Fortinet NSE5_FMG-7.0 Fortinet NSE 5 – FortiManager 7.0 Online Training
Fortinet NSE5_FMG-7.0 Online Training
The questions for NSE5_FMG-7.0 were last updated at Dec 14,2025.
- Exam Code: NSE5_FMG-7.0
- Exam Name: Fortinet NSE 5 - FortiManager 7.0
- Certification Provider: Fortinet
- Latest update: Dec 14,2025
Which two conditions trigger FortiManager to create a new revision history? (Choose two.)
- A . When configuration revision is reverted to previous revision in the revision history
- B . When FortiManager installs device-level changes to a managed device
- C . When FortiManager is auto-updated with configuration changes made directly on a managed device
- D . When changes to device-level database is made on FortiManager
B,D
Explanation:
FortiManager creates a new revision history whenever changes are made to a managed device or to the device-level database. This includes installing new configurations or making changes to existing ones. These revisions are tracked to help with troubleshooting and to provide a record of changes. However, merely reverting to a previous revision or updating with changes made directly on a managed device do not trigger the creation of a new revision history.
Which two statements about the scheduled backup of FortiManager are true? (Choose two.)
- A . It does not back up firmware images saved on FortiManager.
- B . It can be configured using the CLI and GUI.
- C . It backs up all devices and the FortiGuard database.
- D . It supports FTP, SCP, and SFTP.
A,B
Explanation:
FortiManager scheduled backup can be configured using both the command-line interface (CLI) and graphical user interface (GUI). However, it doesn’t include firmware images saved on the FortiManager in its backup process. The other statements are not correct as the scheduled backup doesn’t necessarily back up all devices and the FortiGuard database, and while it can utilize various methods for storing backups, FTP, SCP, and SFTP support may depend on specific settings and versions of the FortiManager software.
An administrator has assigned a global policy package to a new ADOM called ADOM1.
What will happen if the administrator tries to create a new policy package in ADOM1?
- A . When creating a new policy package, the administrator can select the option to assign the global policy package to the new policy package
- B . When a new policy package is created, the administrator needs to reapply the global
policy package to ADOM1. - C . When a new policy package is created, the administrator must assign the global policy package from the global ADOM.
- D . When the new policy package is created, FortiManager automatically assigns the global policy package to the new policy package.
D
Explanation:
Reference: https://help.fortinet.com/fmgr/50hlp/56/5-6-2/FortiManager_Admin_Guide/1200_Policy%20and%20Objects/0800_Managing%20policy%20packages/1200_Assign%20a%20global%20policy%20package.htm
View the following exhibit.
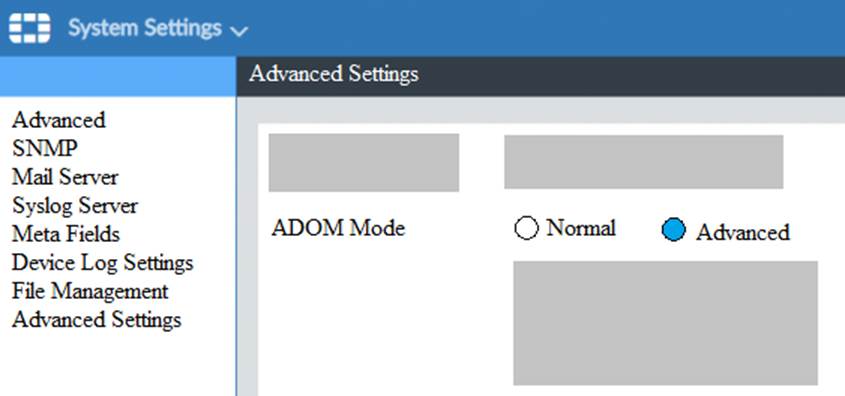
What is the purpose of setting ADOM Mode to Advanced?
- A . The setting allows automatic updates to the policy package configuration for a managed device
- B . The setting enables the ADOMs feature on FortiManager
- C . This setting allows you to assign different VDOMs from the same FortiGate to different ADOMs.
- D . The setting disables concurrent ADOM access and adds ADOM locking
C
Explanation:
Reference: https://docs.fortinet.com/document/fortianalyzer/7.0.0/administration-guide/66530/adom-device-modes
What is the purpose of the Policy Check feature on FortiManager?
- A . To find and provide recommendation to combine multiple separate policy packages into one common policy package
- B . To find and merge duplicate policies in the policy package
- C . To find and provide recommendation for optimizing policies in a policy package
- D . To find and delete disabled firewall policies in the policy package
C
Explanation:
Reference: https://help.fortinet.com/fmgr/50hlp/56/5-6-2/FortiManager_Admin_Guide/1200_Policy%20and%20Objects/0800_Managing%20policy %20packages/2400_Perform%20a%20policy%20consistency%20check.htm
Refer to the exhibit.
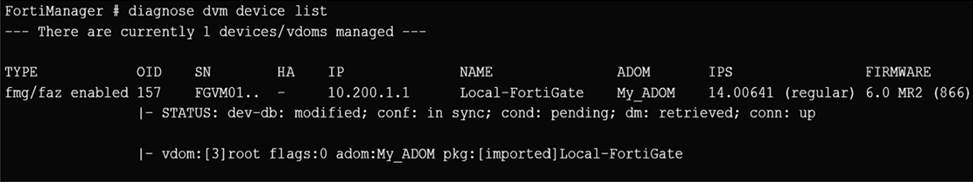
Which two statements about the output are true? (Choose two.)
- A . The latest revision history for the managed FortiGate does match with the FortiGate running configuration
- B . Configuration changes have been installed to FortiGate and represents FortiGate configuration has been changed
- C . The latest history for the managed FortiGate does not match with the device-level database
- D . Configuration changes directly made on the FortiGate have been automatically updated to device-level database
A,C
Explanation:
STATUS: dev-db: modified; conf: in sync; cond: pending; dm: retrieved; conn: up
C dev-db: modified C This is the device setting status which indicates that configuration changes were made on FortiManager.
C conf: in sync C This is the sync status which shows that the latest revision history is in sync with Fortigate’s configuration.
C cond: pending C This is the configuration status which says that configuration changes need to be installed.
Most probably a retrieve was done in the past (dm: retrieved) updating the revision history DB (conf: in sync) and FortiManager device level DB, now there is a new modification on FortiManager device level DB (dev-db: modified) which wasn’t installed to FortiGate (cond: pending), hence; revision history DB is not aware of that modification and doesn’t match device DB.
Conclusion:
C Revision DB does match FortiGate.
C No changes were installed to FortiGate yet.
C Device DB doesn’t match Revision DB.
C No changes were done on FortiGate (auto-update) but configuration was retrieved instead
After an Auto-Update or Retrieve:
device database = latest revision = FGT
Then after a manual change on FMG end (but no install yet):
latest revision = FGT (still) but now device database has been modified (is different).
After reverting to a previous revision in revision history:
device database = reverted revision != FGT
What will happen if FortiAnalyzer features are enabled on FortiManager?
- A . FortiManager will reboot
- B . FortiManager will send the logging configuration to the managed devices so the managed devices will start sending logs to FortiManager
- C . FortiManager will enable ADOMs automatically to collect logs from non-FortiGate devices
- D . FortiManager can be used only as a logging device.
B
Explanation:
FortiAnalyzer features enabled on FortiManager provides analytics-powered security and log management capabilities. Once enabled, the FortiManager will send the logging configuration to the managed devices so that these devices will start sending logs to the FortiManager. The FortiManager can handle logs and offers extensive analytics but it’s not used solely as a logging device. FortiManager is also responsible for configuration and policy management among other things.
In the event that the primary FortiManager fails, which of the following actions must be performed to return the FortiManager HA to a working state?
- A . Secondary device with highest priority will automatically be promoted to the primary role, and manually reconfigure all other secondary devices to point to the new primary device
- B . Reboot one of the secondary devices to promote it automatically to the primary role, and reconfigure all other secondary devices to point to the new primary device.
- C . Manually promote one of the secondary devices to the primary role, and reconfigure all other secondary devices to point to the new primary device.
- D . FortiManager HA state transition is transparent to administrators and does not require any reconfiguration.
C
Explanation:
FortiManager_6.4_Study_Guide-Online C page 346
FortiManager HA doesn’t support IP takeover where an HA state transition is transparent to administrators. If a failure of the primary occurs, the administrator must take corrective action to resolve the problem that may include invoking the state transition.
If the primary device fails, the administrator must do the following in order to return the FortiManager HA to a working state:
In the event that the primary FortiManager fails, which of the following actions must be performed to return the FortiManager HA to a working state?
- A . Secondary device with highest priority will automatically be promoted to the primary role, and manually reconfigure all other secondary devices to point to the new primary device
- B . Reboot one of the secondary devices to promote it automatically to the primary role, and reconfigure all other secondary devices to point to the new primary device.
- C . Manually promote one of the secondary devices to the primary role, and reconfigure all other secondary devices to point to the new primary device.
- D . FortiManager HA state transition is transparent to administrators and does not require any reconfiguration.
C
Explanation:
FortiManager_6.4_Study_Guide-Online C page 346
FortiManager HA doesn’t support IP takeover where an HA state transition is transparent to administrators. If a failure of the primary occurs, the administrator must take corrective action to resolve the problem that may include invoking the state transition.
If the primary device fails, the administrator must do the following in order to return the FortiManager HA to a working state:
In the event that the primary FortiManager fails, which of the following actions must be performed to return the FortiManager HA to a working state?
- A . Secondary device with highest priority will automatically be promoted to the primary role, and manually reconfigure all other secondary devices to point to the new primary device
- B . Reboot one of the secondary devices to promote it automatically to the primary role, and reconfigure all other secondary devices to point to the new primary device.
- C . Manually promote one of the secondary devices to the primary role, and reconfigure all other secondary devices to point to the new primary device.
- D . FortiManager HA state transition is transparent to administrators and does not require any reconfiguration.
C
Explanation:
FortiManager_6.4_Study_Guide-Online C page 346
FortiManager HA doesn’t support IP takeover where an HA state transition is transparent to administrators. If a failure of the primary occurs, the administrator must take corrective action to resolve the problem that may include invoking the state transition.
If the primary device fails, the administrator must do the following in order to return the FortiManager HA to a working state:
Latest NSE5_FMG-7.0 Dumps Valid Version with 65 Q&As
Latest And Valid Q&A | Instant Download | Once Fail, Full Refund

