Microsoft 70-461 Querying Microsoft SQL Server 2012 Online Training
Microsoft 70-461 Online Training
The questions for 70-461 were last updated at Feb 13,2026.
- Exam Code: 70-461
- Exam Name: Querying Microsoft SQL Server 2012
- Certification Provider: Microsoft
- Latest update: Feb 13,2026
You use Microsoft SQL Server 2012 database to develop a shopping cart application.
You need to rotate the unique values of the ProductName field of a table-valued expression into multiple columns in the output.
Which Transact-SQL operator should you use?
- A . CROSS JOIN
- B . CROSS APPLY
- C . PIVOT
- D . UNPIVOT
You administer a Microsoft SQL Server database that supports a shopping application.
You need to retrieve a list of customers who live in territories that do not have a sales person.
Which Transact- SQL query or queries should you use? (Each correct answer presents a complete solution. Choose all that apply.)
- A . SELECT CustomerID FROM Customer
WHERE TerritoryID <> SOME(SELECT TerritoryID FROM Salesperson) - B . SELECT CustomerID FROM Customer
WHERE TerritoryID <> ALL(SELECT TerritoryID FROM Salesperson) - C . SELECT CustomerID FROM Customer
WHERE TerritoryID <> ANY(SELECT TerritoryID FROM Salesperson) - D . SELECT CustomerID FROM Customer
WHERE TerritoryID NOT IN(SELECT TerritoryID FROM Salesperson)
You support a database structure shown in the exhibit. (Click the Exhibit button.)
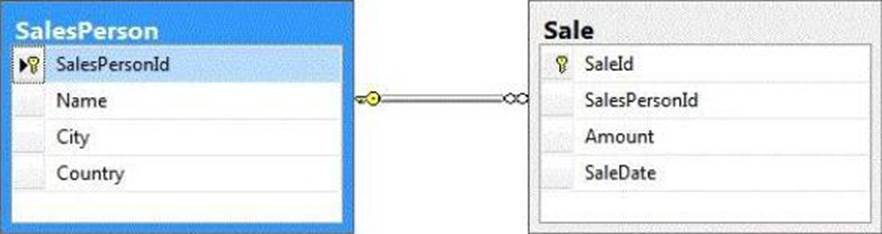
You need to write a query that displays the following details:
• Total sales made by sales people, year, city, and country
• Sub totals only at the city level and country level
• A grand total of the sales amount
Which Transact-SQL query should you use?
- A . SELECT SalesPerson.Name, Country, City,
DatePart(yyyy, SaleDate) AS Year, Sum(Amount) AS Total
FROM Sale INNER JOIN SalesPerson
ON Sale.SalesPersonID = SalesPerson.SalesPersonID
GROUP BY GROUPING SETS((SalesPerson.Name, Country, City, DatePart(yyyy,
SaleDate)), (Country, City), (Country), ()) - B . SELECT SalesPerson.Name, Country, City,
DatePart(yyyy, SaleDate) AS Year, Sum(Amount) AS Total
FROM Sale INNER JOIN SalesPerson
ON Sale.SalesPersonID = SalesPerson.SalesPersonID
GROUP BY CUBE(SalesPerson.Name, Country, City, DatePart(yyyy, SaleDate)) - C . SELECT SalesPerson.Name, Country, City,
DatePart(yyyy, SaleDate) AS Year, Sum(Amount) AS Total
FROM Sale INNER JOIN SalesPerson
ON Sale.SalesPersonID = SalesPerson.SalesPersonID
GROUP BY CUBE(SalesPerson.Name, DatePart(yyyy, SaleDate), City, Country) - D . SELECT SalesPerson.Name, Country, City,
DatePart(yyyy, SaleDate) AS Year, Sum(Amount) AS Total
FROM Sale INNER JOIN SalesPerson
ON Sale.SalesPersonID = SalesPerson.SalesPersonID
GROUP BY ROLLUP(SalesPerson.Name, DatePart(yyyy, SaleDate), City, Country)
You are developing a database that will contain price information.
You need to store the prices that include a fixed precision and a scale of six digits.
Which data type should you use?
- A . Float
- B . Money
- C . Smallmoney
- D . Numeric
You administer a Microsoft SQL Server database that supports a banking transaction management application.
You need to retrieve a list of account holders who live in cities that do not have a branch location.
Which Transact-SQL query or queries should you use? (Each correct answer presents a complete solution. Choose all that apply.)
- A . SELECT AccountHolderID
FROM AccountHolder
WHERE CityID NOT IN (SELECT CityID FROM BranchMaster) - B . SELECT AccountHolderID
FROM AccountHolder
WHERE CityID <> ALL (SELECT CityID FROM BranchMaster) - C . SELECT AccountHolderID
FROM AccountHolder
WHERE CityID <> SOME (SELECT CityID FROM BranchMaster) - D . SELECT AccountHolderID
FROM AccountHolder
WHERE CityID <> ANY (SELECT CityID FROM BranchMaster)
You administer a Microsoft SQL Server 2012 database. The database contains a table named Employee.
Part of the Employee table is shown in the exhibit. (Click the Exhibit button.)
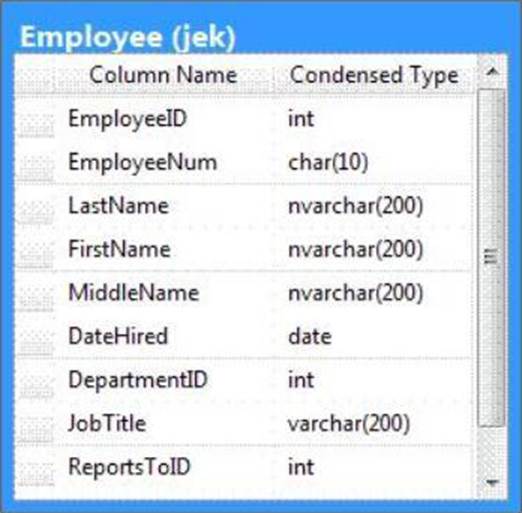
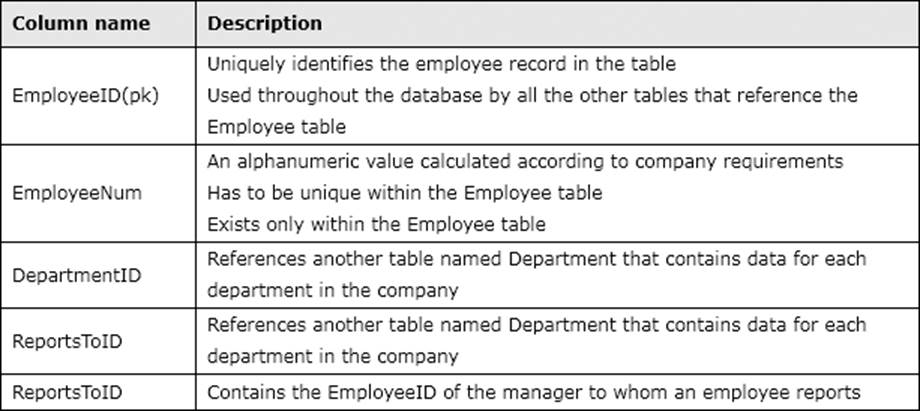
Confidential information about the employees is stored in a separate table named EmployeeData. One record exists within EmployeeData for each record in the Employee table. You need to assign the appropriate constraints and table properties to ensure data integrity and visibility.
On which column in the Employee table should you create a unique constraint?
- A . DateHired
- B . DepartmentID
- C . EmployeeID
- D . EmployeeNum
- E . FirstName
- F . JobTitle
- G . LastName
- H . MiddleName
- I . ReportsToID
You administer a Microsoft SQL Server 2012 database. The database contains a table named Employee.
Part of the Employee table is shown in the exhibit. (Click the Exhibit button.)
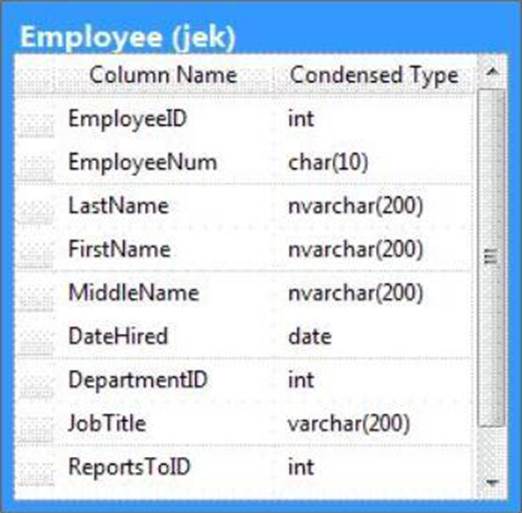
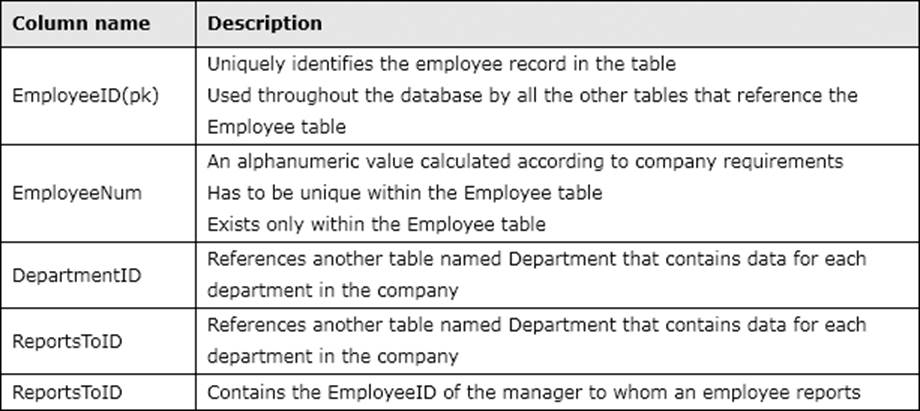
Unless stated above, no columns in the Employee table reference other tables.
Confidential information about the employees is stored in a separate table named EmployeeData. One record exists within EmployeeData for each record in the Employee table.
You need to assign the appropriate constraints and table properties to ensure data integrity and visibility.
On which column in the Employee table should you use an identity specification to include a seed of 1,000 and an increment of 1?
- A . DateHired
- B . DepartmentID
- C . EmployeeID
- D . EmployeeNum
- E . FirstName
- F . JobTitle
- G . LastName
- H . MiddleName
- I . ReportsToID
You administer a Microsoft SQL Server 2012 database that includes a table named Products. The Products table has columns named ProductId, ProductName, and CreatedDateTime.
The table contains a unique constraint on the combination of ProductName and CreatedDateTime.
You need to modify the Products table to meet the following requirements:
-Remove all duplicates of the Products table based on the ProductName column. -Retain only the newest Products row.
Which Transact-SQL query should you use?
- A . WITH CTEDupRecords
AS
(
SELECT MAX(CreatedDateTime) AS CreatedDateTime, ProductName
FROM Products
GROUP BY ProductName
HAVING COUNT(*) > 1
)
DELETE p
FROM Products p
JOIN CTEDupRecords cte ON - B . ProductName = cte.ProductName
AND p.CreatedDateTime > cte.CreatedDateTime - C . WITH CTEDupRecords
AS
(
SELECT MAX(CreatedDateTime) AS CreatedDateTime, ProductName
FROM Products
GROUP BY ProductName
HAVING COUNT(*) > 1
)
DELETE p
FROM Products p
JOIN CTEDupRecords cte ON
cte.ProductName = p.ProductName
AND cte.CreatedDateTime > p.CreatedDateTime - D . WITH CTEDupRecords
AS
(
SELECT MIN(CreatedDateTime) AS CreatedDateTime, ProductName
FROM Products
GROUP BY ProductName
)
DELETE p
FROM Products p
JOIN CTEDupRecords cte ON - E . ProductName = cte.ProductName
- F . WITH CTEDupRecords
AS
(
SELECT MAX(CreatedDateTime) AS CreatedDateTime, ProductName
FROM Products
GROUP BY ProductName
HAVING COUNT(*) > 1
)
DELETE p
FROM Products p
JOIN CTEDupRecords cte ON - G . ProductName = cte.ProductName
You develop three Microsoft SQL Server 2012 databases named Database1, Database2, and Database3. You have permissions on both Database1 and Database2.
You plan to write and deploy a stored procedure named dbo.usp_InsertEvent in Database3. dbo.usp_InsertEvent must execute other stored procedures in the other databases.
You need to ensure that callers that do not have permissions on Database1 or Database2 can execute the stored procedure.
Which Transact-SQL statement should you use?
- A . USE Database2
- B . EXECUTE AS OWNER
- C . USE Database1
- D . EXECUTE AS CALLER
You administer a Microsoft SQL Server 2012 database that has multiple tables in the Sales schema. Some users must be prevented from deleting records in any of the tables in the Sales schema. You need to manage users who are prevented from deleting records in the Sales schema.
You need to achieve this goal by using the minimum amount of administrative effort.
What should you do?
- A . Create a custom database role that includes the users. Deny Delete permissions on the Sales schema for the custom database role.
- B . Include the Sales schema as an owned schema for the db_denydatawriter role. Add the users to the db_denydatawriter role.
- C . Deny Delete permissions on each table in the Sales schema for each user.
- D . Create a custom database role that includes the users. Deny Delete permissions on each table in the Sales schema for the custom database role.
Latest 70-461 Dumps Valid Version with 232 Q&As
Latest And Valid Q&A | Instant Download | Once Fail, Full Refund

