Refer to the exhibit.
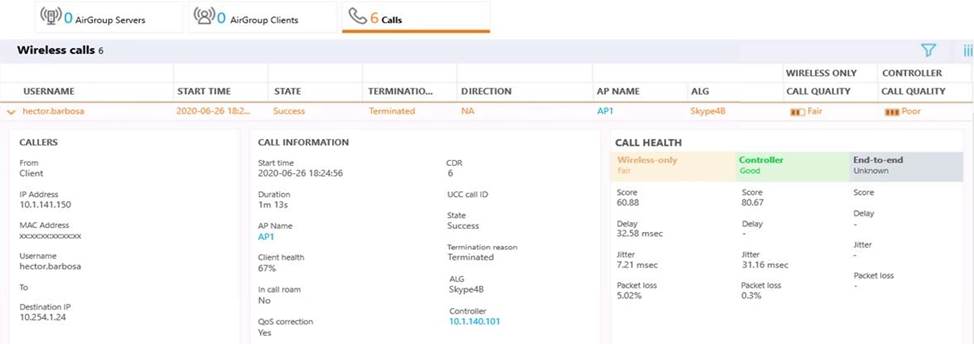
A network administrator has recently enabled WMM on the VAP’s SSID profile and enabled UCC Skype4B ALG at the Mobility Master level. During testing, some voice and video conference calls were made, and it was concluded that the call quality has dramatically improved. However, end to end information isn’t displayed in the call’s details. Also, Skype4B app-sharing’s performance is poor at times.
What must the administrator do next in order to enable end to end call visibility and QoS correction to app-sharing service?
- A . Deploy the SDN API Software in the Skype4B Solution and point to the MM.
- B . Increase the app-sharing DSCP value in the Skype4B ALG profile.
- C . Enable UCC monitoring on the "default-controller’ mgmt.-server profile.
- D . Enable the App-sharing ALG profile at both MM and MD hierarchy levels.
A company with 535 users deploys an Aruba solution with more than 1000 Aruba APs, two 7220 Mobility Controllers, and a single Mobility Master (MM) virtual appliance at the campus server farm. The MCs run a HA Fast failover group in dual mode and operate at 50% AP capacity.
If there is an MM or MC failure, the network administrator must ensure that the network is fully manageable and the MC load does not exceed 80%.
What can the network administrator do to meet these requirements?
- A . Place the APs in the same hierarchy level.
- B . Create a cluster with AP load balancing.
- C . Enable oversubscription in the HA group.
- D . Add an MC and an MM in the server farm.
- E . Add an MM and enable DC redundancy.
- F . Place the APs in two different AP-Groups.
Refer to the exhibit.
An organization provides WiFi access through a corporate SSID with an Aruba Mobility Master (MM) – Mobility Controller (MC) network that includes PEF functions. The organization wants to have a single firewall policy configured and applied to the employee role.
This policy must allow users to reach Web, FTP, and DNS services, as shown in the exhibit. Other services should be exclusive to other roles. The client NICs should receive IP settings dynamically.
Which policy design meets the organization’s requirements while minimizing the number of policy rules?
- A . Option A
- B . Option B
- C . Option C
- D . Option D
Refer to the exhibits.
Exhibit 1
Exhibit 2
Exhibit 3
A network administrator wants to allow contractors to access the corporate WLAN named EmployeesNet with the contractor role in VLAN 40. When users connect, they do not seem to get an IP address. After some verification checks, the network administrator confirms the DHCP server (10.254.1.21) is reachable from the Mobility Controller (MC) and obtains the outputs shown in the exhibits.
What should the network administrator do next to troubleshoot this problem?
- A . Permit UDP67 to the contractor role.
- B . Remove the IP address in VLAN 40.
- C . Configure the DHCP helper address.
- D . Confirm there is an IP pool for VLAN 40.
Refer to the exhibit.
A network administrator adds a Mobility Controller (MC) in the /mm level and notices that the device does not show up in the managed networks hierarchy. The network administrator accesses the CLI. executes the show switches command, and obtains the output shown in the exhibit.
What is the reason that the MC does not appear as a managed device in the hierarchy?
- A . The network administrator added the device using the wrong Pre-Shared Key (PSK).
- B . The network administrator has not moved the device into a group yet.
- C . The digital certificate of the MC is not trusted by the MM.
- D . The IP address of the MC does not match the one that was defined in the MM.
Refer to the exhibit.
A network administrator deploys a Mobility Master (MM) – Mobility Controller (MC) network with Aps in different locations. Users in one of the locations report that the WiFi network works fine for several hours, and then they are suddenly disconnected. This symptom may happen at any time, up to three times every day, and lasts no more than two minutes.
After some research, the network administrator logs into the MM and reviews the output shown in the exhibit.
Based on this information, what is the most likely reason users get disconnected?
- A . Adaptive Radio Management is reacting to RF events.
- B . AirMatch is applying a scheduled optimization solution.
- C . Users in the 2.4 GHz band are being affected by high interference.
- D . AirMatch is reacting to non-scheduled RF events.
A network administrator wants to permit explicit SSH, FTP and HHTP(s) access to servers in the 10.100.20.5 to 10.100.20.31 range, all devices in 10.100.21.0/24 network, and a host with IP address 10.100.22.70. The services must work properly at all times.
Which configuration scripts accomplish this task with the fewer number of lines, while avoiding access to other devices not included in these ranges? (Choose two.)
- A . Option A
- B . Option B
- C . Option C
- D . Option D
- E . Option E
Users run Skype for Business on wireless clients with no WMM support over an Aruba Mobility Master (MM) – Mobility Controller (MC) based network. When traffic arrives at the wired network, it does not include either L2 or L3 markings.
Which configuration steps should the network administrator take to classify and mark voice and video traffic with UCC heuristics mode?
- A . Enable WMM in a VAP profile, and explicitly permit voice and video UDP ports in a firewall policy.
- B . Confirm OpenFlow is enabled in the user role and VAP profile. Then enable WMM in a SSID profile, and explicitly permit voice and video UDP ports in a firewall policy.
- C . Confirm the MC is the Openflow controller of the MMs and Openflow is enabled in VAP and firewall roles. Enable Skype4Business ALG in UCC profiles.
- D . Confirm MM is the Openflow controller of MCs and Openflow is enabled in VAP and firewall roles. Enable Skype4Business ALG in UCC profiles.
Users run encrypted Skype for Business traffic with no WMM support over an Aruba Mobility Master (MM) – Mobility Controller (MC) based network. When voice, video, and application sharing traffic arrive at the wired side of the network, all the flows look alike due to the lack of L2 and L3 markings
How can the network administrator identify these flows and mark QoS accordingly?
- A . Confirm the MC is the Openflow controller of the MMs and Openflow is enabled in VAP and the firewall roles. Then enable WMM in a VAP profile.
- B . Use a media firewall policy that match these three flows, and use permit and TOS actions with 56, 40, and 34 values for voice, video, and application sharing, respectively Then enable the Skype4Business ALG in the UCC profiles.
- C . Confirm the MC is the Openflow controller of the MMs and Openflow is enabled in VAP and the firewall roles. Then enable the Skype4Business ALG in the UCC profiles.
- D . Confirm the MM is the Openflow controller of the MCs and Openflow is enabled in VAP and the firewall roles. Then integrate the MM with the Skype4Business SDN API. and enable the Skype4Business ALG in the UCC profiles.
Refer to the exhibit.
A network administrator has Mobility Master (MM) – Mobility Controller (MC) based network and has fully integrated the MCs with ClearPass for RADIUS-based AAA services. The administrator is testing different ways to run user role derivation.
Based on the show command output, what method has the administrator use for assigning the “corp” role to client with MAC xx:xx:xx:xx:xx:xx?
- A . Dynamic Authorization using VSA attributes.
- B . Dynamic Authorization using IETF attributes.
- C . Server Derivation Rules using IETF attributes.
- D . User Derivation Rules using the client’s MAC.
HOTSPOT
A network administrator wants to receive a warning level alarm every time the noise floor rises above -82 dBm on any of the AP radios.
Which alarm definition must the network administrator create to accomplish this?
Explanation:
Graphical user interface, application
Description automatically generated
Refer to the exhibits.
A network administrator deploys User Based Tunneling (UBT) in a corporate network to unify the security policies enforcement. When users authenticate with 802.1X, ClearPass shows Accept results, and sends the Aruba-User-Role attribute as expected. However, the AOS-CX based switch does not seem to build the tunnel to the Mobility Controller (MC) for this user.
Why does the switch fail to run UBT for the user?
- A . The switch has not fully associated to the MC.
- B . ClearPass is sending the wrong Vendor ID.
- C . The switch is not configured with the gateway-role.
- D . ClearPass is sending the wrong VSA type.
- E . The switch is not configured with the port-access role.
Refer to the exhibits.
Exhibit 1
Exhibit 2
Exhibit 3
Exhibit 4
A captive portal-based solution is deployed in a Mobility Master (MM) – Mobility Controller (MC) network. A wireless station connects to the network and attempts the authentication process. The outputs are shown in the exhibits.
Which names correlate with the authentication and captive portal servers?
- A . ClearPass.23 is the authentication server, and cp.mycompany.com is the captive portal server.
- B . ClearPass.23 is the authentication server, and MC2 is the captive portal server.
- C . Internal database in MC2 is the authentication server, and cp.mycompany.com is the captive portal server.
- D . cp.mycompany.com is the authentication server, and ClearPass.23 is the captive portal server.
A network administrator has deployed an Airwave Management Platform (AMP) server and integrated it with a Mobility Master (MM) C Mobility Controller (MC) based WLAN. The AMP server already has all Aruba Mobility devices including Access Points (APs) in the “UP” devices list.
What are two actions the administrator can execute upon the APs under “Airwave>Devices>Monitor”? (Choose two.)
- A . Open the WebUI of the MC where the AP terminates.
- B . Re-provision the Access Point.
- C . Disable and change the mode of the AP’s radios.
- D . Invoke MC’s show commands for that Access Point.
- E . Run Spectrum Analysis locally.
Refer to the exhibit.
Based on the output shown in the exhibit, with which Aruba devices has Access-1 established tunnels?
- A . a pair of standalone MCs
- B . a pair of switches running VXLAN
- C . a pair of MCs within a L3 cluster
- D . a single standalone MC