Fortinet NSE5_FMG-6.4 Fortinet NSE 5 – FortiManager 6.4 Online Training
Fortinet NSE5_FMG-6.4 Online Training
The questions for NSE5_FMG-6.4 were last updated at Jan 02,2026.
- Exam Code: NSE5_FMG-6.4
- Exam Name: Fortinet NSE 5 - FortiManager 6.4
- Certification Provider: Fortinet
- Latest update: Jan 02,2026
In the event that the primary FortiManager fails, which of the following actions must be performed to return the FortiManager HA to a working state?
- A . Secondary device with highest priority will automatically be promoted to the primary role, and manually
reconfigure all other secondary devices to point to the new primary device - B . Reboot one of the secondary devices to promote it automatically to the primary role, and reconfigure all other secondary devices to point to the new primary device.
- C . Manually promote one of the secondary devices to the primary role, and reconfigure all other secondary devices to point to the new primary device.
- D . FortiManager HA state transition is transparent to administrators and does not require any reconfiguration.
C
Explanation:
FortiManager_6.4_Study_Guide-Online C page 346
FortiManager HA doesn’t support IP takeover where an HA state transition is transparent to administrators. If a failure of the primary occurs, the administrator must take corrective action to resolve the problem that may include invoking the state transition. If the primary device fails, the administrator must do the following in order to return the FortiManager HA to a working state:
In the event that the primary FortiManager fails, which of the following actions must be performed to return the FortiManager HA to a working state?
- A . Secondary device with highest priority will automatically be promoted to the primary role, and manually
reconfigure all other secondary devices to point to the new primary device - B . Reboot one of the secondary devices to promote it automatically to the primary role, and reconfigure all other secondary devices to point to the new primary device.
- C . Manually promote one of the secondary devices to the primary role, and reconfigure all other secondary devices to point to the new primary device.
- D . FortiManager HA state transition is transparent to administrators and does not require any reconfiguration.
C
Explanation:
FortiManager_6.4_Study_Guide-Online C page 346
FortiManager HA doesn’t support IP takeover where an HA state transition is transparent to administrators. If a failure of the primary occurs, the administrator must take corrective action to resolve the problem that may include invoking the state transition. If the primary device fails, the administrator must do the following in order to return the FortiManager HA to a working state:
In the event that the primary FortiManager fails, which of the following actions must be performed to return the FortiManager HA to a working state?
- A . Secondary device with highest priority will automatically be promoted to the primary role, and manually
reconfigure all other secondary devices to point to the new primary device - B . Reboot one of the secondary devices to promote it automatically to the primary role, and reconfigure all other secondary devices to point to the new primary device.
- C . Manually promote one of the secondary devices to the primary role, and reconfigure all other secondary devices to point to the new primary device.
- D . FortiManager HA state transition is transparent to administrators and does not require any reconfiguration.
C
Explanation:
FortiManager_6.4_Study_Guide-Online C page 346
FortiManager HA doesn’t support IP takeover where an HA state transition is transparent to administrators. If a failure of the primary occurs, the administrator must take corrective action to resolve the problem that may include invoking the state transition. If the primary device fails, the administrator must do the following in order to return the FortiManager HA to a working state:
In addition to the default ADOMs, an administrator has created a new ADOM named Training for FortiGate devices. The administrator sent a device registration to FortiManager from a remote FortiGate.
Which one of the following statements is true?
- A . The FortiGate will be added automatically to the default ADOM named FortiGate.
- B . The FortiGate will be automatically added to the Training ADOM.
- C . By default, the unregistered FortiGate will appear in the root ADOM.
- D . The FortiManager administrator must add the unregistered device manually to the unregistered device
manually to the Training ADOM using the Add Device wizard
C
Explanation:
Reference: https://docs.fortinet.com/document/fortimanager/7.0.0/administration-guide/718923/root-adom
View the following exhibit:
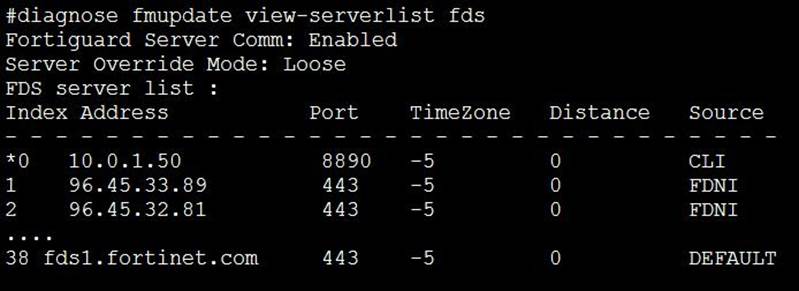
How will FortiManager try to get updates for antivirus and IPS?
- A . From the list of configured override servers with ability to fall back to public FDN servers
- B . From the configured override server list only
- C . From the default server fdsl.fortinet.com
- D . From public FDNI server with highest index number only
A
Explanation:
Reference: https://community.fortinet.com/t5/Fortinet-Forum/Clarification-of-FortiManager-s-quot-Server-Override-Mode-quot/td-p/89973
An administrator would like to create an SD-WAN using central management in the Training ADOM.
To create an SD-WAN using central management, which two steps must be completed? (Choose two.)
- A . Specify a gateway address when you create a default SD-WAN static route
- B . Enable SD-WAN central management in the Training ADOM
- C . Configure and install the SD-WAN firewall policy and SD-WAN static route before installing the SD-WAN template settings
- D . Remove all the interface references such as routes or policies that will be a part of SD-
WAN member
interfaces
B,D
Explanation:
Reference: https://docs.fortinet.com/document/fortigate/6.0.0/cookbook/676493/removing-existing-configuration-references-to-interfaces
Which two conditions trigger FortiManager to create a new revision history? (Choose two.)
- A . When configuration revision is reverted to previous revision in the revision history
- B . When FortiManager installs device-level changes to a managed device
- C . When FortiManager is auto-updated with configuration changes made directly on a managed device
- D . When changes to device-level database is made on FortiManager
B,C
Explanation:
Reference: https://help.fortinet.com/fmgr/50hlp/56/5-6-1/FortiManager_Admin_Guide/1000_Device%20Manager/1500_Manage_device_configs/0 600_Manage%20config%20rev%20history.htm
Which configuration setting for FortiGate is part of a device-level database on FortiManager?
- A . VIP and IP Pools
- B . Firewall policies
- C . Security profiles
- D . Routing
D
Explanation:
The FortiManager stores the FortiGate configuration details in two distinct databases. The device-level database includes configuration details related to device-level settings, such as interfaces, DNS, routing, and more. The ADOM-level database includes configuration details related to firewall policies, objects, and security profiles.
Refer to the exhibit.
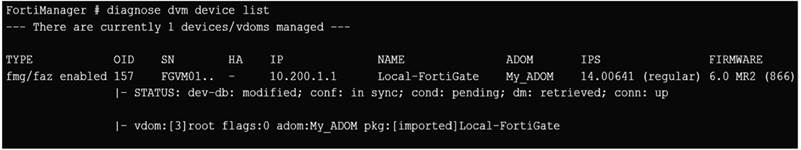
Which two statements about the output are true? (Choose two.)
- A . The latest revision history for the managed FortiGate does match with the FortiGate running configuration
- B . Configuration changes have been installed to FortiGate and represents FortiGate configuration has been changed
- C . The latest history for the managed FortiGate does not match with the device-level database
- D . Configuration changes directly made on the FortiGate have been automatically updated
to device-level
database
A,C
Explanation:
STATUS: dev-db: modified; conf: in sync; cond: pending; dm: retrieved; conn: upC
dev-db: modified C This is the device setting status which indicates that configuration changes were made on FortiManager.C conf: in sync C This is the sync status which shows that the latest revision history is in sync with Fortigate’s configuration.C cond: pending C This is the configuration status which says that configuration changes need to be installed.
Most probably a retrieve was done in the past (dm: retrieved) updating the revision
history DB (conf: in sync) and FortiManager device level DB, now there is a new
modification on FortiManager device level DB (dev-db: modified) which wasn’t installed to FortiGate (cond: pending), hence; revision history DB is not aware of that modification and doesn’t match device DB.
Conclusion:C Revision DB does match FortiGate.C No changes were installed to FortiGate yet.C Device DB doesn’t match Revision DB.C No changes were done on FortiGate (auto-update) but configuration was retrieved instead
After an Auto-Update or Retrieve:device database = latest revision = FGT
Then after a manual change on FMG end (but no install yet):latest revision = FGT (still) but now device database has been modified (is different).
After reverting to a previous revision in revision history:device database = reverted revision != FGT
An administrator would like to review, approve, or reject all the firewall policy changes made by the junior administrators.
How should the Workspace mode be configured on FortiManager?
- A . Set to workflow and use the ADOM locking feature
- B . Set to read/write and use the policy locking feature
- C . Set to normal and use the policy locking feature
- D . Set to disable and use the policy locking feature
A
Explanation:
Reference: https://help.fortinet.com/fmgr/50hlp/52/5-2-0/FMG_520_Online_Help/200_What’s-New.03.03.html
Latest NSE5_FMG-6.4 Dumps Valid Version with 65 Q&As
Latest And Valid Q&A | Instant Download | Once Fail, Full Refund

