HP HPE6-A42 Implementing Aruba WLAN (IAW) 8 Online Training
HP HPE6-A42 Online Training
The questions for HPE6-A42 were last updated at Sep 10,2025.
- Exam Code: HPE6-A42
- Exam Name: Implementing Aruba WLAN (IAW) 8
- Certification Provider: HP
- Latest update: Sep 10,2025
A company has an Aruba solution. The company wants to host a guest login portal with this solution, and the login portal must gie guests the option to create their own login accounts.
How can a network administrator help meet these criteria?
- A . Choose the Internal captive portal with email registration option for the guest WLAN.
- B . Make sure to create a guest provisioning account for the guest WLAN.
- C . Disable authentication in the captive portal profile for the guest WLAN.
- D . Choose ClearPass or the other external captive portal option for the guest WLAN.
A network administrator needs to configure firewall rules for three roles:
– Finance
– Sales
– Employee
Several rules apply to both the Employee and Sales roles, but not to the Finance role.
What is the simplest way to configure these rules?
- A . Define the Employee and Sales roles as internal roles, and then configure the rules as global rules for internal users.
- B . Apply these rules as a subnet-based policy, and then ensure that only Employee and Sales users are assigned IP addresses in that subnet.
- C . Select either the Employee or Sales role, and then configure these rules within the global policy.
- D . Create a policy with these rules, and then apply that policy to the Employee and Sales roles.
An Aruba Mobility Master (MM)-based solution has a WLAN that uses WPA2-Enterprise security. A test login on a wireless client fails.
How can a network administrator determine whether the RADIUS server rejected the credentials or another issue occurred?
- A . View Technical Support information for the MM.
- B . Ping the IP address configured as the RADIUS server.
- C . Use the MM AAA Server Test Diagnostic tool.
- D . Use the tools in the MM Dashboard > Security window.
What does an Aruba Mobility Master (MM) do before it deploys a configuration to a Mobility Controller (MC)?
- A . It encrypts the configuration to be deployed and backs it up to a secure archive.
- B . It obtains the current configuration, encrypts it, and backs it up to a secure archive.
- C . It synchronizes the configuration with templates on Aruba AirWave.
- D . It removes any commands that are not supported on that MC or have dependency errors.
Refer to the exhibit.
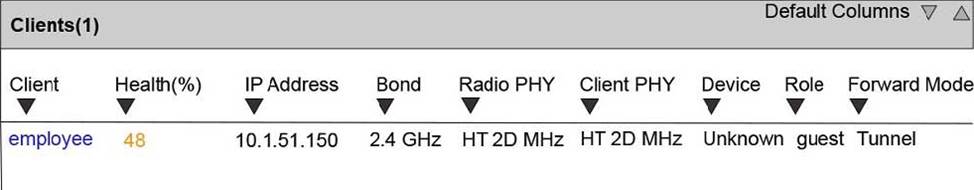
The exhibit shows output from a Mobility Master (MM) dashboard.
What does the health status indicate?
- A . It takes the AP about twice as long to send data to the client as expected if all transmissions succeeded.
- B . About half of the heartbeats the client sends reaches the Mobility Manager (MM).
- C . The maximum data rate that 802.11ac supports is about twice as high as the data rate the client uses.
- D . The client device only complies with about half of the rules in the endpoint health policy.
A network administrator creates the role employees and adds the rule to it:
user any any permit
The first several wireless clients assigned to the employees role are assigned IP addresses in the 10.10.10.0/24 subnet. Several other wireless clients with the employees role are then assigned IP addresses in the 10.10.20.0/24.
When the Aruba firewall matches traffic from these clients to the user any any permit rule, what does it do?
- A . It drops traffic from wireless clients in both the 10.10.0/24 subnet and 10.10.20.0/24 subnet.
- B . It permits traffic from wireless clients in both the 10.10.10.0/24 and 10.10.20.0/24 subnet as long as the packet has a source IP.
- C . It permits the traffic from wireless clients in the 10.10.20.0/24 subnet, but drops the traffic from wireless clients in the 10.10.10.0/24 subnet.
- D . It permits the traffic from wireless clients in the 10.10.0/24 subnet, but drops the traffic from wireless clients in the 10.10.20.0/24 subnet.
A company has an Aruba solution. A network administrator wants to prevent wireless users from accessing shopping web sites with a bad reputation.
What should the administrator set up to deny such traffic?
- A . an AppRF engine
- B . application filters in the Traffic Analysis dashboard
- C . firewall access control rules that specify HTTP and HTTPS services
- D . firewall application rules
Refer to the exhibits.
Exhibit 1
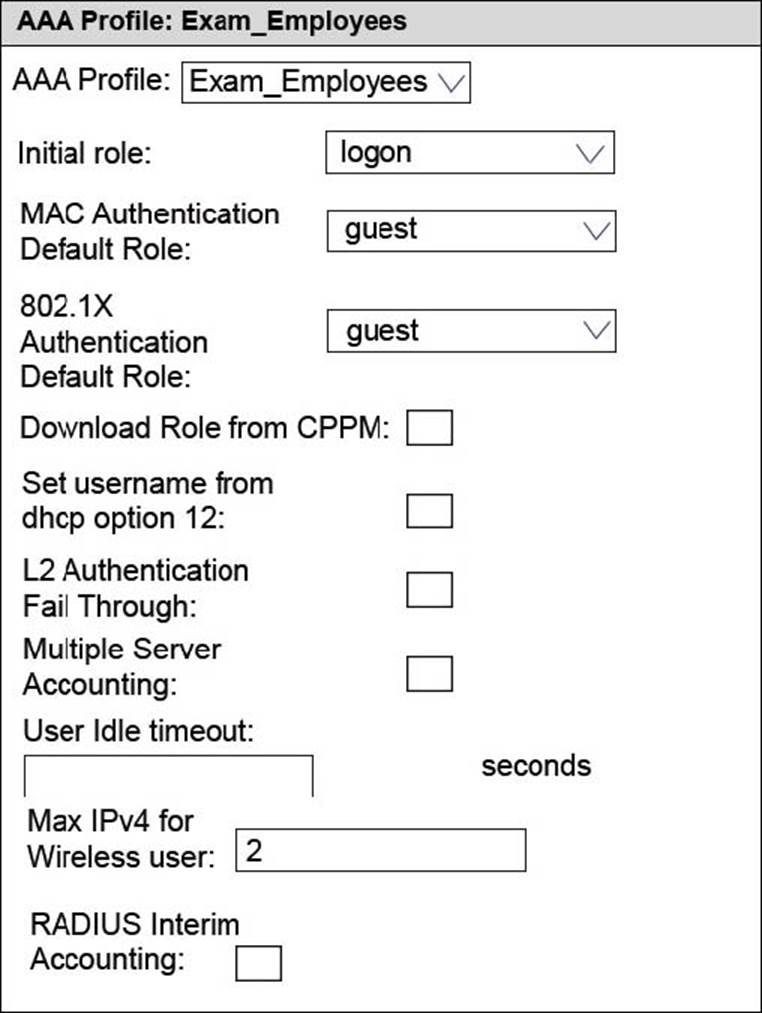
Exhibit 2
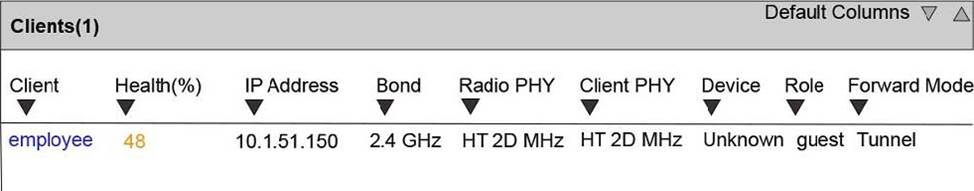
An Aruba solution supports a WLAN that uses WPA2-Enterprise security. Exhibit 1 shows the AAA policy for the WLAN. Users are supposed to be assigned to different roles after authentication. Network administrators test a connection with the employee user account. Exhibit 2 shows the status for the client after this test.
What is a possible reason for the issue shown in Exhibit 2?
- A . The shared key configured for the ClearPass server is incorrect.
- B . The RADIUS server is not correctly set up to send a user role for the employee account.
- C . MAC authentication is enabled on the WLAN, and the test device does not have an authorized address.
- D . The administrators entered the wrong password for the employee account.
A company has a single Aruba Mobility Master (MM)-based solution with two Mobility Controllers (MCs). Network administrators want APs in building 1 to support a WLAN but do not want APs in building 2 to support the WLAN.
How can administrator ensure that they can enforce this rule as they set up the WLAN in the Mobility Master (MM) Interface?
- A . Place APs in different buildings in different AP Groups.
- B . Assign APs in different buildings to different MM nodes.
- C . Configure APs in different buildings to use different frequency bands.
- D . Assign different radio profiles to APs in different buildings.
What is one difference between captive portal authentication and 802.1X authentication?
- A . 802.1X authentication always authenticates the wireless client, while captive portal authentication always authenticates the wireless user.
- B . 802.1X authentication occurs at Layer 2, while captive portal authentication occurs at Layer 3.
- C . 802.1X authentication must use an LDAP server, while captive portal authentication can use a RADIUS server or an LDAP server.
- D . 802.1X authentication is typically implemented without encryption, while captive authentication is often combined with WPA or WPA2.
Latest HPE6-A42 Dumps Valid Version with 129 Q&As
Latest And Valid Q&A | Instant Download | Once Fail, Full Refund

