In the event that the primary FortiManager fails, which of the following actions must be performed to return the FortiManager HA to a working state?
- A . Secondary device with highest priority will automatically be promoted to the primary role, and manually
reconfigure all other secondary devices to point to the new primary device - B . Reboot one of the secondary devices to promote it automatically to the primary role, and reconfigure all other secondary devices to point to the new primary device.
- C . Manually promote one of the secondary devices to the primary role, and reconfigure all other secondary devices to point to the new primary device.
- D . FortiManager HA state transition is transparent to administrators and does not require any reconfiguration.
C
Explanation:
FortiManager_6.4_Study_Guide-Online C page 346
FortiManager HA doesn’t support IP takeover where an HA state transition is transparent to administrators. If a failure of the primary occurs, the administrator must take corrective action to resolve the problem that may include invoking the state transition. If the primary device fails, the administrator must do the following in order to return the FortiManager HA to a working state:
In the event that the primary FortiManager fails, which of the following actions must be performed to return the FortiManager HA to a working state?
- A . Secondary device with highest priority will automatically be promoted to the primary role, and manually
reconfigure all other secondary devices to point to the new primary device - B . Reboot one of the secondary devices to promote it automatically to the primary role, and reconfigure all other secondary devices to point to the new primary device.
- C . Manually promote one of the secondary devices to the primary role, and reconfigure all other secondary devices to point to the new primary device.
- D . FortiManager HA state transition is transparent to administrators and does not require any reconfiguration.
C
Explanation:
FortiManager_6.4_Study_Guide-Online C page 346
FortiManager HA doesn’t support IP takeover where an HA state transition is transparent to administrators. If a failure of the primary occurs, the administrator must take corrective action to resolve the problem that may include invoking the state transition. If the primary device fails, the administrator must do the following in order to return the FortiManager HA to a working state:
In the event that the primary FortiManager fails, which of the following actions must be performed to return the FortiManager HA to a working state?
- A . Secondary device with highest priority will automatically be promoted to the primary role, and manually
reconfigure all other secondary devices to point to the new primary device - B . Reboot one of the secondary devices to promote it automatically to the primary role, and reconfigure all other secondary devices to point to the new primary device.
- C . Manually promote one of the secondary devices to the primary role, and reconfigure all other secondary devices to point to the new primary device.
- D . FortiManager HA state transition is transparent to administrators and does not require any reconfiguration.
C
Explanation:
FortiManager_6.4_Study_Guide-Online C page 346
FortiManager HA doesn’t support IP takeover where an HA state transition is transparent to administrators. If a failure of the primary occurs, the administrator must take corrective action to resolve the problem that may include invoking the state transition. If the primary device fails, the administrator must do the following in order to return the FortiManager HA to a working state:
In addition to the default ADOMs, an administrator has created a new ADOM named Training for FortiGate devices. The administrator sent a device registration to FortiManager from a remote FortiGate.
Which one of the following statements is true?
- A . The FortiGate will be added automatically to the default ADOM named FortiGate.
- B . The FortiGate will be automatically added to the Training ADOM.
- C . By default, the unregistered FortiGate will appear in the root ADOM.
- D . The FortiManager administrator must add the unregistered device manually to the unregistered device
manually to the Training ADOM using the Add Device wizard
C
Explanation:
Reference: https://docs.fortinet.com/document/fortimanager/7.0.0/administration-guide/718923/root-adom
View the following exhibit:
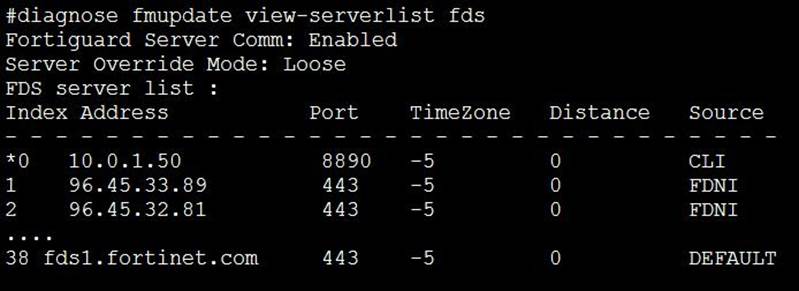
How will FortiManager try to get updates for antivirus and IPS?
- A . From the list of configured override servers with ability to fall back to public FDN servers
- B . From the configured override server list only
- C . From the default server fdsl.fortinet.com
- D . From public FDNI server with highest index number only
A
Explanation:
Reference: https://community.fortinet.com/t5/Fortinet-Forum/Clarification-of-FortiManager-s-quot-Server-Override-Mode-quot/td-p/89973
An administrator would like to create an SD-WAN using central management in the Training ADOM.
To create an SD-WAN using central management, which two steps must be completed? (Choose two.)
- A . Specify a gateway address when you create a default SD-WAN static route
- B . Enable SD-WAN central management in the Training ADOM
- C . Configure and install the SD-WAN firewall policy and SD-WAN static route before installing the SD-WAN template settings
- D . Remove all the interface references such as routes or policies that will be a part of SD-
WAN member
interfaces
B,D
Explanation:
Reference: https://docs.fortinet.com/document/fortigate/6.0.0/cookbook/676493/removing-existing-configuration-references-to-interfaces
Which two conditions trigger FortiManager to create a new revision history? (Choose two.)
- A . When configuration revision is reverted to previous revision in the revision history
- B . When FortiManager installs device-level changes to a managed device
- C . When FortiManager is auto-updated with configuration changes made directly on a managed device
- D . When changes to device-level database is made on FortiManager
B,C
Explanation:
Reference: https://help.fortinet.com/fmgr/50hlp/56/5-6-1/FortiManager_Admin_Guide/1000_Device%20Manager/1500_Manage_device_configs/0 600_Manage%20config%20rev%20history.htm
Which configuration setting for FortiGate is part of a device-level database on FortiManager?
- A . VIP and IP Pools
- B . Firewall policies
- C . Security profiles
- D . Routing
D
Explanation:
The FortiManager stores the FortiGate configuration details in two distinct databases. The device-level database includes configuration details related to device-level settings, such as interfaces, DNS, routing, and more. The ADOM-level database includes configuration details related to firewall policies, objects, and security profiles.
Refer to the exhibit.
Which two statements about the output are true? (Choose two.)
- A . The latest revision history for the managed FortiGate does match with the FortiGate running configuration
- B . Configuration changes have been installed to FortiGate and represents FortiGate configuration has been changed
- C . The latest history for the managed FortiGate does not match with the device-level database
- D . Configuration changes directly made on the FortiGate have been automatically updated
to device-level
database
A,C
Explanation:
STATUS: dev-db: modified; conf: in sync; cond: pending; dm: retrieved; conn: upC
dev-db: modified C This is the device setting status which indicates that configuration changes were made on FortiManager.C conf: in sync C This is the sync status which shows that the latest revision history is in sync with Fortigate’s configuration.C cond: pending C This is the configuration status which says that configuration changes need to be installed.
Most probably a retrieve was done in the past (dm: retrieved) updating the revision
history DB (conf: in sync) and FortiManager device level DB, now there is a new
modification on FortiManager device level DB (dev-db: modified) which wasn’t installed to FortiGate (cond: pending), hence; revision history DB is not aware of that modification and doesn’t match device DB.
Conclusion:C Revision DB does match FortiGate.C No changes were installed to FortiGate yet.C Device DB doesn’t match Revision DB.C No changes were done on FortiGate (auto-update) but configuration was retrieved instead
After an Auto-Update or Retrieve:device database = latest revision = FGT
Then after a manual change on FMG end (but no install yet):latest revision = FGT (still) but now device database has been modified (is different).
After reverting to a previous revision in revision history:device database = reverted revision != FGT
An administrator would like to review, approve, or reject all the firewall policy changes made by the junior administrators.
How should the Workspace mode be configured on FortiManager?
- A . Set to workflow and use the ADOM locking feature
- B . Set to read/write and use the policy locking feature
- C . Set to normal and use the policy locking feature
- D . Set to disable and use the policy locking feature
A
Explanation:
Reference: https://help.fortinet.com/fmgr/50hlp/52/5-2-0/FMG_520_Online_Help/200_What’s-New.03.03.html
Which two settings must be configured for SD-WAN Central Management? (Choose two.)
- A . SD-WAN must be enabled on per-ADOM basis
- B . You can create multiple SD-WAN interfaces per VDOM
- C . When you configure an SD-WAN, you must specify at least two member interfaces.
- D . The first step in creating an SD-WAN using FortiManager is to create two SD-WAN firewall policies.
When an installation is performed from FortiManager, what is the recovery logic used between FortiManager and FortiGate for an FGFM tunnel?
- A . After 15 minutes, FortiGate will unset all CLI commands that were part of the installation that caused the tunnel to go down.
- B . FortiManager will revert and install a previous configuration revision on the managed FortiGate.
- C . FortiGate will reject the CLI commands that will cause the tunnel to go down.
- D . FortiManager will not push the CLI commands as a part of the installation that will cause the tunnel to go down.
A
Explanation:
Reference: https://fortinetweb.s3.amazonaws.com/docs.fortinet.com/v2/attachments/067f5236-ca6d-11e9-8977-00505692583a/FGFM-6.2-Communications_Protocol_Guide.pdf page 17
You are moving managed FortiGate devices from one ADOM to a new ADOM.
Which statement correctly describes the expected result?
- A . Any pending device settings will be installed automatically
- B . Any unused objects from a previous ADOM are moved to the new ADOM automatically
- C . The shared policy package will not be moved to the new ADOM
- D . Policy packages will be imported into the new ADOM automaticallyD
C
Explanation:
Reference: https://community.fortinet.com/t5/FortiManager/Technical-Note-How-to-move-objects-to-new-ADOM-on-FortiManager/ta-p/198342
What will happen if FortiAnalyzer features are enabled on FortiManager?
- A . FortiManager will reboot
- B . FortiManager will send the logging configuration to the managed devices so the managed devices will start sending logs to FortiManager
- C . FortiManager will enable ADOMs automatically to collect logs from non-FortiGate devices
- D . FortiManager can be used only as a logging device.
A
Explanation:
Reference: https://help.fortinet.com/fmgr/50hlp/56/5-6-1/FortiManager_Admin_Guide/1800_FAZ%20Features/0200_Enable%20FAZ%20Features.htm
View the following exhibit.
What is the purpose of setting ADOM Mode to Advanced?
- A . The setting allows automatic updates to the policy package configuration for a managed device
- B . The setting enables the ADOMs feature on FortiManager
- C . This setting allows you to assign different VDOMs from the same FortiGate to different ADOMs.
- D . The setting disables concurrent ADOM access and adds ADOM locking
C
Explanation:
Reference: https://docs.fortinet.com/document/fortianalyzer/7.0.0/administration-guide/66530/adom-device-modes
View the following exhibit.
Which statement is true regarding this failed installation log?
- A . Policy ID 2 is installed without a source address
- B . Policy ID 2 will not be installed
- C . Policy ID 2 is installed in disabled state
- D . Policy ID 2 is installed without a source device
Which two statements about the scheduled backup of FortiManager are true? (Choose two.)
- A . It does not back up firmware images saved on FortiManager.
- B . It can be configured using the CLI and GUI.
- C . It backs up all devices and the FortiGuard database.
- D . It supports FTP, SCP, and SFTP.
A,D
Explanation:
Reference: https://docs.ansible.com/ansible/latest/collections/fortinet/fortimanager/fmgr_system_backu p_allsettings_module.html
Refer to the exhibits.
Exhibit one.
Exhibit two.
An administrator created a new system template named Training with two new DNS addresses on FortiManager. During the installation preview stage, the administrator notices that many unset commands need to be pushed.
What can be the main reason for these unset commands?
- A . The DNS addresses in the default system settings are the same as the Training system template
- B . The Training system template has other default settings
- C . The ADOM is locked by another administrator
- D . The Training system template does not have assigned devices
An administrator wants to delete an address object that is currently referenced in a firewall policy.
What can the administrator expect to happen?
- A . FortiManager will not allow the administrator to delete a referenced address object
- B . FortiManager will disable the status of the referenced firewall policy
- C . FortiManager will replace the deleted address object with the none address object in the
referenced firewall policy - D . FortiManager will replace the deleted address object with all address object in the referenced firewall policy
C
Explanation:
Reference: https://help.fortinet.com/fmgr/50hlp/56/5-6-2/FortiManager_Admin_Guide/1200_Policy%20and%20Objects/1200_Managing%20object s/0800_Remove%20an%20object.htm
An administrator run the reload failure command: diagnose test deploymanager reload config <deviceid> on FortiManager.
What does this command do?
- A . It downloads the latest configuration from the specified FortiGate and performs a reload
operation on the device database. - B . It installs the latest configuration on the specified FortiGate and update the revision history database.
- C . It compares and provides differences in configuration on FortiManager with the current running
configuration of the specified FortiGate. - D . It installs the provisioning template configuration on the specified FortiGate.
A
Explanation:
Reference: https://community.fortinet.com/t5/FortiManager/Technical-Note-Retrieve-configuration-file-using-CLI-from-a/ta-p/191000?externalID=FD36387
Which two items does an FGFM keepalive message include? (Choose two.)
- A . FortiGate uptime
- B . FortiGate license information
- C . FortiGate IPS version
- D . FortiGate configuration checksum
C,D
Explanation:
Reference: https://docs.fortinet.com/document/fortimanager/6.2.0/fortigate-fortimanager-communications-protocol-guide/579138/keep-alive-messages
What are two outcomes of ADOM revisions? (Choose two.)
- A . ADOM revisions can significantly increase the size of the configuration backups.
- B . ADOM revisions can save the current size of the whole ADOM
- C . ADOM revisions can create System Checkpoints for the FortiManager configuration
- D . ADOM revisions can save the current state of all policy packages and objects for an ADOM
A,D
Explanation:
Reference: https://docs2.fortinet.com/document/fortimanager/6.0.0/best-practices/101837/adom-revisions