that can be directly shared with business users
- B . Measurements of the effectiveness of the application network based on the level of reuse
- C . Data on past API invocations to help identify anomalies and usage patterns across various APIs
- D . Proactive identification of likely future policy violations that exceed a given threat threshold
C
Explanation:
Reference: https://usermanual.wiki/Document/APAAppNetstudentManual02may2018.991784750.pdf
What is true about the technology architecture of Anypoint VPCs?
- A . The private IP address range of an Anypoint VPC is automatically chosen by CloudHub.
- B . Traffic between Mule applications deployed to an Anypoint VPC and on-premises systems can stay within a private network.
- C . Each CloudHub environment requires a separate Anypoint VPC.
- D . VPC peering can be used to link the underlying AWS VPC to an on-premises (non AWS) private network.
B
Explanation:
Reference: https://docs.mulesoft.com/runtime-manager/vpc-connectivity-methods-concept
An API implementation is deployed on a single worker on CloudHub and invoked by external API clients (outside of CloudHub).
How can an alert be set up that is guaranteed to trigger AS SOON AS that API implementation stops responding to API invocations?
- A . Implement a heartbeat/health check within the API and invoke it from outside the Anypoint Platform and alert when the heartbeat does not respond.
- B . Configure a “worker not responding” alert in Anypoint Runtime Manager.
- C . Handle API invocation exceptions within the calling API client and raise an alert from that API client when the API is unavailable.
- D . Create an alert for when the API receives no requests within a specified time period.
The implementation of a Process API must change.
What is a valid approach that minimizes the impact of this change on API clients?
- A . Update the RAML definition of the current Process API and notify API client developers by sending them links to the updated RAML definition.
- B . Postpone changes until API consumers acknowledge they are ready to migrate to a new Process API or API version.
- C . Implement required changes to the Process API implementation so that, whenever possible, the Process API’s RAML definition remains unchanged.
- D . Implement the Process API changes in a new API implementation, and have the old API implementation return an HTTP status code 301 – Moved Permanentlyto inform API clients they should be calling the new API implementation.
Refer to the exhibit.
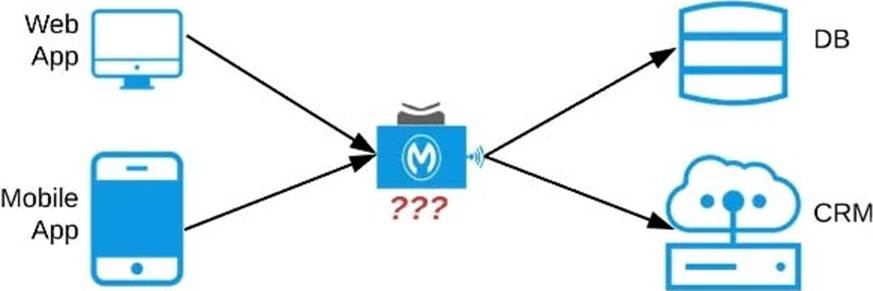
An organization needs to enable access to their customer data from both a mobile app and a web application, which each need access to common fields as well as certain unique fields.
The data is available partially in a database and partially in a 3rd-party CRM system.
What APIs should be created to best fit these design requirements?
- A . A Process API that contains the data required by both the web and mobile apps, allowing these applications to invoke it directly and access the data they need thereby providing the flexibility to add more fields in the future without needing API changes.
- B . One set of APIs (Experience API, Process API, and System API) for the web app, and another set for the mobile app.
- C . Separate Experience APIs for the mobile and web app, but a common Process API that invokes separate System APIs created for the database and CRM system
- D . A common Experience API used by both the web and mobile apps, but separate Process APIs for the web and mobile apps that interact with the database and the CRM System.
Refer to the exhibit.
A developer is building a client application to invoke an API deployed to the STAGING environment that is governed by a client ID enforcement policy.
What is required to successfully invoke the API?
- A . The client ID and secret for the Anypoint Platform account owning the API in the STAGING environment
- B . The client ID and secret for the Anypoint Platform account’s STAGING environment
- C . The client ID and secret obtained from Anypoint Exchange for the API instance in the STAGING environment
- D . A valid OAuth token obtained from Anypoint Platform and its associated client ID and secret
C
Explanation:
Reference: https://docs.mulesoft.com/api-manager/2.x/policy-mule3-client-id-based-policies
In an organization, the InfoSec team is investigating Anypoint Platform related data traffic.
From where does most of the data available to Anypoint Platform for monitoring and alerting originate?
- A . From the Mule runtime or the API implementation, depending on the deployment model
- B . From various components of Anypoint Platform, such as the Shared Load Balancer, VPC, and Mule runtimes
- C . From the Mule runtime or the API Manager, depending on the type of data
- D . From the Mule runtime irrespective of the deployment model
When designing an upstream API and its implementation, the development team has been advised to NOT set timeouts when invoking a downstream API, because that downstream API has no SLA that can be relied upon. This is the only downstream API dependency of that upstream API.
Assume the downstream API runs uninterrupted without crashing.
What is the impact of this advice?
- A . An SLA for the upstream API CANNOT be provided.
- B . The invocation of the downstream API will run to completion without timing out.
- C . A default timeout of 500 ms will automatically be applied by the Mule runtime in which the upstream API implementation executes.
- D . A load-dependent timeout of less than 1000 ms will be applied by the Mule runtime in which the downstream API implementation executes.
What best explains the use of auto-discovery in API implementations?
- A . It makes API Manager aware of API implementations and hence enables it to enforce policies.
- B . It enables Anypoint Studio to discover API definitions configured in Anypoint Platform.
- C . It enables Anypoint Exchange to discover assets and makes them available for reuse.
- D . It enables Anypoint Analytics to gain insight into the usage of APIs.
A
Explanation:
Reference: https://docs.mulesoft.com/api-manager/2.x/api-auto-discovery-new-concept
What should be ensured before sharing an API through a public Anypoint Exchange portal?
- A . The visibility level of the API instances of that API that need to be publicly accessible should be set to public visibility.
- B . The users needing access to the API should be added to the appropriate role in Anypoint Platform.
- C . The API should be functional with at least an initial implementation deployed and accessible for users to interact with.
- D . The API should be secured using one of the supported authentication/authorization mechanisms to ensure that data is not compromised.
A
Explanation:
Reference: https://docs.mulesoft.com/exchange/to-share-api-asset-to-portal
Refer to the exhibit.
A RAML definition has been proposed for a new Promotions Process API, and has been published to Anypoint Exchange.
The Marketing Department, who will be an important consumer of the Promotions API, has important requirements and expectations that must be met.
What is the most effective way to use Anypoint Platform features to involve the Marketing Department in this early API design phase?
- A . Ask the Marketing Department to interact with a mocking implementation of the API using the automatically generated API Console.
- B . Organize a design workshop with the DBAs of the Marketing Department in which the database schema of the Marketing IT systems is translated into RAML.
- C . Use Anypoint Studio to implement the API as a Mule application, then deploy that API implementation to CloudHub an
Department to interact with it.
- D . Export an integration test suite from API designer and have the Marketing Department execute the tests in that suite to ensure they pass.