How do you correct this Issue with minimal configuration changes?
Refer to the exhibit
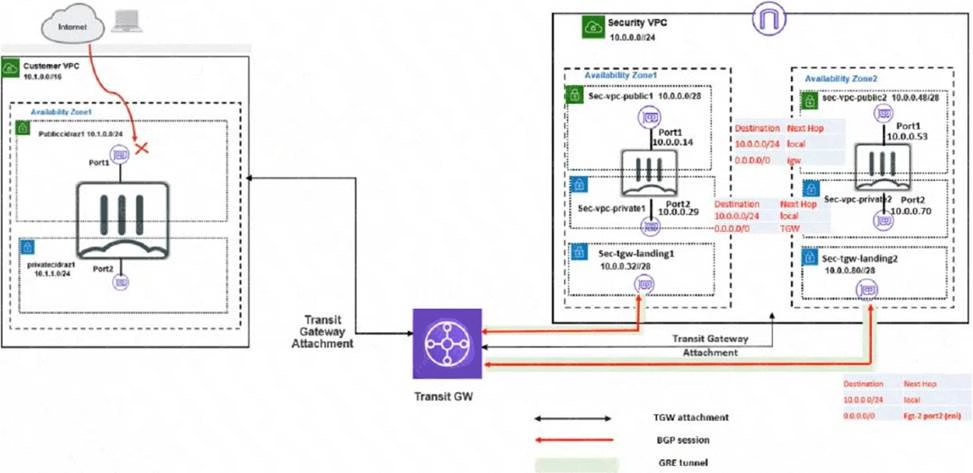
In your Amazon Web Services (AWS), you must allow inbound HTTPS access to the Customer VPC FortiGate VM from the internet However, your HTTPS connection to the FortiGate VM in the Customer VPC is not successful.
Also, you must ensure that the Customer VPC FortiGate VM sends all the outbound Internet traffic through the Security VPC.
How do you correct this Issue with minimal configuration changes?
(Choose three.)
A . Add a route With your local internet public IP address as the destination and target transit gateway
B . Add route destination 0 0.0 0/0 to target the transit gateway
C . Add a route With your local internet public IP address as the destination and target internet gateway
D . Deploy an internet gateway, associate an EIP in the private subnet, edit route tables, and add a new route destination 0.0.0.0/0 to the target internet gateway
E . Deploy an internet gateway, associate an EIP in the public subnet, and attach the internet gateway to the Customer VPC,
Answer: BDE
Explanation:
B) Add route destination 0.0.0.0/0 to target the transit gateway. This will ensure that the Customer VPC FortiGate VM sends all the outbound internet traffic through the Security VPC, where it can be inspected by the Security VPC FortiGate VMs1. The transit gateway is a network device that connects multiple VPCs and on-premises networks in a hub-and-spoke model2.
D) Deploy an internet gateway, associate an EIP in the private subnet, edit route tables, and add a new route destination 0.0.0.0/0 to the target internet gateway. This will allow inbound HTTPS access to the Customer VPC FortiGate VM from the internet, by creating a public route for the private subnet where the FortiGate VM is located3. An internet gateway is a service that enables communication between your VPC and the internet4. An EIP is a public IPv4 address that you can allocate to your AWS account and associate with your resources.
E. Deploy an internet gateway, associate an EIP in the public subnet, and attach the internet gateway to the Customer VPC. This will also allow inbound HTTPS access to the Customer VPC FortiGate VM from the internet, by creating a public route for the public subnet where the FortiGate VM is located3. This is an alternative solution to option D, depending on which subnet you want to use for the FortiGate VM.
The other options are incorrect because:
Adding a route with your local internet public IP address as the destination and target transit gateway will not allow inbound HTTPS access to the Customer VPC FortiGate VM from the internet, because it will only apply to traffic coming from your specific IP address, not from any other source on the internet1. Moreover, it will not ensure that the outbound internet traffic goes through the Security VPC, because it will only apply to traffic going to your specific IP address, not to any other destination on the internet1.
Adding a route with your local internet public IP address as the destination and target internet gateway will not allow inbound HTTPS access to the Customer VPC FortiGate VM from the internet, because it will bypass the Security VPC and send the traffic directly to the Customer VPC1. Moreover, it will not ensure that the outbound internet traffic goes through the Security VPC, because it will only apply to traffic going to your specific IP address, not to any other destination on the internet1.
Latest NSE7_PBC-7.2 Dumps Valid Version with 37 Q&As
Latest And Valid Q&A | Instant Download | Once Fail, Full Refund

