Facebook 200-101 Facebook Certified Marketing Science Professional Online Training
Facebook 200-101 Online Training
The questions for 200-101 were last updated at Dec 11,2025.
- Exam Code: 200-101
- Exam Name: Facebook Certified Marketing Science Professional
- Certification Provider: Facebook
- Latest update: Dec 11,2025
An online retailer knows their incremental effect from Facebook ads from their previous Conversion Lift test. They want an always-on attribution solution that allows them to allocate its budget across publishers on an ongoing basis. The challenge is identifying a model that is as close to their true business value as possible.
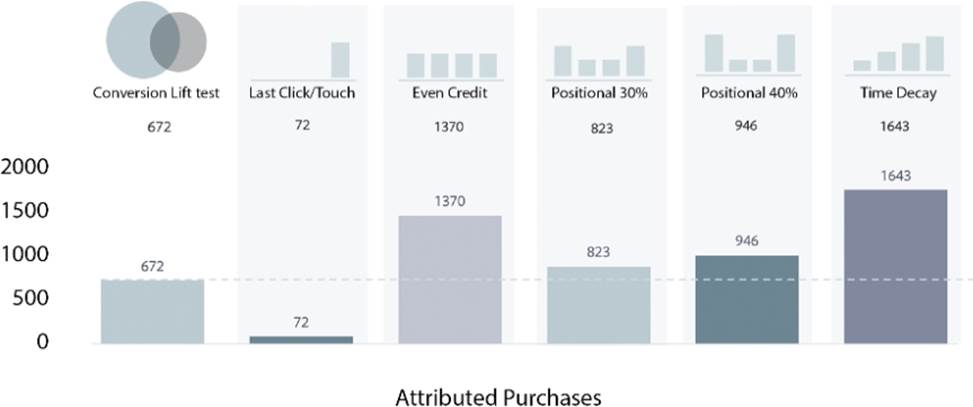
Which Attribution model should the retailer choose?
- A . Positional 30%
- B . Even credit
- C . Positional 40%
- D . Time decay
An ecommerce brand runs a multi-cell Conversion Lift test. The brand needs to determine if bidding in the Facebook auction based on user value calculated from its LTV model versus demographic targeting improves performance by 10%. The p-value for the test is calculated as p = 0.95.
How should the analyst interpret bidding based on user value?
- A . It cannot be concluded that 95% of the performance increase is due to bidding based on user value.
- B . It cannot be concluded that 10% of the performance increase is due to bidding based on user value.
- C . Ten percent of the performance increase is due to bidding based on user value.
- D . Bidding based on user value is responsible for 95% of the performance increase.
An advertiser recently ran a month-long campaign on a new media platform. This campaign targeted customers who had purchased from the advertiser in the past year. Of the 10 million customers targeted, 3 million were reached. The average frequency for the campaign was three impressions over the month. The advertiser spent $100,000 on this media buy.
After the campaign, an analyst from the media platform noticed that customers who received six or more impressions were twice as likely to purchase than those who received three or fewer impressions. To increase the number of users who receive six or more impressions, the analyst recommends that the advertiser double their spend. The goal is to increase the frequency from three to six in order to drive a significant increase in incremental return on ad spend.
What primary concern should the advertiser’s in-house measurement team have about this conclusion?
- A . The demographic makeup of the groups that received <=3 and >=6 impressions are different
- B . This is an observational finding rather than an experimental finding
- C . This is a new platform, so the results must be validated multiple times before changing strategy
- D . The campaign was not long enough to capture adequate data
A startup ecommerce company is beginning to run media campaigns to increase sales. It is having trouble taking action from its media campaigns because of the high number of KPIs it is considering when analyzing results.
The startup company has been in the growth phase, so the focus has been on increasing the number of people who see ads for their products on Facebook. As the company grows, the focus is shifting towards generating sales. For its Facebook campaigns, the business is considering incremental purchases, incremental reach, CPMs, website visits, clicks and impressions.
Which metric should be prioritized to support the company’s new Facebook marketing strategy?
- A . Website visits
- B . Incremental purchases
- C . Incremental reach
- D . Click-through rate
A start-up ecommerce brand that sells pet products wants to test campaign structure. It would like to determine if it should have separate ad sets targeting different pet interest groups or consolidate all interest groups into one ad set.
The brand sets up a multi-cell Conversion Lift test for one month. At the end of the test, no results are available to review, due to insufficient statistical power.
Which two approaches should the analyst recommend? (Choose 2)
- A . Run a campaign-level A/B test instead
- B . Run a multi-cell Conversion Lift with fewer interest groups
- C . Run a multi-cell Conversion Lift test with an increased holdout percentage
- D . Review campaign results in Ads Manager instead
A brand needs to measure how frequency affects conversions and ROI. Currently the brand runs a campaign on 2x frequency for seven days.
How should the brand set up a test to understand how frequency affects incremental conversions?
- A . A Conversion Lift test with a 2x frequency for seven days
- B . A multi-cell Conversion Lift test: Cell 1 with a 2x frequency for seven days, Cell 2 with 4x frequency for seven days
- C . A multi-cell A/B test: Cell 1 with a 2x frequency for seven days, Cell 2 with 4x frequency for seven days
- D . A Conversion Lift with 4x frequency for seven days
An advertiser is running an A/B test on Facebook with the goal of finding whether creative strategy A or B achieves the most conversions.
What is the null hypothesis of this test design?
- A . Conversions (A) = Conversions (B)
- B . Conversions (A) <> 0, Conversions (B) <> 0
- C . Conversions (A) = 0, Conversions (B) = 0
- D . Conversions (A) <> Conversions (B)
A brand that has traditionally focused on TV campaigns has recently started advertising on digital channels like Facebook and YouTube. The brand manager has advised the company to invest in developing mobile-optimized creative and that its TV ads are too long to perform well online.
A post-campaign analysis was run to assess the relationship between complete video views and video duration in order to make the case that videos with shorter duration tend to achieve a greater number of complete views.
This scatter plot demonstrates the findings of the analysis.
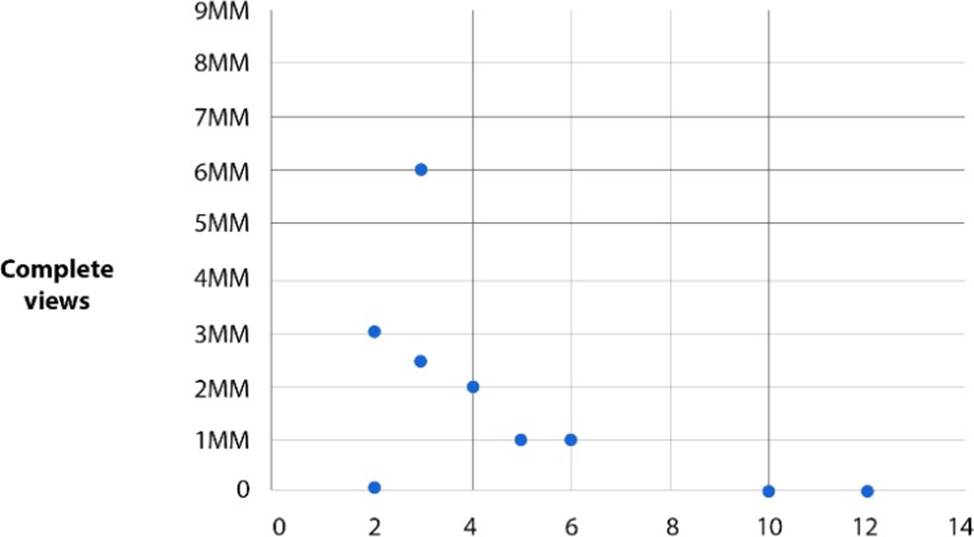
How many of these data points are likely to skew the findings of this analysis?
- A . 2
- B . 1
- C . 4
- D . 3
A marketing analyst wants to understand the relationship between campaign frequency and additional return on ad spend (ROAS) across 150 CPG Facebook campaigns. The analyst has the following information on these campaigns: reach, frequency, duration, budget, product category, buying strategies, and outcomes like additional sales and ROAS.
The analyst suspects that campaign frequency is related to other campaign characteristics and is planning to run the following statistical model:
ROAS Lift = bO + b1.reach + b2.frequency + b3.duration + b4.budget + b5.product category + b6.buying strategy
What two additional statistical analysis are required to test the analyst’s hypothesis? (Choose 2)
- A . Correlation matrix of campaign frequency and other predictors of ROAS Lift
- B . Logistic regression including all relevant campaign characteristics
- C . Simple linear regression of frequency and ROAS Lift
- D . Multiple linear regression including non-linear and interaction terms
An analyst for a primarily brick-and-mortar retailer is reviewing measurement results from the last half for all marketing. The media plan was 50% TV spend, with some Facebook (10%), search (10%), print (10%), and radio (20%).
No solution provides the same numbers for a single point in time. The analyst needs to recommend how to allocate budget across channels to maximize sales for the next business quarter.
Which measurement solution should be the primary source of the analyst’s recommendation?
- A . Marketing mix model
- B . Multi-cell Conversion Lift
- C . Multi-touch attribution
- D . Nielsen Total Ads Ratings

