Google Professional Cloud Developer Professional Cloud Developer Online Training
Google Professional Cloud Developer Online Training
The questions for Professional Cloud Developer were last updated at Feb 08,2026.
- Exam Code: Professional Cloud Developer
- Exam Name: Professional Cloud Developer
- Certification Provider: Google
- Latest update: Feb 08,2026
Your application is built as a custom machine image. You have multiple unique deployments of the machine image. Each deployment is a separate managed instance group with its own template. Each deployment requires a unique set of configuration values. You want to provide these unique values to each deployment but use the same custom machine image in all deployments. You want to use out-of-the-box features of Compute Engine.
What should you do?
- A . Place the unique configuration values in the persistent disk.
- B . Place the unique configuration values in a Cloud Bigtable table.
- C . Place the unique configuration values in the instance template startup script.
- D . Place the unique configuration values in the instance template instance metadata.
Your application performs well when tested locally, but it runs significantly slower when you deploy it to App Engine standard environment. You want to diagnose the problem.
What should you do?
- A . File a ticket with Cloud Support indicating that the application performs faster locally.
- B . Use Stackdriver Debugger Snapshots to look at a point-in-time execution of the application.
- C . Use Stackdriver Trace to determine which functions within the application have higher latency.
- D . Add logging commands to the application and use Stackdriver Logging to check where the latency problem occurs.
You have an application running in App Engine. Your application is instrumented with Stackdriver Trace. The /product-details request reports details about four known unique products at /sku-details as shown below. You want to reduce the time it takes for the request to complete.
What should you do?
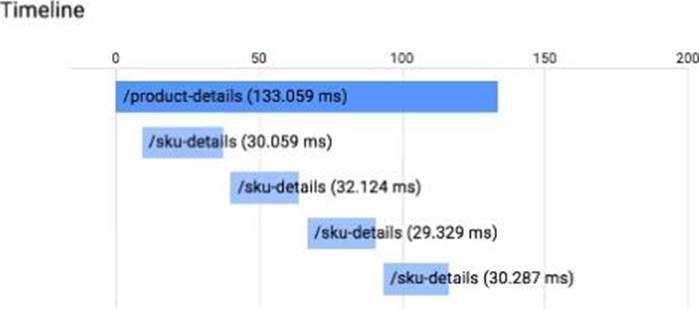
- A . Increase the size of the instance class.
- B . Change the Persistent Disk type to SSD.
- C . Change /product-details to perform the requests in parallel.
- D . Store the /sku-details information in a database, and replace the webservice call with a database query.
Your company has a data warehouse that keeps your application information in BigQuery. The BigQuery data warehouse keeps 2 PBs of user data. Recently, your company expanded your user base to include EU users and needs to comply with these requirements:
Your company must be able to delete all user account information upon user request.
All EU user data must be stored in a single region specifically for EU users.
Which two actions should you take? (Choose two.)
- A . Use BigQuery federated queries to query data from Cloud Storage.
- B . Create a dataset in the EU region that will keep information about EU users only.
- C . Create a Cloud Storage bucket in the EU region to store information for EU users only.
- D . Re-upload your data using to a Cloud Dataflow pipeline by filtering your user records out.
- E . Use DML statements in BigQuery to update/delete user records based on their requests.
Your App Engine standard configuration is as follows:
service: production
instance_class: B1
You want to limit the application to 5 instances.
Which code snippet should you include in your configuration?
- A . manual_scaling:instances: 5min_pending_latency: 30ms
- B . manual_scaling:max_instances: 5idle_timeout: 10m
- C . basic_scaling:instances: 5min_pending_latency: 30ms
- D . basic_scaling:max_instances: 5idle_timeout: 10m
Your analytics system executes queries against a BigQuery dataset. The SQL query is executed in batch and passes the contents of a SQL file to the BigQuery CLI. Then it redirects the BigQuery CLI output to another process. However, you are getting a permission error from the BigQuery CLI when the queries are executed. You want to resolve the issue.
What should you do?
- A . Grant the service account BigQuery Data Viewer and BigQuery Job User roles.
- B . Grant the service account BigQuery Data Editor and BigQuery Data Viewer roles.
- C . Create a view in BigQuery from the SQL query and SELECT* from the view in the CLI.
- D . Create a new dataset in BigQuery, and copy the source table to the new dataset Query the new dataset and table from the CLI.
Your application is running on Compute Engine and is showing sustained failures for a small number of requests. You have narrowed the cause down to a single Compute Engine instance, but the instance is unresponsive to SSH.
What should you do next?
- A . Reboot the machine.
- B . Enable and check the serial port output.
- C . Delete the machine and create a new one.
- D . Take a snapshot of the disk and attach it to a new machine.
You configured your Compute Engine instance group to scale automatically according to overall CPU usage. However, your application’s response latency increases sharply before the cluster has finished adding up instances. You want to provide a more consistent latency experience for your end users by changing the configuration ot the instance group autoscaler.
Which two configuration changes should you make? (Choose two.)
- A . Add the label “AUTOSCALE” to the instance group template.
- B . Decrease the cool-down period for instances added to the group.
- C . Increase the target CPU usage for the instance group autoscaler.
- D . Decrease the target CPU usage for the instance group autoscaler.
- E . Remove the health-check for individual VMs in the instance group.
You have an application controlled by a managed instance group. When you deploy a new version of the application, costs should be minimized and the number of instances should not increase. You want to ensure that, when each new instance is created, the deployment only continues if the new instance is healthy.
What should you do?
- A . Perform a rolling-action with maxSurge set to 1, maxUnavailable set to 0.
- B . Perform a rolling-action with maxSurge set to 0, maxUnavailable set to 1
- C . Perform a rolling-action with maxHealthy set to 1, maxUnhealthy set to 0.
- D . Perform a rolling-action with maxHealthy set to 0, maxUnhealthy set to 1.
Your application requires service accounts to be authenticated to GCP products via credentials stored on its host Compute Engine virtual machine instances. You want to distribute these credentials to the host instances as securely as possible.
What should you do?
- A . Use HTTP signed URLs to securely provide access to the required resources.
- B . Use the instance’s service account Application Default Credentials to authenticate to the required resources.
- C . Generate a P12 file from the GCP Console after the instance is deployed, and copy the credentials to the host instance before starting the application.
- D . Commit the credential JSON file into your application’s source repository, and have your CI/CD process package it with the software that is deployed to the instance.
Latest Professional Cloud Developer Dumps Valid Version with 75 Q&As
Latest And Valid Q&A | Instant Download | Once Fail, Full Refund

