Microsoft PL-300 Microsoft Power BI Data Analyst Online Training
Microsoft PL-300 Online Training
The questions for PL-300 were last updated at Feb 21,2026.
- Exam Code: PL-300
- Exam Name: Microsoft Power BI Data Analyst
- Certification Provider: Microsoft
- Latest update: Feb 21,2026
You merge data from Sales.Region, Region_Manager, Sales_Manager, and Manager into a single table named Region.
What should you do next to meet the reporting requirements of the executives?
- A . Apply row-level security (RLS) to the Region table based on the sales manager username.
- B . Configure a bi-directional relationship between Region and Sales.Region.
- C . Create a DAX calculated column that retrieves the region manager from the Weekly.Returns table based on the sales.regionjd column.
- D . In the Region table, create a hierarchy that has the manager name, and then the sales manager name.
HOTSPOT
You publish the semantic model to powerbi.com.
For each of the following statements, select Yes if the statement is true. Otherwise, select No. NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point.

Topic 2, Contoso Ltd, Case Study
Contoso Ltd. is a manufacturing company that produces sports equipment. Contoso holds quarterly board meetings for which financial analysts manually prepare Microsoft Excel reports, including balance sheets and profit and loss statements for each of the company s four business units.
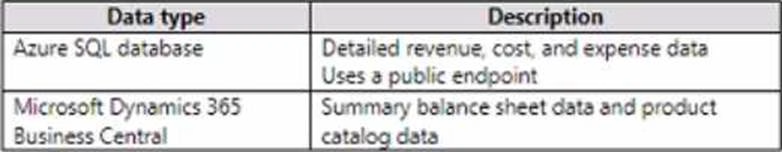
Data for the reports comes from the sources shown in the following table.
The balance sheet data is unrelated to the profit and loss results other than they both relate to dates.
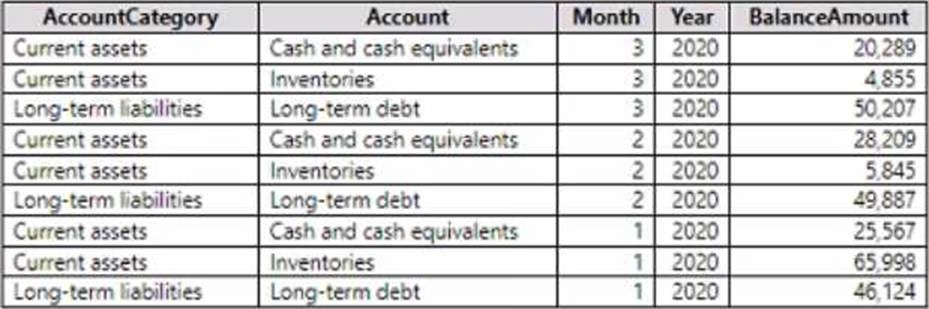
The balance sheet data is imported and includes the final monthly balances of each account in the format shown in the following table.
The balance sheet data always includes a row for each account for each month.
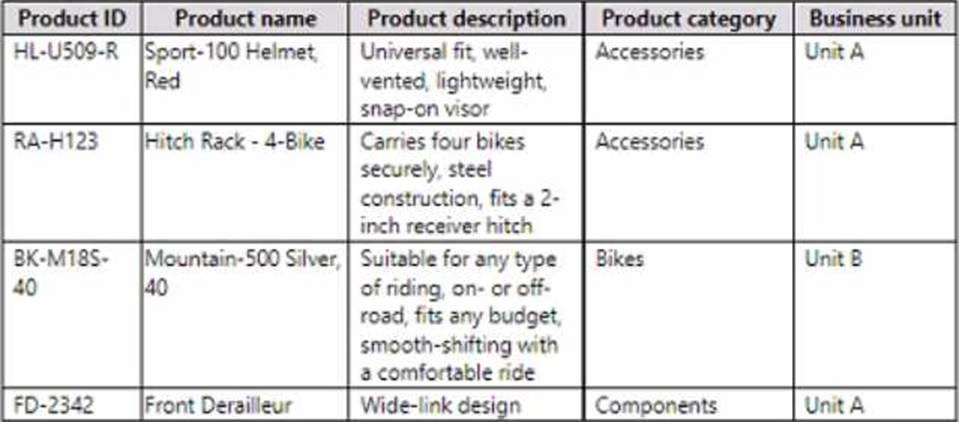
The product catalog shows how products roll up to product categories, which roll up to the business units the product list is provided in the format shown in the following table.
Revenue data is provided at the date and product level. Expense data is provided at the date and department level.
Contoso wants the reports and datasets refreshed with minimum manual effort.
The company wants to provide the board with 3 single package of reports that will contain custom navigation and links to supplementary information.
Maintenance, including maturity updating data and access, must be minimized as much as possible.
The reports must be made available to the board from powerbi.com. A group in Microsoft Azure Active Director)’ (Azure AD), part of Microsoft Entra. will be used to share information with the board.
Contoso identifies the following security requirements for analyst access:
• Analysts must be able to access all balance sheet and product catalog data.
• Analysts must be able to access only the profit and loss data of their respective business unit
• Analysts must be able to create new reports from the dataset that contains the profit and loss data, but the reports built by the analysts must NOT be included in the quarterly reports for the board.
• Analysts must NOT be able to share the quarterly reports with anyone.
• Analysts must NOT be able to make new reports by using the balance sheet data.
You plan to relate the balance sheet table to a date table in Power Bl in a many-to-one relationship based on the last day of the month. At least one of the balance sheet reports in the quarterly reporting package must show the ending balances for the quarter, as well as for the previous quarter.
The date table will contain the columns shown in the following table.
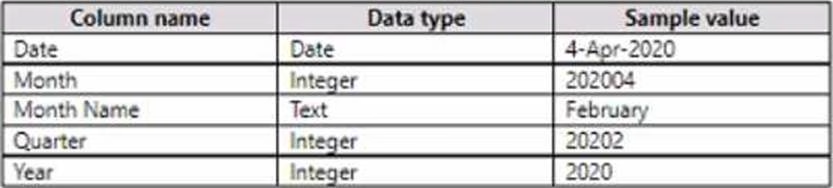
The definitions and attributes for the products departments, and business units must be consistent across all the reports.
The board must be able to get the following information from the quarterly reports:
• Revenue trends over time
• The ending balances of each account
• Changes m long-term liabilities from the previous quarter
• The percent of total revenue contributed by each product category
• A comparison of quarterly revenue versus the same quarter from the previous year
The reports must be updated with the latest data by 5 AM each day.
Overview
This is a case study. Case studies are not timed separately. You can use as much exam time as you
would like to complete each case. However, there may be additional case studies and sections on this exam. You must manage your time to ensure that you are able to complete all questions included on this exam in the time provided.
To answer the questions included in a case study, you will need to reference information that is provided in the case study. Case studies might contain exhibits and other resources that provide more information about the scenario that is described in the case study. Each question is independent of the other questions in this case study.
At the end of this case study, a review screen will appear. This screen allows you to review your answers and to make changes before you move to the next section of the exam. After you begin a new section, you cannot return to this section.
To start the case study
To display the first question in this case study, click the Next button. Use the buttons in the left pane to explore the content of the case study before you answer the questions. Clicking these buttons displays information such as business requirements, existing environment and problem statements. If the case study has an All Information tab, note that the information displayed is identical to the information displayed on the subsequent tabs. When you are ready to answer a question, click the Question button to return to the question.
Existing Environment
Contoso, Ltd. is a manufacturing company that produces outdoor equipment Contoso has quarterly board meetings for which financial analysts manually prepare Microsoft Excel reports, including profit and loss statements for each of the company’s four business units, a company balance sheet, and net income projections for the next quarter.
Data and Sources
Data for the reports comes from three sources. Detailed revenue, cost and expense data comes from an Azure SQL database. Summary balance sheet data comes from Microsoft Dynamics 365 Business Central. The balance sheet data is not related to the profit and loss results; other than they both relate to dates.
Monthly revenue and expense projections for the next quarter come from a Microsoft SharePoint Online list. Quarterly projections relate to the profit and loss results by using the following shared dimensions: date, business unit, department, and product category.
Net Income Projection Data
Net income projection data is stored in a SharePoint Online list named Projections in the format shown in the following table.
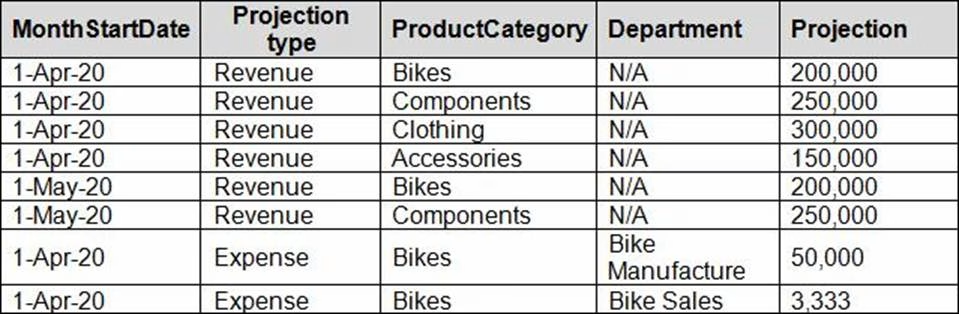
Revenue projections are set at the monthly level and summed to show projections for the quarter.
Balance Sheet Data
The balance sheet data is imported with final balances for each account per month in the format shown in the following table.
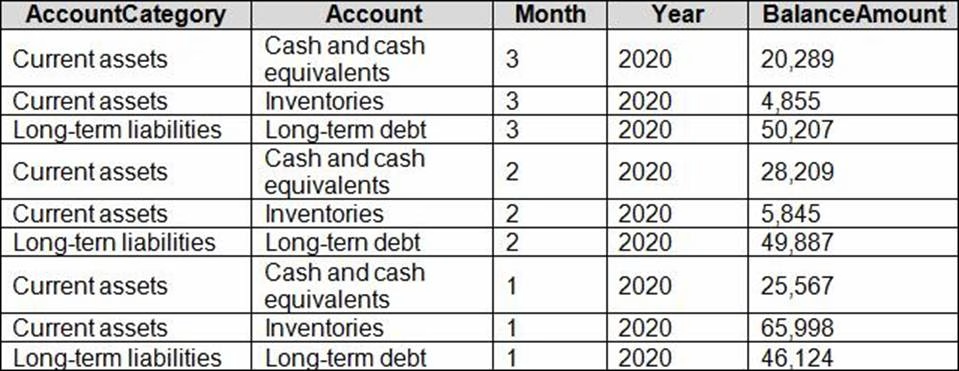
There is always a row for each account for each month in the balance sheet data.
Dynamics 365 Business Central Data
Business Central contains a product catalog that shows how products roll up to product categories, which roll up to business units. Revenue data is provided at the date and product level. Expense data is provided at the date and department level.
Business Issues
Historically, it has taken two analysts a week to prepare the reports for the quarterly board meetings. Also, there is usually at least one issue each quarter where a value in a report is wrong because of a bad cell reference in an Excel formula. On occasion, there are conflicting results in the reports because the products and departments that roll up to each business unit are not defined consistently.
Planned Changes
Contoso plans to automate and standardize the quarterly reporting process by using Microsoft Power Bl. The company wants to how long it takes to populate reports to less than two days. The company wants to create common logic for business units, products, and departments to be used across all reports, including, but not limited, to the quarterly reporting for the board.
Technical Requirements
Contoso wants the reports and datasets refreshed with minimal manual effort
The company wants to provide a single package of reports to the board that contains custom navigation and links to supplementary information.
Maintenance, including manually updating data and access, must be minimized as much as possible.
Security Requirements
The reports must be made available to the board from powerbi.com. A mail-enabled security group will be used to share information with the board.
The analysts responsible for each business unit must see all the data the board sees, except the profit and loss data, which must be restricted to only their business unit’s data. The analysts must be able to build new reports from the dataset that contains the profit and loss data, but any reports that the analysts build must not be included in the quarterly reports for the board. The analysts must not be able to share the quarterly reports with anyone.
Report Requirements
You plan to relate the balance sheet to a standard date table in Power Bl in a many-to-one relationship based on the last day of the month. At least one of the balance sheet reports in the quarterly reporting package must show the ending balances for the quarter, as well as for the previous quarter.
Projections must contain a column named RevenueProjection that contains the revenue projection amounts. A relationship must be created from Projections to a table named Date that contains the columns shown in the following table.
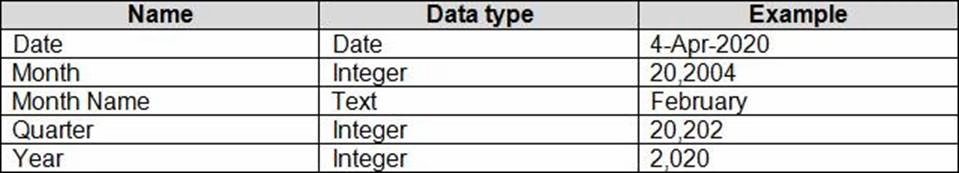
The relationships between products and departments to business units must be consistent across all reports.
The board must be able to get the following information from the quarterly reports:
• Revenue trends over time
• Ending balances for each account
• A comparison of expenses versus projections by quarter
• Changes in long-term liabilities from the previous quarter
• A comparison of quarterly revenue versus the same quarter during the prior year
DRAG DROP
You need to create a DAX measure in the data model that only allows users to see projections at the appropriate levels of granularity.
How should you complete the measure? To answer, drag the appropriate values to the correct targets. Each value may be used once, more than once, or not at all. You may need to drag the split bar between panes or scroll to view content. NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point.
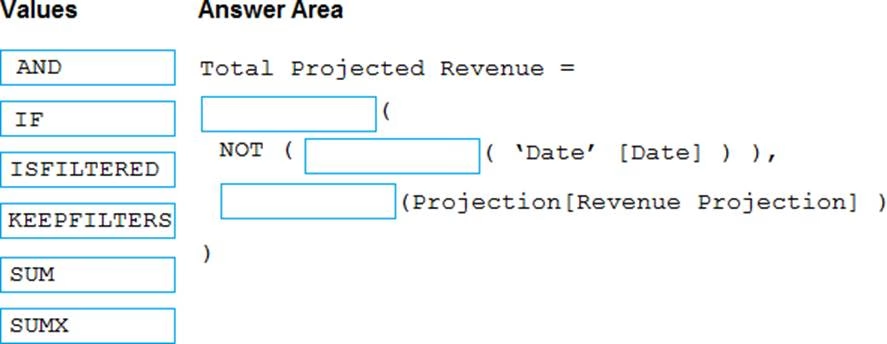
HOTSPOT
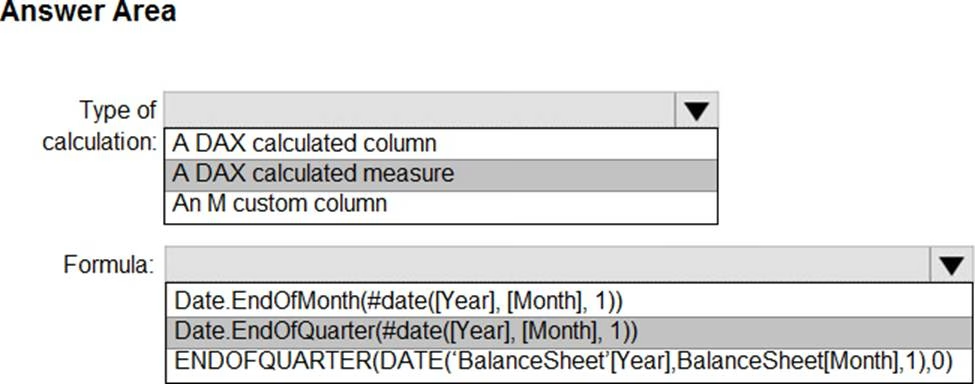
You need to calculate the last day of the month in the balance sheet data to ensure that you can relate the balance sheet data to the Date table.
Which type of calculation and which formula should you use? To answer, select the appropriate options in the answer area. NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point.
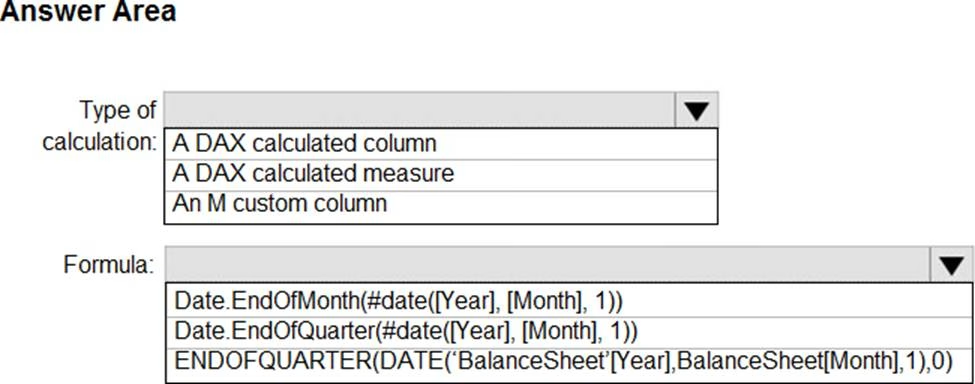
HOTSPOT
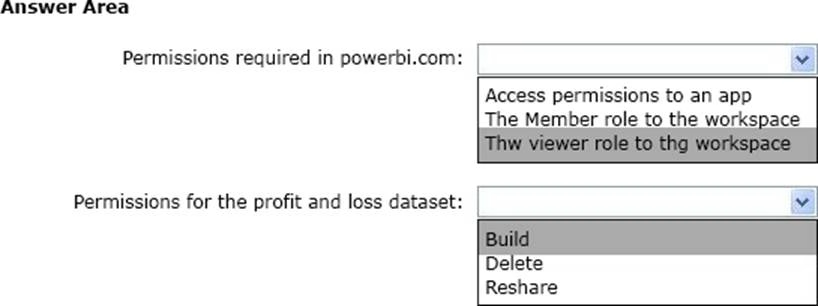
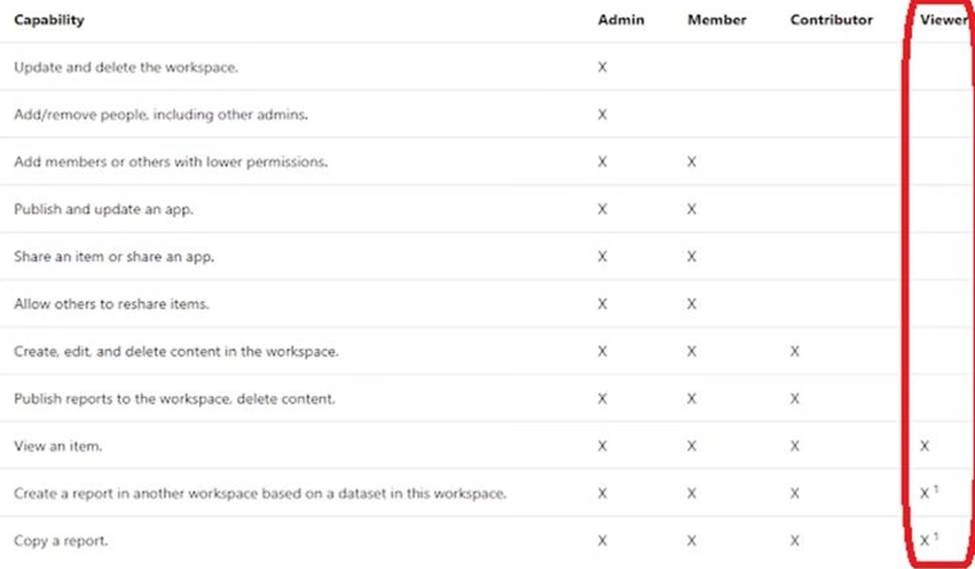
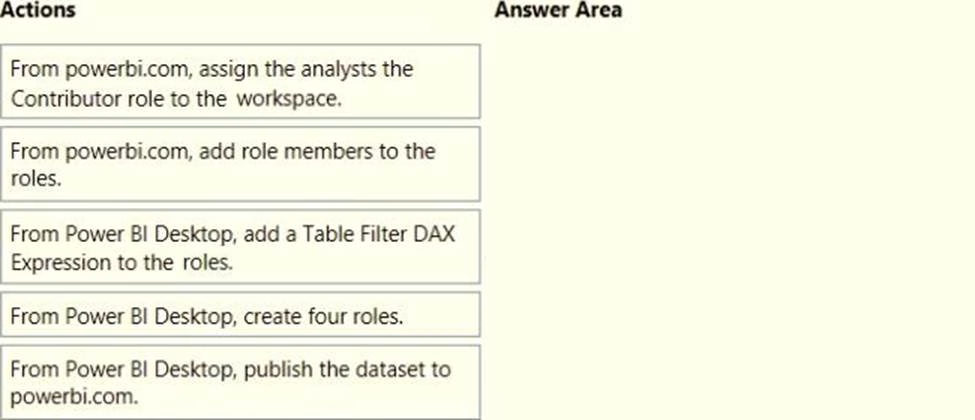
You need to grant access to the business unit analysts.
What should you configure? To answer, select the appropriate options in the answer area. NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point.

You need to recommend a strategy to consistently define the business unit, department, and product category data and make the data usable across reports.
What should you recommend?
- A . Create a shared dataset for each standardized entity.
- B . Create dataflows for the standardized data and make the dataflows available for use in all imported datasets.
- C . For every report, create and use a single shared dataset that contains the standardized data.
- D . For the three entities, create exports of the data from the Power Bl model to Excel and store the data in Microsoft OneDrive for others to use as a source.
DRAG DROP
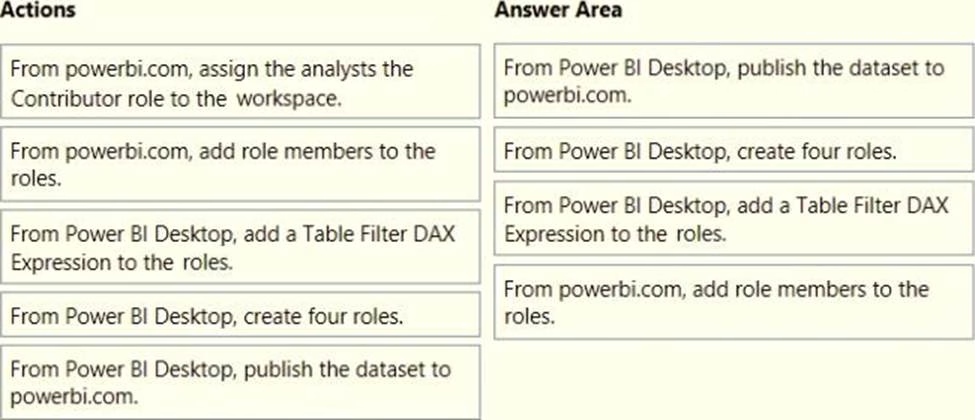
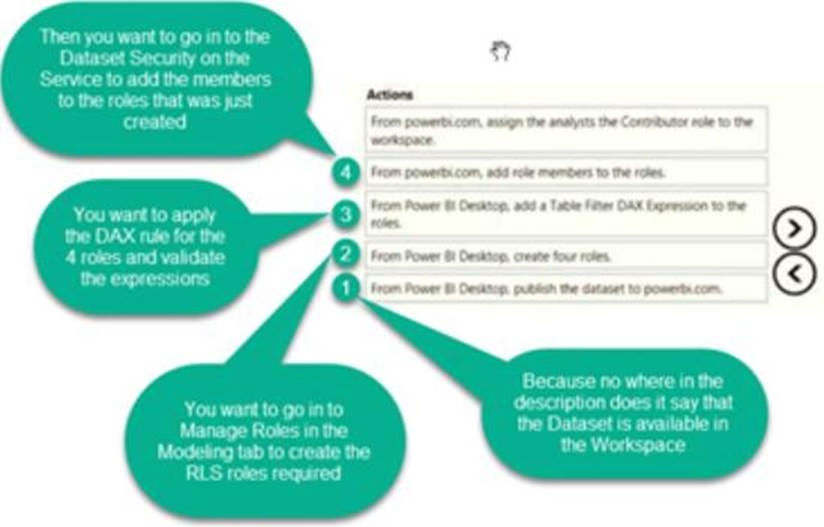
Once the profit and loss dataset is created, which four actions should you perform in sequence to ensure that the business unit analysts see the appropriate profit and loss data? To answer, move the appropriate actions from the list of actions to the answer area and arrange them in the correct order.
What is the minimum number of datasets and storage modes required to support the reports?
- A . two imported datasets
- B . a single DirectQuery dataset
- C . two DirectQuery datasets
- D . a single imported dataset
Which DAX expression should you use to get the ending balances in the balance sheet reports?
- A . CALCULATE (
SUM( BalanceSheet [BalanceAmount] ),
DATESQTD( ‘Date'[Date] )
) - B . CALCULATE (
SUM( BalanceSheet [BalanceAmount] ),
LASTDATE( ‘Date'[Date] )
) - C . FIRSTNONBLANK ( ‘Date’ [Date]
SUM( BalanceSheet[BalanceAmount] )
) - D . CALCULATE (
MAX( BalanceSheet[BalanceAmount] ),
LASTDATE( ‘Date’ [Date] )
)
Which two types of visualizations can be used in the balance sheet reports to meet the reporting goals? Each correct answer presents part of the solution. NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point.
- A . a line chart that shows balances by quarter filtered to account categories that are long-term liabilities.
- B . a clustered column chart that shows balances by date (x-axis) and account category (legend) without
filters. - C . a clustered column chart that shows balances by quarter filtered to account categories that are long-term liabilities.
- D . a pie chart that shows balances by account category without filters.
- E . a ribbon chart that shows balances by quarter and accounts in the legend.
Latest PL-300 Dumps Valid Version with 131 Q&As
Latest And Valid Q&A | Instant Download | Once Fail, Full Refund