Microsoft 70-761 Querying Data with Transact-SQL Online Training
Microsoft 70-761 Online Training
The questions for 70-761 were last updated at Feb 18,2026.
- Exam Code: 70-761
- Exam Name: Querying Data with Transact-SQL
- Certification Provider: Microsoft
- Latest update: Feb 18,2026
Note: This question is part of a series of questions that use the same scenario. For your convenience, the scenario is repeated in each question. Each question presents a different goal and answer choices, but the text of the scenario is exactly the same in each question in this series.
You have a database that tracks orders and deliveries for customers in North America. System versioning is enabled for all tables. The database contains the Sales.Customers, Application.Cities, and Sales.CustomerCategories tables.
Details for the Sales.Customers table are shown in the following table:
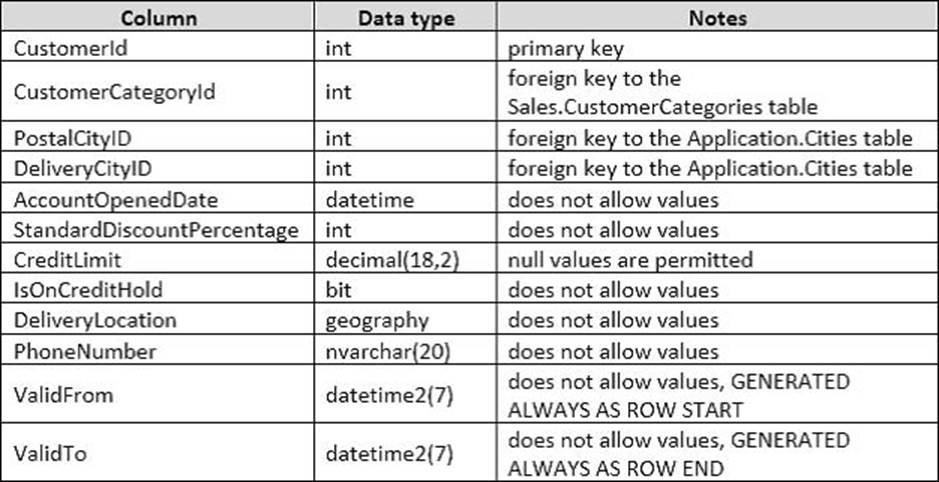
Details for the Application.Cities table are shown in the following table:

Details for the Sales.CustomerCategories table are shown in the following table:

You need to create a query that meets the following requirements:
– For customers that are not on a credit hold, return the CustomerID and the latest recorded population
for the delivery city that is associated with the customer.
– For customers that are on a credit hold, return the CustomerID and the latest recorded population for the postal city that is associated with the customer.
Which two Transact-SQL queries will achieve the goal? Each correct answer presents a complete solution.
A)

B)

C)

D)

- A . Option A
- B . Option B
- C . Option C
- D . Option D
Note: This question is part of a series of questions that use the same scenario. For your convenience, the scenario is repeated in each question. Each question presents a different goal and answer choices, but the text of the scenario is exactly the same in each question in this series.
You have a database that tracks orders and deliveries for customers in North America. System versioning is enabled for all tables.
The database contains the Sales.Customers, Application.Cities, and Sales.CustomerCategories tables.
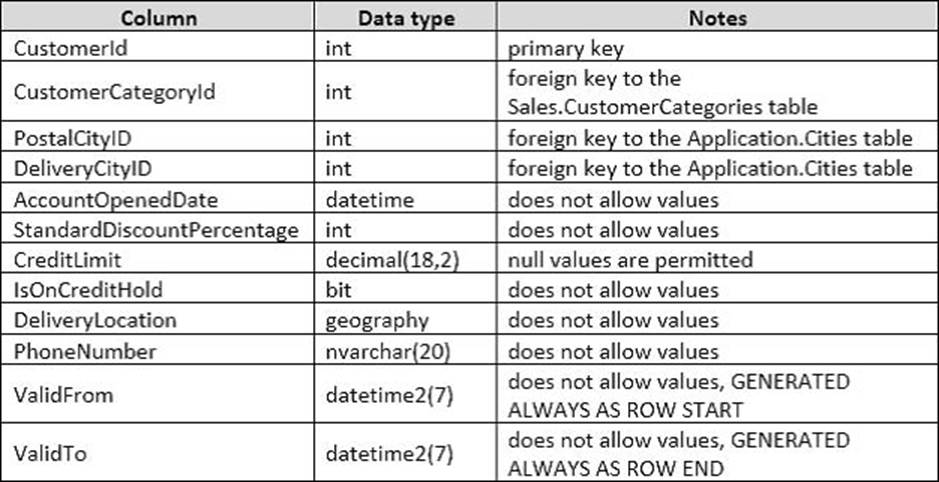
Details for the Application.Cities table are shown in the following table:

Details for the Sales.CustomerCategories table are shown in the following table:

You discover an application bug that impacts customer data for records created on or after January 1, 2014. In order to fix the data impacted by the bug, application programmers require a report that contains customer data as it existed on December 31, 2013.
You need to provide the query for the report.
Which Transact-SQL statement should you use?
- A . DECLARE @sdate DATETIME, @edate DATETIME
SET @sdate = DATEFROMPARTS (2013, 12, 31)
SET @edate = DATEADD (d, 1, @sdate)
SELECT * FROM Sales.Customers FOR SYSTEM_TIME ALL
WHERE ValidFrom > @sdate AND ValidTo < @edate - B . DECLARE @sdate DATETIME, @edate DATETIME
SET @sdate = DATEFROMPARTS (2013, 12, 31)
SET @edate = DATEADD (d, -1, @sdate)
SELECT * FROM Sales.Customers
FOR SYSTEM_TIME BETWEEN @sdate AND @edate - C . DECLARE @date DATE
SET @date = DATEFROMPARTS (2013, 12, 31)
SELECT * FROM Sales.Customers
FOR SYSTEM_TIME ALL AS OF @date - D . DECLARE @date DATE
SET @date = DATEFROMPARTS (2013, 12, 31)
SELECT * FROM [Sales].[Customers] FOR SYSTEM_TIME ALL
WHERE @date BETWEEN ValidFrom AND ValidTo - E . DECLARE @date DATE
SET @date = DATEFROMPARTS (2013, 12, 31)
SELECT * FROM [Sales].[Customers] FOR SYSTEM_TIME ALL
WHERE SYSDATETIME = @date
DRAG DROP
Note: This question is part of a series of questions that use the same scenario. For your convenience, the scenario is repeated in each question. Each question presents a different goal and answer choices, but the text of the scenario is exactly the same in each question in this series.
You have a database that tracks orders and deliveries for customers in North America. System versioning is enabled for all tables. The database contains the Sales.Customers, Application.Cities, and Sales.CustomerCategories tables.
Details for the Sales.Customers table are shown in the following table:
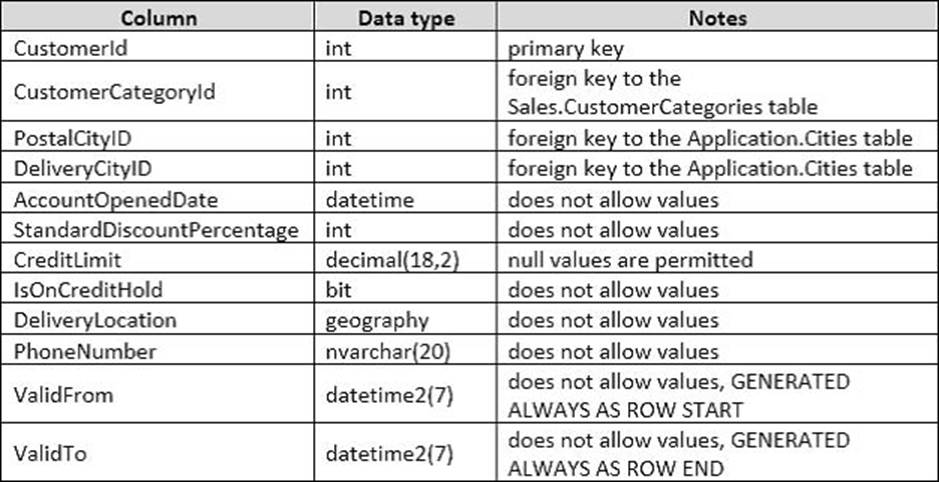
Details for the Application.Cities table are shown in the following table:

Details for the Sales.CustomerCategories table are shown in the following table:

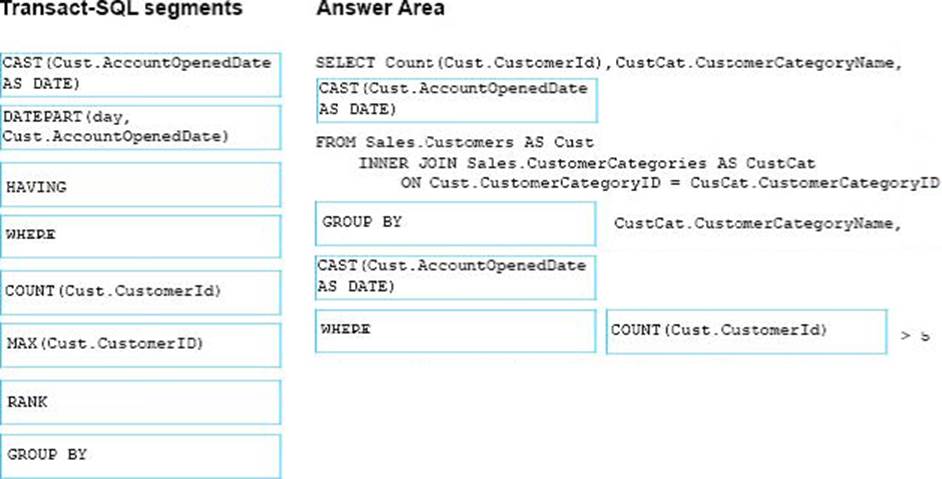
You are creating a report to measure the impact of advertising efforts that were designed to attract new customers. The report must show the number of new customers per day for each customer category, but only if the number of new customers is greater than five.
You need to write the query to return data for the report.
How should you complete the Transact-SQL statement? To answer, drag the appropriate Transact-SQL segments to the correct locations. Each Transact-SQL segment may be used once, more than once, or not at all. You may need to drag the split bar between panes or scroll to view content.
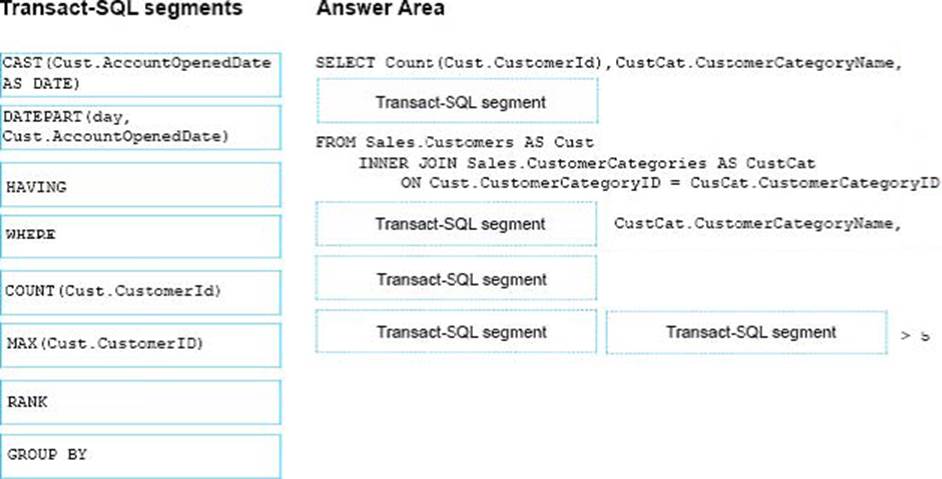
DRAG DROP
Note: This question is part of a series of questions that use the same scenario. For your convenience, the scenario is repeated in each question. Each question presents a different goal and answer choices, but the text of the scenario is exactly the same in each question in this series.
You have a database that tracks orders and deliveries for customers in North America. System versioning is enabled for all tables. The database contains the Sales.Customers, Application.Cities, and Sales.CustomerCategories tables.
Details for the Sales.Customers table are shown in the following table:
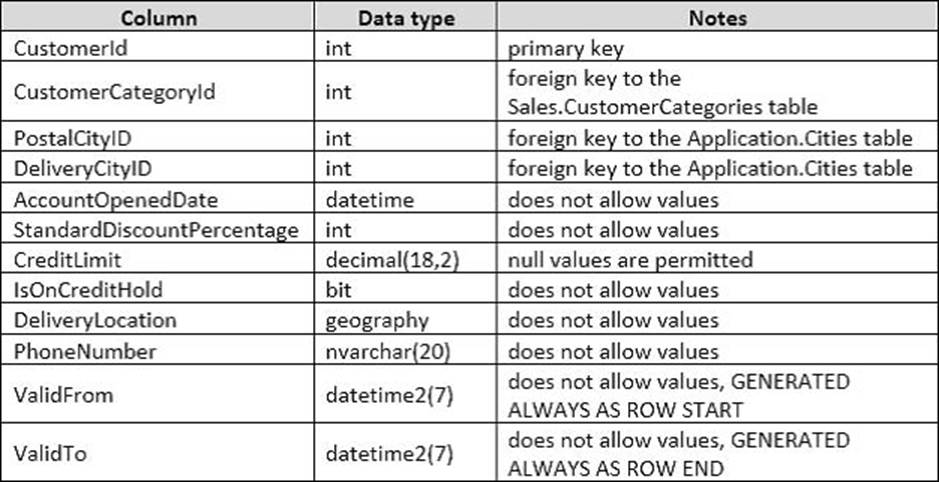
Details for the Application.Cities table are shown in the following table:

Details for the Sales.CustomerCategories table are shown in the following table:

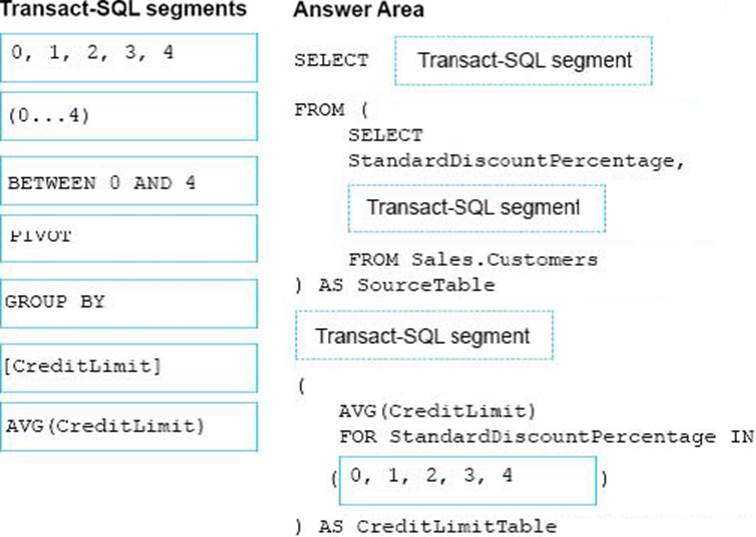
The marketing department is performing an analysis of how discounts affect credit limits. They need to know the average credit limit per standard discount percentage for customers whose standard discount percentage is between zero and four.
You need to create a query that returns the data for the analysis.
How should you complete the Transact-SQL statement? To answer, drag the appropriate Transact-SQL segments to the correct locations. Each Transact-SQL segments may be used once, more than once, or not at all. You may need to drag the split bar between panes or scroll to view content.
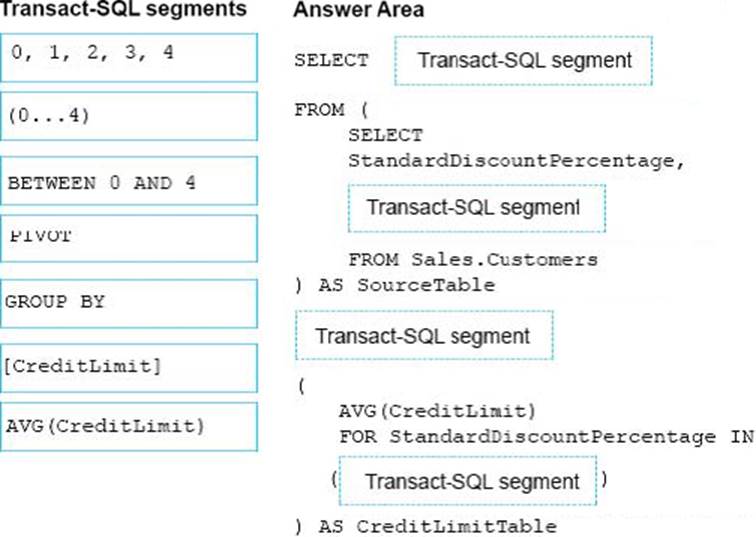
DRAG DROP
Note: This question is part of a series of questions that use the same scenario. For your convenience, the scenario is repeated in each question. Each question presents a different goal and answer choices, but the text of the scenario is exactly the same in each question in this series.
You have a database that tracks orders and deliveries for customers in North America. System versioning is enabled for all tables. The database contains the Sales.Customers, Application.Cities, and Sales.CustomerCategories tables.
Details for the Sales.Customers table are shown in the following table:
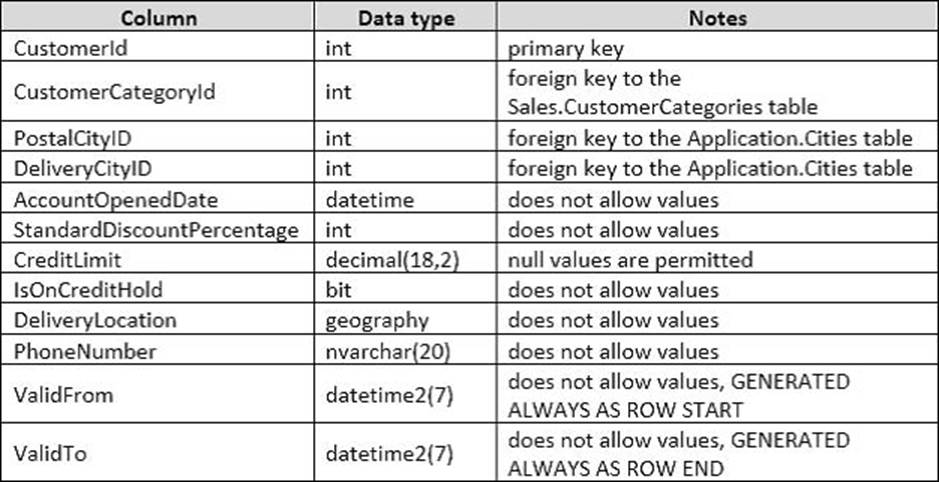
Details for the Application.Cities table are shown in the following table:

Details for the Sales.CustomerCategories table are shown in the following table:

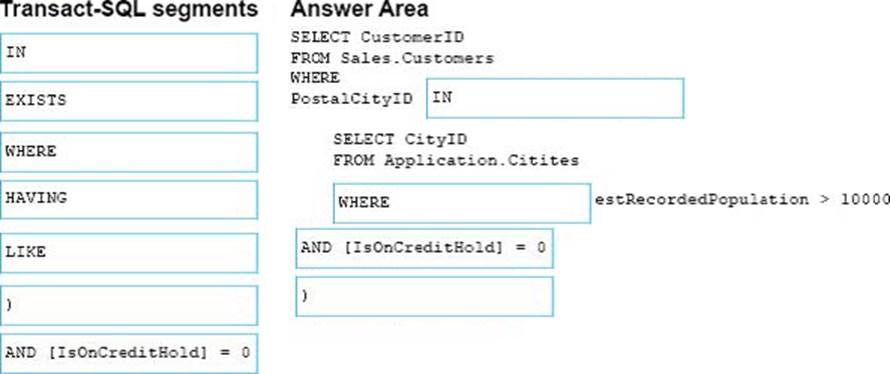
You are preparing a promotional mailing. The mailing must only be sent to customers in good standing that live in medium and large cities. You need to write a query that returns all customers that are not on credit hold who live in cities with a population greater than 10,000.
How should you complete the Transact-SQL statement? To answer, drag the appropriate Transact-SQL segments to the correct locations. Each Transact-SQL segment may be used once, more than once, or not at all. You may need to drag the split bar between panes or scroll to view content.
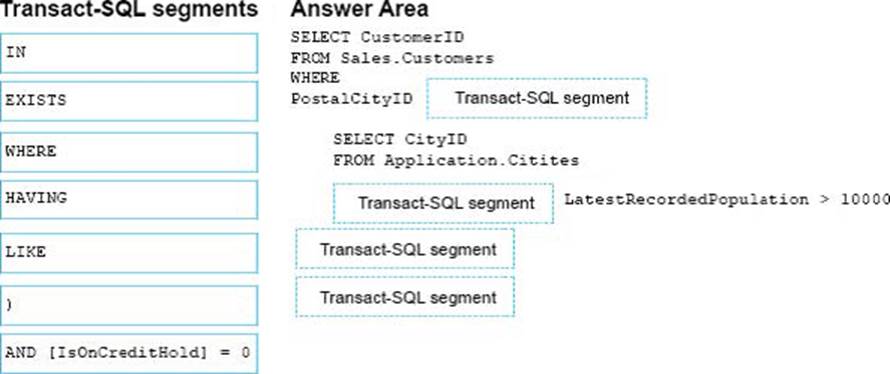
Note: This question is part of a series of questions that use the same or similar answer choices. An answer choice may be correct for more than one question in the series. Each question is independent of the other questions in this series. Information and details provided in a question apply only to that question.
You have a table named Products that contains information about the products that your company sells. The table contains many columns that do not always contain values.
You need to implement an ANSI standard method to convert the NULL values in the query output to the phrase “Not Applicable”.
What should you implement?
- A . the COALESCE function
- B . a view
- C . a table-valued function
- D . the TRY_PARSE function
- E . a stored procedure
- F . the ISNULL function
- G . a scalar function
- H . the TRY_CONVERT function
Note: This question is part of a series of questions that use the same or similar answer choices. An answer choice may be correct for more than one question in the series. Each question is independent of the other questions in this series. Information and details provided in a question apply only to that question.
You have a database that is denormalized. Users make frequent changes to data in a primary table.
You need to ensure that users cannot change the tables directly, and that changes made to the primary table also update any related tables.
What should you implement?
- A . the COALESCE function
- B . a view
- C . a table-valued function
- D . the TRY_PARSE function
- E . a stored procedure
- F . the ISNULL function
- G . a scalar function
- H . the TRY_CONVERT function
Note: This question is part of a series of questions that use the same or similar answer choices. An answer choice may be correct for more than one question in the series. Each question is independent of the other questions in this series. Information and details provided in a question apply only to that question.
You have a database that stores sales and order information.
Users must be able to extract information from the tables on an ad hoc basis. They must also be able to reference the extracted information as a single table.
You need to implement a solution that allows users to retrieve the data required, based on variables defined at the time of the query.
What should you implement?
- A . the COALESCE function
- B . a view
- C . a table-valued function
- D . the TRY_PARSE function
- E . a stored procedure
- F . the ISNULL function
- G . a scalar function
- H . the TRY_CONVERT function
Note: This question is part of a series of questions that use the same or similar answer choices. An answer choice may be correct for more than one question in the series. Each question is independent of the other questions in this series. Information and details provided in a question apply only to that question.
You have a table named AuditTrail that tracks modifications to data in other tables. The AuditTrail table is updated by many processes. Data input into AuditTrail may contain improperly formatted date time values. You implement a process that retrieves data from the various columns in AuditTrail, but sometimes the process throws an error when it is unable to convert the data into valid date time values. You need to convert the data into a valid date time value using the en-US format culture code. If the conversion fails, a null value must be returned in the column output. The conversion process must not throw an error.
What should you implement?
- A . the COALESCE function
- B . a view
- C . a table-valued function
- D . the TRY_PARSE function
- E . a stored procedure
- F . the ISNULL function
- G . a scalar function
- H . the TRY_CONVERT function
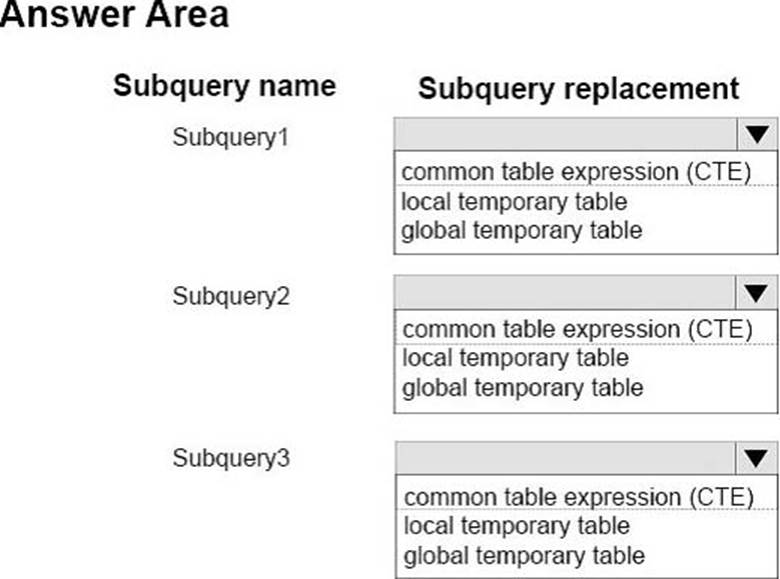
HOTSPOT
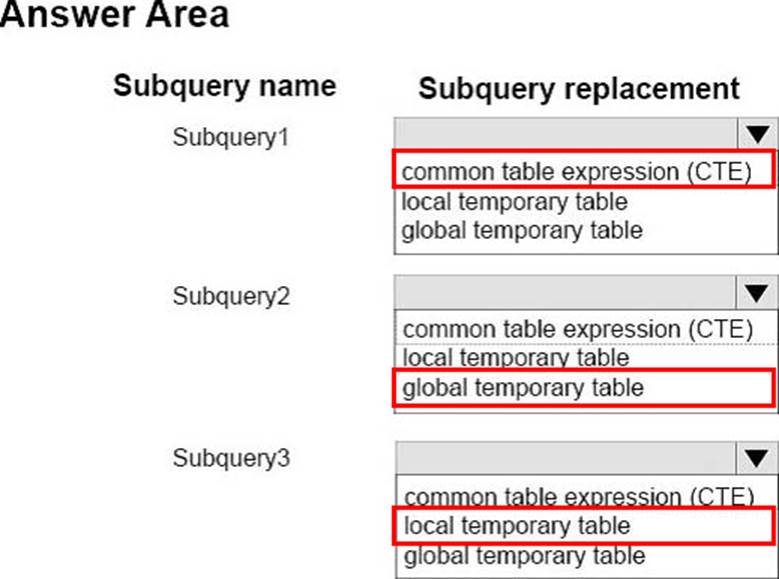
You have the following subqueries: Subquery1, Subquery2, and Subquery3.
You need to replace the three subqueries with named result sets or temporary tables.
The following requirements must be met:

Which replacement techniques should you use? To answer, select the appropriate options in the answer area.
Latest 70-761 Dumps Valid Version with 212 Q&As
Latest And Valid Q&A | Instant Download | Once Fail, Full Refund