ISTQB CTFL Foundation ISTQB Certified Tester Foundation Level Online Training
ISTQB CTFL Foundation Online Training
The questions for CTFL Foundation were last updated at Dec 16,2025.
- Exam Code: CTFL Foundation
- Exam Name: ISTQB Certified Tester Foundation Level
- Certification Provider: ISTQB
- Latest update: Dec 16,2025
Topic 5, Scenario 4, V2 "Test Management Tool"
The project situation after 11 months is:
– The first increment was released one week late but contained sufficient functionality to be declared fit for purpose’. However, there were 20 outstanding incidents deferred to increment two.
– The amount of voluntary overtime worked PV the test team has reduced the second Increment slippage to just 3 weeks.
– There is talk of reducing the scope of requirements. The purpose of this is to first deliver the application with support for manual testing and then to provide a delivery * weeks later to resolve any remaining points and provide support for automated testing (i.e. the link to the capture-replay tool).
– Concerns have been expressed by a section of the user community, that in some places the usability is very poor.
Which test management control option is most appropriate to adopt under these circumstances? 2 credits
- A . Introduce mandatory evening and weekend working to retrieve the 3 week slippage.
- B . Reconsider the exit criteria and review the test plan in the context of the current situation.
- C . Advise the user community regarding the reduced scope of requirements and the additional incremental delivery.
- D . Arrange a meeting with the user community representatives to discuss the user interface.
Which of the following is a project risk mitigation step you might take as test manager? 1 credit
- A . Testing for performance problems
- B . Hiring a contractor after a test analyst leaves the company
- C . Arranging a back-up test environment in case the existing one fails during testing
- D . Performing a project retrospective meeting using the test results after each increment
Which of the following is least likely to be used as a technique to identify project and product risks? 1 credit
- A . Brainstorming
- B . Inspections
- C . Expert interviews
- D . Independent assessments
Risks should be constantly reviewed. Given the current situation, which one of the following factors is most likely to lead to a revised view of product risk? 3 credits
- A . The concerns over the user interface may lead to changes to the interface which cannot be implemented by development in time for the second test iteration.
- B . The concerns over the user interface raises the likelihood of a risk in that area and increases the amount of test effort needed for the user interface, thereby limiting the test effort available for other parts of the test management tool.
- C . The delivery of the application without the interface changes may upset the user community.
- D . The method used for test estimation is not accurate enough and hence the money spent on testing exceeded its budget.
Topic 6, Scenario 5, V1"Human Resource System"
You have recently been employed as a test manager for a software house producing Human Resource (HR) systems, namely Payroll, Personnel and Recruitment systems. The company is relatively new and wants to make a major impact in the market by producing a worldwide enterprise HR product.
You have been asked to write a testing strategy for the company .
Which statement best explains how risk can be addressed within the testing strategy? 1 credit
- A . A test strategy should address identified generic product risks and present a process for mitigating those risks in line with the testing policy.
- B . A test strategy identifies the specific product for a project risk and defines the approach for the test project.
- C . A test strategy is derived from the test policy and describes the way risk assessments are performed in projects.
- D . A test strategy is the result of a project risk analysis and defines the approach and resources for testing.
Part of the testing strategy indicates that you are going to be using systematic test design techniques. Your manager has asked that you present the main advantages of using these techniques at the next board meeting. Identify THREE main benefits of using systematic test design techniques within this company. 2 credits (for 2 out of 3 correct 1 credit)
- A . Easier to quickly adapt testing to changing requirements compared to experienced-based testing
- B . Targets certain types of faults
- C . Will guide experienced testers to find defects
- D . Provides a way to differentiate depth of testing based on product risks by using different techniques
- E . More enhanced documentation and therefore higher repeatability and reproducibility
- F . Will make non-systematic testing redundant
- G . Will reduce the need for early reviews
In addition to risk, identify TWO other components of a testing strategy. 1 credit
- A . The entry and exit criteria for each test phase
- B . Test training needs for the project resources
- C . The test design techniques to be used
- D . Test performance indicators
- E . The test schedule
Topic 7, Scenario 5, V2 "Human Resource System"
For the first increment of the new enterprise HR product you have performed a product risk analysis using the FMEA method. Five risk items have been identified and the likelihood and impact have been scored using scoring tables.
This has resulted in the following scores:
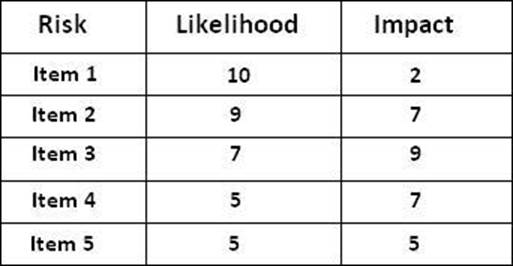
What is the Risk Priority Number for risk item number 2? 2 credits
- A . 16
- B . 2
- C . 1
- D . 63
What would be a test approach regarding the test design techniques to be applied that would fit an item with the highest risk? 2 credits
- A . Component testing: decision testing; System testing: exploratory testing
- B . Component testing: decision testing; System testing: decision table testing
- C . Component testing: statement testing; System testing: equivalence partitioning
- D . Component testing: statement testing; System testing: decision table partitioning
What would be a test approach regarding the test design techniques to be applied that would fit an item with the highest risk? 2 credits
- A . Component testing: decision testing; System testing: exploratory testing
- B . Component testing: decision testing; System testing: decision table testing
- C . Component testing: statement testing; System testing: equivalence partitioning
- D . Component testing: statement testing; System testing: decision table partitioning
Latest CTFL Foundation Dumps Valid Version with 338 Q&As
Latest And Valid Q&A | Instant Download | Once Fail, Full Refund

