HP HPE6-A41 Applying Aruba Switching Fundamentals for Mobility Online Training
HP HPE6-A41 Online Training
The questions for HPE6-A41 were last updated at Oct 18,2025.
- Exam Code: HPE6-A41
- Exam Name: Applying Aruba Switching Fundamentals for Mobility
- Certification Provider: HP
- Latest update: Oct 18,2025
An ArubaOS switch operates at its factory default settings. A network administrator connects the switch to a VLAN with a DHCP server. The switch-to-switch connection carries untagged traffic. The administrator wants to use Telnet log in to the switch CLI.
How should the administrator contact the switch and log in?
- A . Contact the switch at its default IP address 172.16.0.254/24 and log in without entering a password.
- B . Contact the switch at its default IP address 192.168.1.1/24 and log in with me default password admin.
- C . Contact the switch at its DHCP-assigned IP address and log in without entering a password.
- D . Contact the switch at its DHCP-assigned IP address and log in with the default password aruba.
Refer to the exhibit.
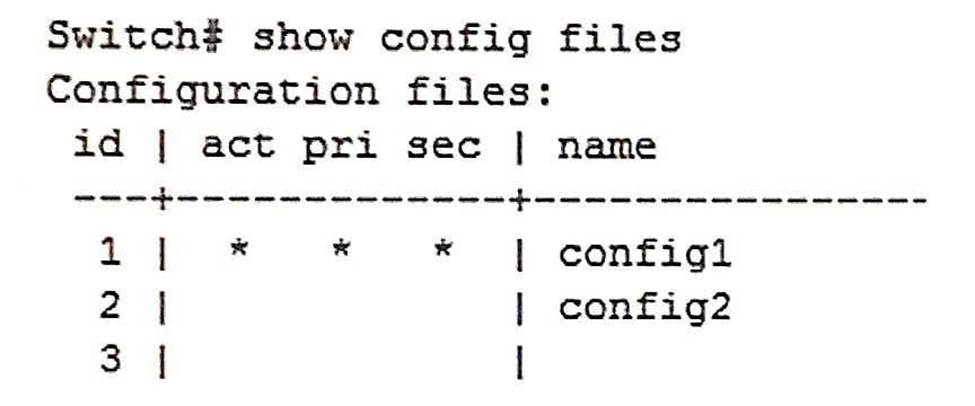
A network administrator views the configuration files on an ArubaOS switch and sees the output in the exhibit. The administrator enters this command:
Switch# boot system flash primary config config2
After the switch boots, the administrator makes some configuration changes and saves the configuration with the write memory command.
The administrator then enters this command:
Switch# boot
After the switch boots, the configuration changes just made are not present.
How can the administrator restore the configuration with the changes?
- A . Use the boot set-default command to configure the switch to use the secondary software. Then reboot the switch.
- B . Reboot the switch and interrupt the boot process. Find the temporary file with the configuration changes and apply that file to the startup-config.
- C . Rename the config2 file to config1. Then reboot the switch.
- D . Use the startup-default command to configure the switch to use the config2 file with the primary software. Then reboot the switch.
For which task does a network administrator need to access the enable context on an ArubaOS switch?
- A . to view interface statistics
- B . to view CPU statistics
- C . to ping an IP address
- D . to view configuration files
A network administrator prepares an ArubaOS switch to be monitored and managed by AirWave.
Which credentials are required for AirWave to change configuration settings on the switch?
- A . RADIUS shared secret
- B . SNMPv2c community with manager unrestricted privileges
- C . Telnet or SSH password
- D . SNMPv3c user in the ManagerPriv group
A company has an Aruba 5400R switch, switch 1, at the network core of its campus. This switch routes all traffic for the campus and is the RSTP root. The company now wants to add another Aruba 5400R switch to the core in order to enhance resiliency. The company wants to use the option that provides the best Layer 2 and Layer 3 resiliency and also the simplest setup.
What should the administrator do to add the new 5400R switch?
- A . Add the new switch and migrate to MSTP with two instances.
- B . Add the new switch and set up OSPF on all switches.
- C . Add the new switch as a secondary root bridge in RSTP.
- D . Add the new switch as a standby member in a VSF fabric with switch 1.
Which settings should match on physical interfaces before a network combines them in a link aggregation?
- A . speed and duplex mode
- B . DSCP and media
- C . speed and VLANs
- D . LLDP TLVs and VLAns
Two switches are members of a Virtual Switching Framework (VSF) fabric.
Which statement correctly describes how the switches handle routing?
- A . Only the commander runs routing protocols and builds the IP routing table, but it programs the standby member to route traffic.
- B . Both members build their own IP routing tables, which they synchronize. Only static IP routing is supported with VSF.
- C . Only the commander runs routing protocols and builds the IP routing table, and all routed traffic must pass through the commander.
- D . Both members run routing protocols and build their own IP routing tables, and they synchronize the tables over VSF links.
A server connects to a port on an ArubaOS switch. The network administrator wants to ensure that the port remains forwarding during MSTP topology changes, and changes in the port status do not cause MSTP topology changes.
Which statement describes how the administrator can accomplish this?
- A . The administrator can accept the default behavior of auto-edge.
- B . The administrator can lower the port’s root path cost to zero.
- C . The administrator can manually disable STP on the edge port.
- D . The administrator can configure the port as an MSTP master port.
Refer to the exhibit.
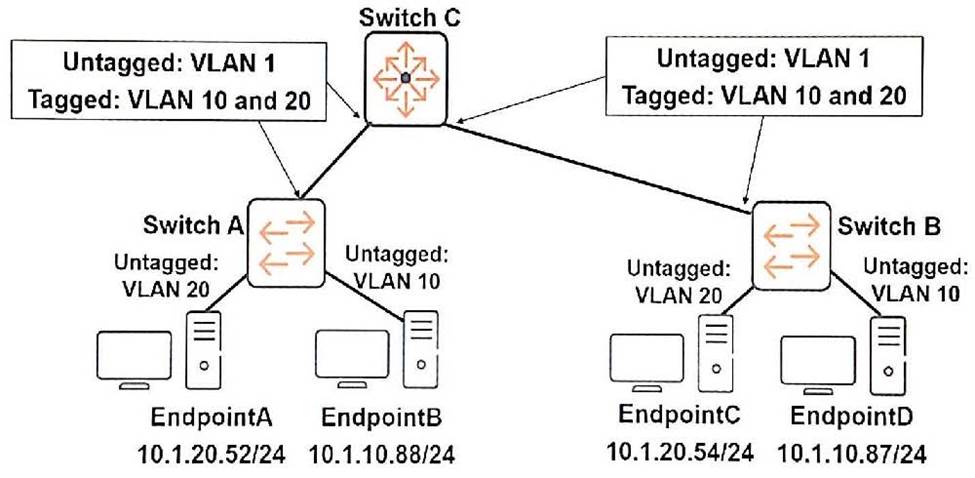
Endpoint A sends broadcast ARP requests.
Where are these requests received?
- A . at EndpointC
- B . at EndpointB
- C . at EndpointB, at EndpointC, and at EndpointD
- D . at EndpointB and at EndpointC
A network administrator wants to be able to access an Aruba Instant cluster at the same IP address even if the current master fails.
How can the administrator achieve this goal?
- A . Configure a VC IP address that is a reserved IP address in the AP’s subnet.
- B . Configure the AirWave IP address in the instant cluster System > Admin settings.
- C . Assign static IP addresses, rather than DHCP ones, to all APs in the instant cluster.
- D . Assign a static IP addresses, rather than a DHCP one, to the AP that is elected master.
Latest HPE6-A41 Dumps Valid Version with 125 Q&As
Latest And Valid Q&A | Instant Download | Once Fail, Full Refund

