GAQM CTFL Certified Software Tester – Foundation Level (CSTFL) Online Training
GAQM CTFL Online Training
The questions for CTFL were last updated at Mar 01,2026.
- Exam Code: CTFL
- Exam Name: Certified Software Tester - Foundation Level (CSTFL)
- Certification Provider: GAQM
- Latest update: Mar 01,2026
Topic 11, Scenario 11 "Incident Management"
The following is the current incident handling process in used at the company.
Step 1: Incident is documented in the incident Tile with the following information:
– Software module or area where the fault occurred
– Who has reported the fault
– Hardware configuration used for the test that found the fault
– The sequential incident number (1 greater than the last one recorded)
Step 2: Developer assigned to fix the fault
Step 3: Developer fixes the fault
Step 4: Developer signs off the incident as closed, and it is then removed from the incident file
Regarding the process described above, what is the most important recommendation you would make using IEEE 1044 as a guide? 2 credits
- A . No priority or severity assigned
- B . Incident numbering is manual rather than automated
- C . No mentioning of reproduceability
- D . No classification on type of incident
Topic 12, Scenario 12 “Automatic Teller Machine (ATM)”
You are a test manager in charge of integration, system and acceptance testing for a bank. You are working on a project to upgrade an existing ATM to allow customers to obtain cash advances from supported credit cards. The system should allow cash advances from 20 to 500, inclusively, for all supported credit cards. The supported credit cards are American Express, VISA, Eurocard and Mastercard.
In the master test plan the following items are listed in the section named “items and/or features to be tested”:
I All supported credit cards
II Language localization
II Valid and invalid advances IV Usability
V Response time
Relying only on the information provided in the scenario, select the TWO items and/or features for which sufficient information is available to proceed with test design. 2 credits
- A . All supported credit cards
- B . Language localization
- C . Valid and invalid advances
- D . Usability
- E . Response time
Given the following figures for the testing on a project, and assuming the failure rate for initial tests remains constant and that all retests pass, what number of tests remain to be run? 3 credits
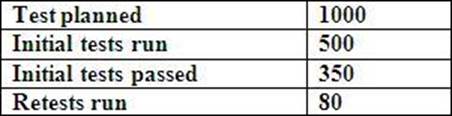
- A . 700
- B . 720
- C . 784
- D . 570
Continuing with the Scenario described in the previous question, which of the following topics would you need to address in detail in the master test plan? 3 credits
- A . An approach to regression testing
- B . A list of boundary values for “advance amount”
- C . A description of dependencies between test cases
- D . A logical collection of test cases
Given is the following defect removal chart reported at the end of system testing – showing total defects detected and closed defects (fixed and successfully retested). A number of open defects are classified as critical. All tests have been executed.
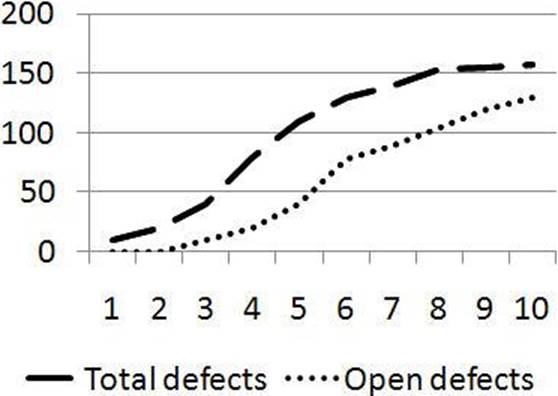
Based on the chart above, what is the most appropriate next test phase? 1 credit
- A . Acceptance testing to verify the business process
- B . Acceptance testing to verify operational requirements
- C . Requirements testing as part of testing regulatory compliance
- D . Another system test cycle to verify defect resolution
Topic 13, Mix Questions
What benefits do static analysis tools have over test execution tools?
- A . Static analysis tools find defects earlier in the life cycle.
- B . Static analysis tools can be used before code is written.
- C . Static analysis tools test that the delivered code meets business requirements.
- D . Static analysis tools are particularly effective for regression testing.
The difference between re-testing and regression testing is:
- A . Re-testing is running a test again; regression testing looks for unexpected side effects
- B . Re-testing looks for unexpected side effects; regression testing is repeating those tests
- C . Re-testing is done after faults are fixed; regression testing is done earlier
- D . Re-testing uses different environments, regression testing uses the same environment
- E . Re-testing is done by developers, regression testing is done by independent testers
Boundary value testing:
- A . Is the same as equivalence partitioning tests
- B . Test boundary conditions on, below and above the edges of input and output equivalence classes
- C . Tests combinations of input circumstances
- D . Is used in white box testing strategy
Tests are prioritized so that:
- A . You shorten the time required for testing
- B . You do the best testing in the time available
- C . You do more effective testing
- D . You find more faults
Which of the following is not a type of incremental testing approach?
- A . Top down
- B . Big-bang
- C . Bottom up
- D . Functional incrementation.
Latest CTFL Dumps Valid Version with 219 Q&As
Latest And Valid Q&A | Instant Download | Once Fail, Full Refund

