HP HPE6-A45 Implementing Aruba Campus Switching solutions Online Training
HP HPE6-A45 Online Training
The questions for HPE6-A45 were last updated at Dec 13,2025.
- Exam Code: HPE6-A45
- Exam Name: Implementing Aruba Campus Switching solutions
- Certification Provider: HP
- Latest update: Dec 13,2025
A network administrator configures DHCP snooping on VLAN 2.
How does the switch handle DHCP traffic that arrives in this VLAN on an untrusted interface?
- A . It accepts packets from a DHCP server, but drops client packets.
- B . It drops all DHCP traffic and logs a security event.
- C . It accepts both client and server packets as long as they match the DHCP binding table.
- D . It accepts client packets, but drops packets from a DHCP server.
Refer to the exhibit.
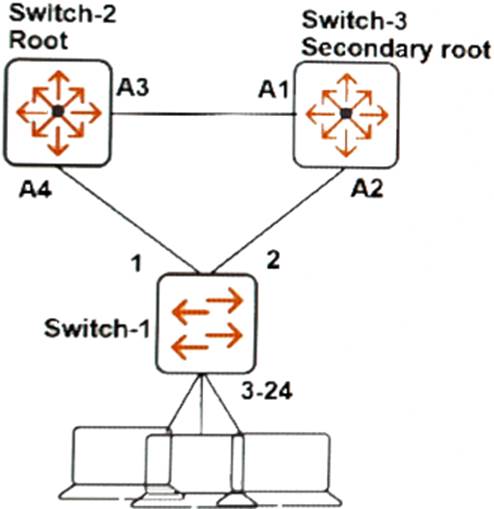
A network administrator wants to add the protections of root guard to the network.
Based on the spanning tree topology, on which ports should the network administrator implement root guard?
- A . 3-24
- B . 1 and 2
- C . A1 and A2
- D . 2 and A3
The implementation plan for AOS-Switches calls for them to implement port-based tunneled node. The Aruba Mobility Controllers that will support the AOS-Switches run software 8.1. The controllers will also support APs, are managed by Mobility Master, and use clustering.
Which issue with this plan needs to be addressed?
- A . The controllers cannot support tunneled node with AOS-Switches when they are managed by the Mobility Master.
- B . The switches cannot connect to controllers that also support APs.
- C . The controllers must have their software updated before they can support the switches.
- D . The switches must use role-based tunneled node to work with clustering controllers.
What is one difference between BPDU protection and root guard?
- A . BPDU protection works with RPVST+, RSTP, and MSTP. Root guard works with RSTP or MSTP, but not RPVST+.
- B . BPDU protection blocks a port if it receives any BPDU, but root guard blocks a port only if the BPDU indicates a better root path.
- C . BPDU protection is typically implemented on edge ports, but root guard is typically implemented on uplinks with the root port role.
- D . BPDU protection drops BPDUs received on a port, but does not block the port. Root guard blocks the port if it receives a BPDU.
Refer to the exhibit.

The exhibit shows configurations for interface 5 and VLAN 20. Note that DHCP snooping and ARP protection are also enabled.
A network administrator finds that interface 5 on an AOS-Switch is disabled. The administrator re-enables the interface, but it shuts down again.
What should the administrator investigate?
- A . a device that sends too much unicast traffic
- B . rogue DHCP server
- C . a loop on the interface
- D . a device that sends unauthorized ARP messages
Refer to the exhibit.

Switch-1 and Switch-2 connect on interface A23. The switches experience a connectivity issue. The network administrator sees that both switches show this interface as up. The administrator sees the output shown in the exhibit on Switch-1.
What is a typical issue that could cause this output?
- A . asymmetric routing introduced by a routing protocol
- B . an issue with VLAN mismatch
- C . mismatched subnet mask on the VLAN for the link
- D . a jumbo frame mismatch
What is a reason to implement PIM-DM as opposed to PIM-SM?
- A . to control exactly which multicast groups are routed through the network
- B . to permit a higher density of RP routers in the network core
- C . to conserve bandwidth over WAN links
- D . to use on high-bandwidth routed connections
An AOS-Switch enforces 802.1X. It receives an Access-Accept with this HPE VSA from its Radius server:
Attribute Name and ID = HPE-User-Role (25) Value = contractor
The switch then rejects the client.
What is one requirement for the switch to accept the message and authorize the client?
- A . The initial user role must be set to the factory default permit any role.
- B . User role authorization must be enabled globally on the switch.
- C . An aaa authentication local user group must have the contractor name.
- D . The RADIUS server settings must permit dynamic authorization.
Network administrators need to configure a BGP neighbor on an AOS-Switch.
What defines the neighbor as an iBGP neighbor?
- A . It has BGP synchronization enabled.
- B . It has an AS number in the range of 64512 to 64535.
- C . Its update source is set to a private company IP address.
- D . Its remote-AS is the same as the AOS-Switch BGP AS.
Refer to the exhibits.
Exhibit 1
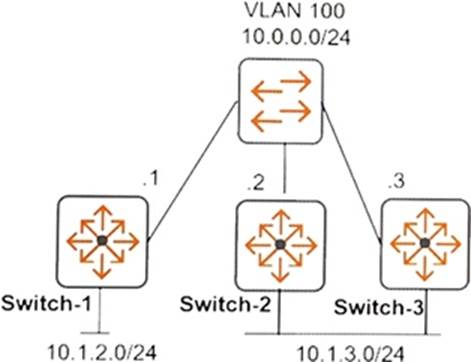
Exhibit 2

Exhibit 1 shows the topology for the network. The network administrator sees the log entries shown in Exhibit 2.
Which type of failure is indicated?
- A . A link between Switch-1 and Switch-2 went down. BFD detected the lost connectivity and behaved as expected.
- B . Graceful restart helper was not enabled on Switch-2, so BFD was unable to operate correctly, and the session was taken down.
- C . A hardware issue caused a unidirectional link; BFD detected the issue at Layer 2 and prevented a broadcast storm.
- D . BFD was set up incorrectly on Switch-2, so it caused Switch-2 to lose adjacency with Switch-1 rather than repair the session.
Latest HPE6-A45 Dumps Valid Version with 167 Q&As
Latest And Valid Q&A | Instant Download | Once Fail, Full Refund


nice experience please provide more quiz