Refer to the exhibit.
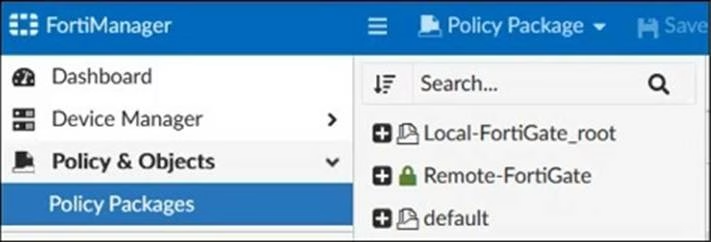
Given the configuration shown in the exhibit, which two statements are true? (Choose two.)
- A . An administrator can also lock the Local-FortiGate_root policy package.
- B . FortiManager is in workflow mode.
- C . The FortiManager ADOM is locked by the administrator.
- D . The FortiManager ADOM workspace mode is set to Normal.
An administrator enabled workspace mode and now wants to delete an address object that is currently referenced in a firewall policy.
Which two results can the administrator expect? (Choose two.)
- A . FortiManager will temporarily change the status of the referenced firewall policy to disabled.
- B . FortiManager will disable the status of the address object until the changes are installed.
- C . FortiManager will not allow the administrator to delete a referenced address object until they lock the ADOM.
- D . FortiManager will replace the deleted address object with the none address object in the referenced firewall policy.
What is the purpose of ADOM revisions?
- A . To save the current state of the whole ADOM
- B . To save the current state of all policy packages and objects for an ADOM
- C . To revert individual policy packages and device-level settings for a managed FortiGate
- D . To save the FortiManager configuration in the System Checkpoints
Refer to the exhibit.
An administrator has created a firewall address object that is used in multiple policy packages for multiple FortiGate devices in an ADOM.
After the installation operation is performed, which IP/netmask is shown on FortiManager for this firewall address object for devices without a Per-Device Mapping set?
- A . FortiManager generates an error for each FortiGate without a per-device mapping defined for that object.
- B . 192.168. 1. 0/24
- C . 192.168. 1. 0/28
- D . FortiManager replaces the address object to none.
Refer to the exhibit.
Which two statements about the output are true? (Choose two.)
- A . The latest revision history for the managed FortiGate does not match the device-level database.
- B . Configuration changes have been installed on FortiGate, which means the FortiGate configuration has been changed.
- C . Configuration changes directly made on FortiGate have been automatically updated to the device-level database.
- D . The latest revision history for the managed FortiGate does match the FortiGate running configuration.
Refer to the exhibit.
Given the configuration shown in the exhibit, what are two results from this configuration? (Choose two.)
- A . You can validate administrator login attempts through external servers.
- B . The same administrator can lock more than one ADOM at the same time.
- C . Two or more administrators can make configuration changes at the same time, in the same ADOM.
- D . Concurrent read-write access to an ADOM is disabled.
Which statement about the policy lock feature on FortiManager is true?
- A . Policy locking is available in workspace normal mode.
- B . Locking a policy takes precedence over a locked ADOM.
- C . When a policy is locked, the ADOM that contains it is also locked.
- D . Administrators in the approval group can work concurrently on a locked policy.
Refer to the exhibit.
An administrator would like to create three ADOMs on FortiManager with different access levels based on departments .
What two conclusions can you draw from the design shown in the exhibit? (Choose two.)
- A . The FortiManager administrator must set the ADOM device mode to Advanced.
- B . Policies and objects databases can be shared between the Financial and HR ADOMs.
- C . An administrator with the super user profile can access all the VDOMs.
- D . The administrator must configure FortiManager in workspace normal mode.
Which two items does an FGFM keepalive message include? (Choose two.)
- A . FortiGate IPS version
- B . FortiGate license information
- C . FortiGate configuration checksum
- D . FortiGate uptime
Refer to the exhibit.
Given the configuration shown in the exhibit, which two conclusions can you draw from the installation targets in the Install On column? (Choose two.)
- A . Policy seq.# 3 will be installed on all managed devices and VDOMs that are listed under Installation Targets.
- B . Policy seq.# 3 will be skipped because no installation targets are specified.
- C . Policy seq.# 2 will not be installed on the Local-FortiGate root VDOM because there is no root VDOM in the Installation Target.
- D . Policy seq.# 1 will be installed on the ISFW device root[NAT] and Student[NAT] VDOMs only.
What will be the result of reverting to a previous revision version in the revision history?
- A . It will install configuration changes to managed device automatically.
- B . It will tag the device settings status as Auto-Update.
- C . It will modify the device-level database.
- D . It will generate a new version ID and remove all other revision history versions.
An administrator wants to create a policy on an ADOM that is in backup mode and install it on a FortiGate device in the same ADOM.
How can the administrator perform this task?
- A . The administrator must use the Policy & Objects section to create a policy first.
- B . The administrator must use a FortiManager script.
- C . The administrator must disable the FortiManager offline mode first.
- D . The administrator must change the ADOM mode to Advanced to bring the FortiManager online.
Refer to the exhibit.
What can you conclude from the failed installation log shown in the exhibit?
- A . Policy ID 2 is installed in the disabled state.
- B . Policy ID 2 is installed without the remote user student.
- C . Policy ID 2 will not be installed.
- D . Policy ID 2 is installed without a source address.
In the event that one of the secondary FortiManager devices fails, which action must be performed to return the FortiManager HA manual mode to a working state?
- A . The FortiManager HA state transition is transparent to administrators and does not require any reconfiguration.
- B . Reboot the failed device to remove its IP from the primary device.
- C . Manually promote one of the working secondary devices to the primary role, and reboot the old primary device to remove the peer IP of the failed device.
- D . Reconfigure the primary device to remove the peer IP of the failed device.
An administrator has assigned a global policy package to custom ADOM 1. Then the administrator creates a new policy package, Fortinet, in the custom ADOM 1.
What happens to the Fortinet policy package when it is created?
- A . You must assign the global policy package from the global ADOM.
- B . The global policy package is automatically assigned.
- C . You must reapply the global policy package to ADOM 1.
- D . You can select the option to assign the global policies.
Which output is displayed right after moving the ISFW device from one ADOM to another?
A)
B)
C)
D)
- A . Option A
- B . Option B
- C . Option C
- D . Option D
An administrator has enabled Service Access on FortiManager.
What is the purpose of Service Access on the FortiManager interface?
- A . It allows administrative access to FortiManager.
- B . It allows FortiManager to respond to requests for FortiGuard services from FortiGate devices.
- C . It allows third-party applications to gain read/write access to FortiManager.
- D . It allows FortiManager to determine the connection status of managed devices.
Refer to the exhibit.
A junior administrator is troubleshooting a FortiManager connectivity issue that is occurring with a managed FortiGate device.
Given the FortiManager device manager settings shown in the exhibit, what can you conclude from this scenario?
- A . The administrator must refresh the device to restore connectivity.
- B . FortiManager lost internet connectivity, therefore, the device appears to be down.
- C . The administrator can reclaim the FortiGate to FortiManager protocol (FGFM) tunnel to get the device online.
- D . The administrator recently restored a FortiManager configuration file.
Refer to the exhibit.
You are using the Quick Install option to install configuration changes on the managed FortiGate.
Which two statements correctly describe the result? (Choose two.)
- A . It installs provisioning template changes on the FortiGate device.
- B . It provides the option to preview only the policy package changes before installing them.
- C . It installs all the changes in the device database first and the administrator must reinstall the changes on the FortiGate device.
- D . It installs device-level changes on the FortiGate device without launching the Install Wizard.
Refer to the exhibit.
What percent of the available RAM is being used by the process in charge of downloading the web and email filter databases from the public FortiGuard servers?
- A . 2.9
- B . 3.1
- C . 1. 5
- D . 4.1
