HP HPE6-A44 Scalable WLAN Design and Implementation (SWDI) 8 Online Training
HP HPE6-A44 Online Training
The questions for HPE6-A44 were last updated at Dec 16,2025.
- Exam Code: HPE6-A44
- Exam Name: Scalable WLAN Design and Implementation (SWDI) 8
- Certification Provider: HP
- Latest update: Dec 16,2025
Which network components are tracked by Aruba Clarity? (Choose two.)
- A . Wireless associations
- B . DNS lookups
- C . AP and controller health
- D . WLAN health
- E . Client health
Refer to the exhibit.

An administrator configures policies to allow RAPs to connect to the corporate office and remote users to access resources.
Which function does the VPN address pool serve in this situation?
- A . Assigns an inner IP address to the RAP used within the VPN
- B . Assigns a public IP address that the RAP should use on its internet port
- C . Assigns IP addresses for remote users
- D . Assigns a DHCP address pool for the RAP
When they operate in a cluster, Aruba APs obtain AP Group configuration information form which device?
- A . Mobility Master
- B . AirWave
- C . ClearPass
- D . Mobility Controller
Refer to the exhibit.
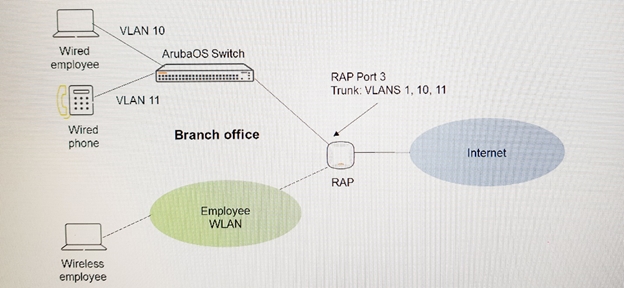
An administrator configures a policy for an AP Group. Port 3 of a RAP is a trunk that connects to a switch at a branch office. VLAN 1 is untagged and VLANs 10 (for data) and 11 (for voice) are tagged. The administrator applies an ACL inbound on Port 3 of the RAP.
How does this configuration affect traffic on Port 3?
- A . It filters traffic from VLAN 10 and 11, but allows traffic from VLAN1.
- B . It filters traffic form VLAN 1, but allows traffic from VLANs 10 and 11.
- C . It allows all traffic form VLANs 1, 10, and 11.
- D . It filters traffic from VLANs 1, 10, and 11.
An administrator supports a network that contains ArubaOS-Switches and Mobility Controllers (MCs).
Restrictive MC firewall policies, control wireless access. The administrator wants to implement a feature to apply the same MC firewall policies to users connected to the Ethernet switch ports.
Which ArubaOS-Switch feature provides this capability?
- A . Port Security
- B . Tunneled node
- C . IPSec site-to-site tunneling
- D . VSF
An administrator purchases a RAP and has it shipped directly to a branch office. The branch office plugs in the RAP and the RAP contacts Aruba Activate. The RAP learns the Mobility Controller (MC) IP address and connects to it.
However, the connection fails. Upon verifying the MC IP address in Aruba Activate, what should the administrator do to allow the RAP connection to succeed?
- A . Whitelist the RAP’s IP address on the MC.
- B . Define the RAP’s IPSec pre-shared key in Activate.
- C . Whitelist the RAP’s certificate on the MC.
- D . Configure a VPN address pool in Activate.
An administrator has a standalone controller that runs ArubaOS 8.x software and wants to upgrade it to a newer release. The upgrade will be performed from the front panel of the physical controller. The administrator places the new software in the root directory of a USB drive. On the controller’s LCD panel, no image is found.
What is the cause of this problem?
- A . The image must be placed in the /Upgrade subdirectory.
- B . The image must be placed in the /Images subdirectory.
- C . The image must be placed in the /ArubaImage subdirectory.
- D . The upgrade must be performed from the controller’s WebUI.
What is true about Aruba controllers under normal operations in a Mobility Master (MM)-Mobility Controller (MC) architecture?
- A . The Mobility Master can push a full configuration to a Mobility Controller.
- B . ARM must be used to optimize wireless performance.
- C . The APs can terminate on both Mobility Masters and Mobility Controllers.
- D . Any controller can perform local configurations.
Refer to the exhibit.
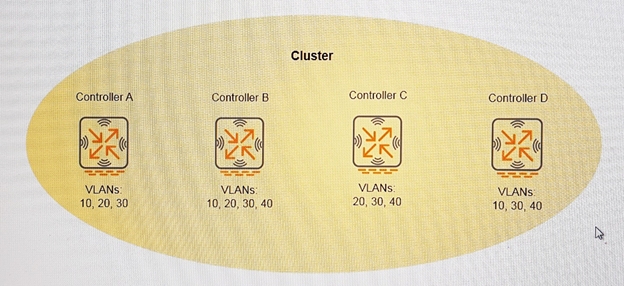
An administrator configures a cluster with only the members shown in the exhibit. AP load balancing is enabled. There are no other cluster parameters configured.
What occurs when a cluster member experiences a failure?
- A . High value sessions are synchronized.
- B . APs and clients are fully replicated.
- C . Connected users are de-authenticated
- D . APs reboot and rejoin the cluster.
Refer to the exhibit.
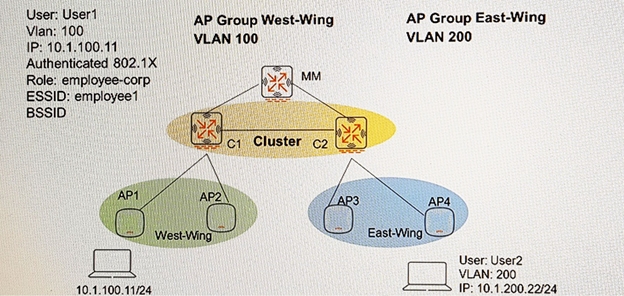
Controllers are configured in a cluster as shown in the exhibit.
These are the network details.
– A Mobility Master (MM) managers the cluster.
– The cluster contains two controllers: C1 and C2.
– AP1 and AP2 use C1 as their Active AP Anchor Controller (A-AAC), with C2 as their Standby AAC (SAAC).
– AP3 and AP4 use C2 as their A-AAC with, C1 as their S-AAC.
User1 establishes a wireless connection via AP1, where the Active User Controller (U-UAC) assigned is C1, with C2 as the standby.
What happens when User1 roams the wireless network and eventually their session is handled by AP3?
- A . The AP3’s A-AAC switches to C1, and the user’s A-UAC remains on C1.
- B . The AP3’s A-AAC switches to C2, and the user’s A-UAC remains on C2.
- C . The AP3’s A-AAC switches to C1, and the user’s A-UAC remains on C2.
- D . The AP3’s A-AAC switches to C2, and the user’s A-UAC remains on C1.
Latest HPE6-A44 Dumps Valid Version with 163 Q&As
Latest And Valid Q&A | Instant Download | Once Fail, Full Refund

