HP HPE6-A71 Aruba Certified Mobility Professional Exam Online Training
HP HPE6-A71 Online Training
The questions for HPE6-A71 were last updated at Dec 11,2025.
- Exam Code: HPE6-A71
- Exam Name: Aruba Certified Mobility Professional Exam
- Certification Provider: HP
- Latest update: Dec 11,2025
Which network components are tracked by Aruba Clarity? (Choose two.)
- A . Wireless associations
- B . DNS lookups
- C . AP and controller health
- D . WLAN health
- E . Client health
Refer to the exhibit.
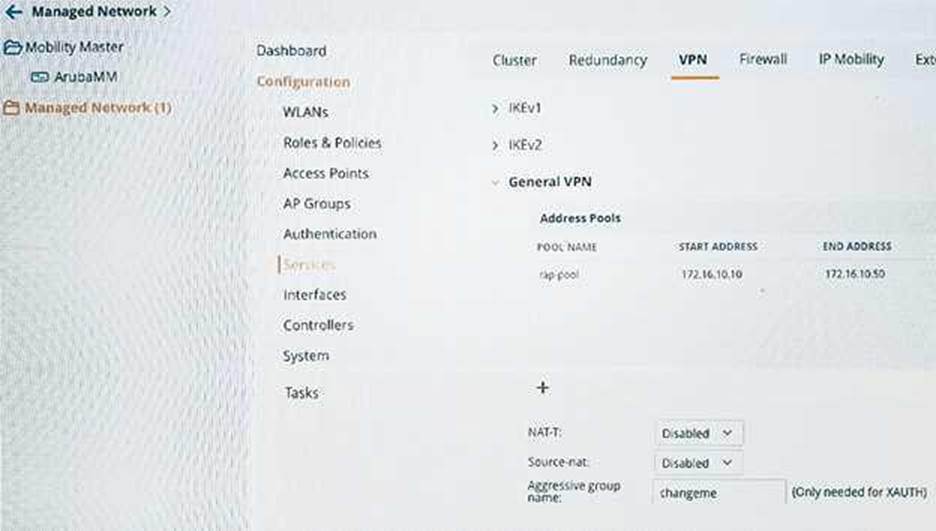
An administrator configures policies to allow RAPs to connect to the corporate office and remote users to access resources .
Which function does the VPN address pool serve in this situation?
- A . Assigns an inner IP address to the RAP used within the VPN
- B . Assigns a public IP address that the RAP should use on its internet port
- C . Assigns IP addresses for remote users
- D . Assigns a DHCP address pool for the RAP
When they operate in a cluster, Aruba APs obtain AP Group configuration information form which device?
- A . Mobility Master
- B . AirWave
- C . ClearPass
- D . Mobility Controller
Refer to the exhibit.
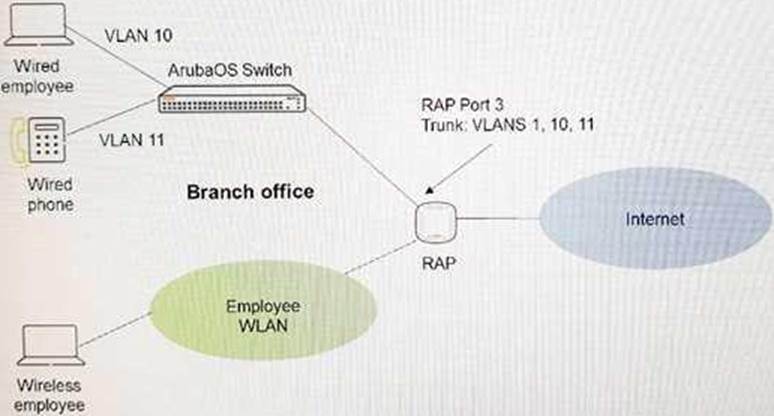
An administrator configures a policy for an AP Group. Port 3 of a RAP is a trunk that connects to a switch at a branch office. VLAN 1 is untagged and VLANs 10 (for data) and 11 (for voice) are tagged. The administrator applies an ACL inbound on Port 3 of the RAP .
How does this configuration affect traffic on Port 3?
- A . It filters traffic from VLAN 10 and 11, but allows traffic from VLAN1.
- B . It filters traffic form VLAN 1, but allows traffic from VLANs 10 and 11.
- C . It allows all traffic form VLANs 1, 10, and 11.
- D . It filters traffic from VLANs 1, 10, and 11.
An administrator supports a network that contains ArubaOS-Switches and Mobility Controllers (MCs). Restrictive MC firewall policies, control wireless access. The administrator wants to implement a feature to apply the same MC firewall policies to users connected to the Ethernet switch ports.
Which ArubaOS-Switch feature provides this capability?
- A . Port Security
- B . Tunneled node
- C . IPSec site-to-site tunneling
- D . VSF
An administrator purchases a RAP and has it shipped directly to a branch office. The branch office plugs in the RAP and the RAP contacts Aruba Activate. The RAP learns the Mobility Controller (MC) IP address and connects to it .
How ever, the connection fails.
Upon verifying the MC IP address in Aruba Activate, what should the administrator do to allow the RAP connection to succeed?
- A . Whitelist the RAP’s IP address on the MC.
- B . Define the RAP’s IPSec pre-shared key in Activate.
- C . Whitelist the RAP’s certificate on the MC.
- D . Configure a VPN address pool in Activate.
An administrator has a standalone controller that runs ArubaOS 8.x software and wants to upgrade it
to a newer release. The upgrade will be performed from the front panel of the physical controller.
The administrator places the new software in the root directory of a USB drive. On the controller’s LCD panel, no image is found.
What is the cause of this problem?
- A . The image must be placed in the /Upgrade subdirectory.
- B . The image must be placed in the /Images subdirectory.
- C . The image must be placed in the /ArubaImage subdirectory.
- D . The upgrade must be performed from the controller’s WebUI.
What is true about Aruba controllers under normal operations in a Mobility Master (MM)-Mobility Controller (MC) architecture?
- A . The Mobility Master can push a full configuration to a Mobility Controller.
- B . ARM must be used to optimize wireless performance.
- C . The APs can terminate on both Mobility Masters and Mobility Controllers.
- D . Any controller can perform local configurations.
Refer to the exhibit.
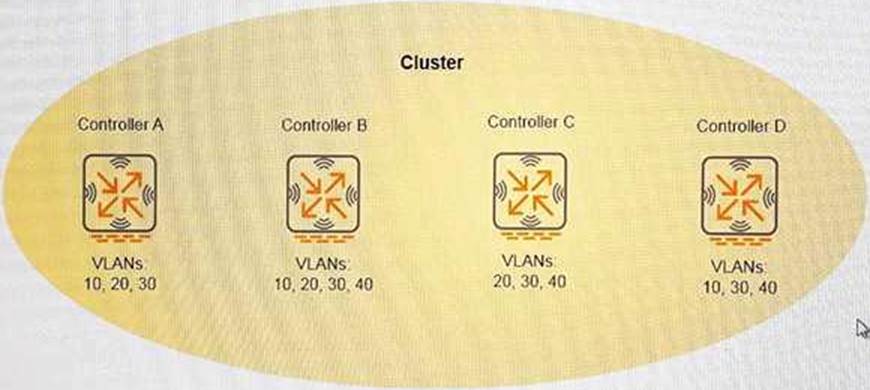
An administrator configures a cluster with only the members shown in the exhibit. AP load balancing is enabled. There are no other cluster parameters configured .
What occurs when a cluster member experiences a failure?
- A . High value sessions are synchronized.
- B . APs and clients are fully replicated.
- C . Connected users are de-authenticated
- D . APs reboot and rejoin the cluster.
Refer to the exhibit.
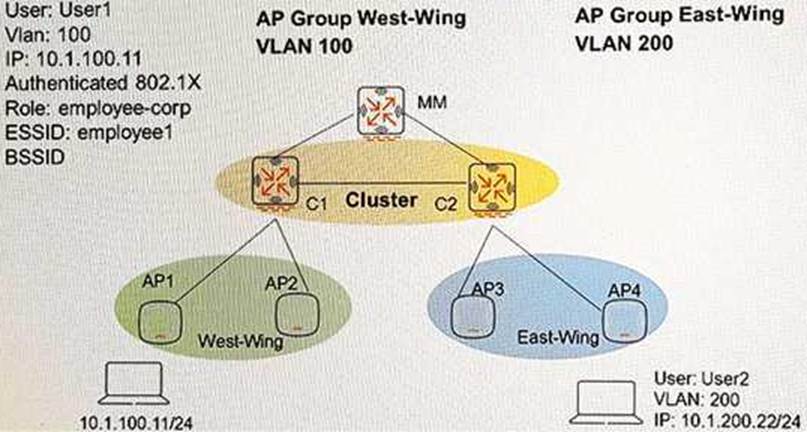
Controllers are configured in a cluster as shown in the exhibit.
These are the network details.
– A Mobility Master (MM) managers the cluster.
– The cluster contains two controllers: C1 and C2.
– AP1 and AP2 use C1 as their Active AP Anchor Controller (A-AAC), with C2 as their Standby AAC (S-AAC).
– AP3 and AP4 use C2 as their A-AAC with, C1 as their S-AAC.
User1 establishes a wireless connection via AP1, where the Active User Controller (U-UAC) assigned is C1, with C2 as the standby .
What happens when User1 roams the wireless network and eventually their session is handled by AP3?
- A . The AP3’s A-AAC switches to C1, and the user’s A-UAC remains on C1.
- B . The AP3’s A-AAC switches to C2, and the user’s A-UAC remains on C2.
- C . The AP3’s A-AAC switches to C1, and the user’s A-UAC remains on C2.
- D . The AP3’s A-AAC switches to C2, and the user’s A-UAC remains on C1.
Latest HPE6-A71 Dumps Valid Version with 166 Q&As
Latest And Valid Q&A | Instant Download | Once Fail, Full Refund

