EC-Council CEH-001 Certified Ethical Hacker (CEH) Online Training
EC-Council CEH-001 Online Training
The questions for CEH-001 were last updated at Dec 18,2025.
- Exam Code: CEH-001
- Exam Name: Certified Ethical Hacker (CEH)
- Certification Provider: EC-Council
- Latest update: Dec 18,2025
SNMP is a connectionless protocol that uses UDP instead of TCP packets (True or False)
- A . true
- B . false
Ursula is a college student at a University in Amsterdam. Ursula originally went to college to study engineering but later changed to marine biology after spending a month at sea with her friends. These friends frequently go out to sea to follow and harass fishing fleets that illegally fish in foreign waters. Ursula eventually wants to put companies practicing illegal fishing out of business. Ursula decides to hack into the parent company’s computers and destroy critical data knowing fully well that, if caught, she probably would be sent to jail for a very long time.
What would Ursula be considered?
- A . Ursula would be considered a gray hat since she is performing an act against illegal activities.
- B . She would be considered a suicide hacker.
- C . She would be called a cracker.
- D . Ursula would be considered a black hat.
A rootkit is a collection of tools (programs) that enable administrator-level access to a computer. This program hides itself deep into an operating system for malicious activity and is extremely difficult to detect. The malicious software operates in a stealth fashion by hiding its files, processes and registry keys and may be used to create a hidden directory or folder designed to keep out of view from a user’s operating system and security software.
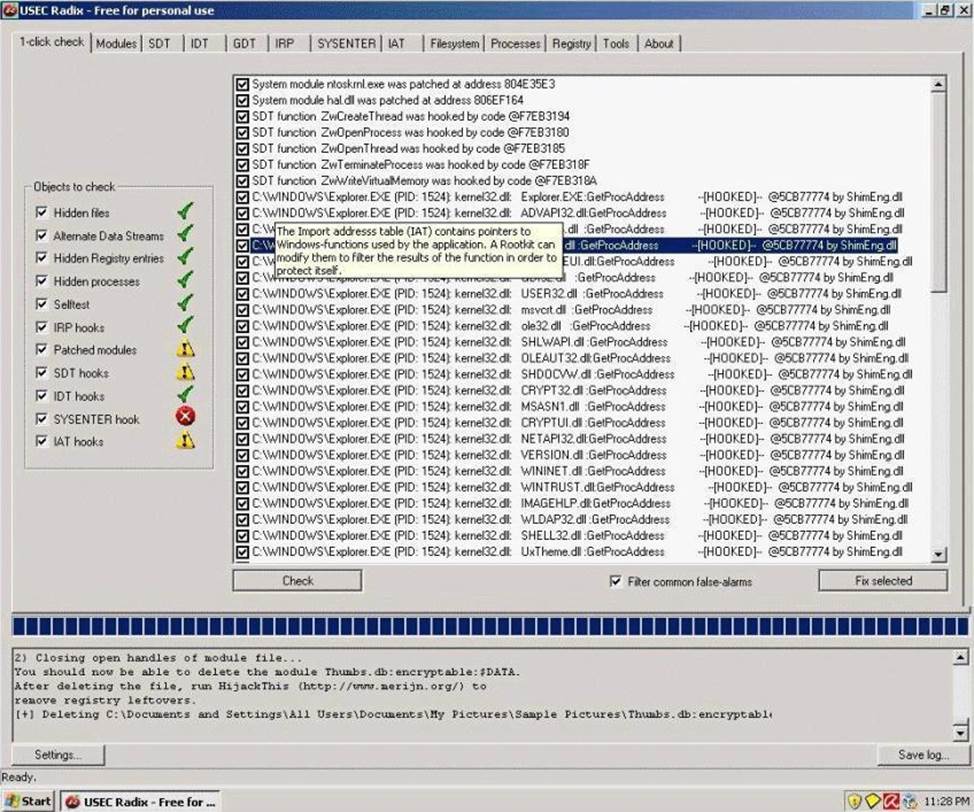
What privilege level does a rootkit require to infect successfully on a Victim’s machine?
- A . User level privileges
- B . Ring 3 Privileges
- C . System level privileges
- D . Kernel level privileges
What type of session hijacking attack is shown in the exhibit?
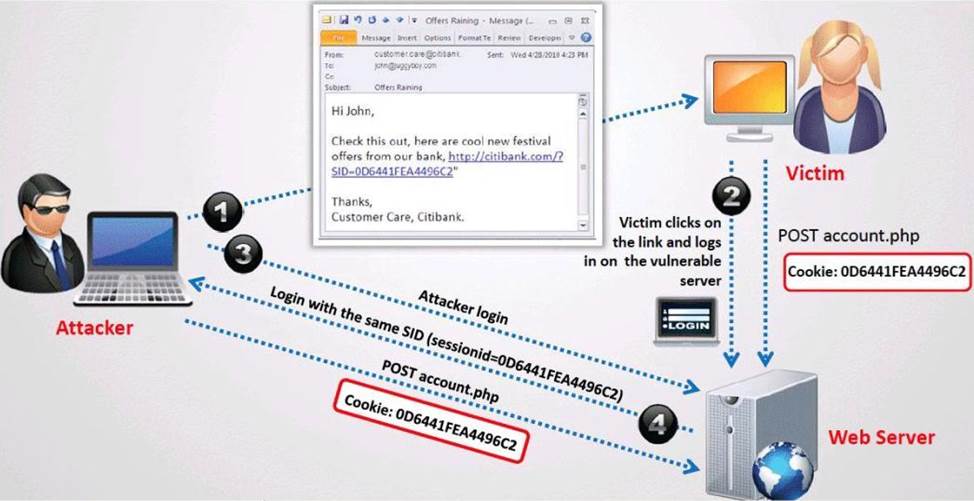
- A . Cross-site scripting Attack
- B . SQL Injection Attack
- C . Token sniffing Attack
- D . Session Fixation Attack
Cyber Criminals have long employed the tactic of masking their true identity. In IP spoofing, an attacker gains unauthorized access to a computer or a network by making it appear that a malicious message has come from a trusted machine, by "spoofing" the IP address of that machine.
How would you detect IP spoofing?
- A . Check the IPID of the spoofed packet and compare it with TLC checksum. If the numbers match then it is spoofed packet
- B . Probe a SYN Scan on the claimed host and look for a response SYN/FIN packet, if the connection completes then it is a spoofed packet
- C . Turn on ‘Enable Spoofed IP Detection’ in Wireshark, you will see a flag tick if the packet is spoofed
- D . Sending a packet to the claimed host will result in a reply. If the TTL in the reply is not the same as the packet being checked then it is a spoofed packet
What does ICMP (type 11, code 0) denote?
- A . Source Quench
- B . Destination Unreachable
- C . Time Exceeded
- D . Unknown Type
Attacking well-known system defaults is one of the most common hacker attacks. Most software is shipped with a default configuration that makes it easy to install and setup the application. You should change the default settings to secure the system.
Which of the following is NOT an example of default installation?
- A . Many systems come with default user accounts with well-known passwords that administrators forget to change
- B . Often, the default location of installation files can be exploited which allows a hacker to retrieve a file from the system
- C . Many software packages come with "samples" that can be exploited, such as the sample programs on IIS web services
- D . Enabling firewall and anti-virus software on the local system
Samuel is the network administrator of DataX Communications, Inc. He is trying to configure his firewall to block password brute force attempts on his network. He enables blocking the intruder’s IP address for a period of 24 hours’ time after more than three unsuccessful attempts. He is confident that this rule will secure his network from hackers on the Internet.
But he still receives hundreds of thousands brute-force attempts generated from various IP addresses around the world. After some investigation he realizes that the intruders are using a proxy somewhere else on the Internet which has been scripted to enable the random usage of various proxies on each request so as not to get caught by the firewall rule.
Later he adds another rule to his firewall and enables small sleep on the password attempt so that if the password is incorrect, it would take 45 seconds to return to the user to begin another attempt. Since an intruder may use multiple machines to brute force the password, he also throttles the number of connections that will be prepared to accept from a particular IP address. This action will slow the intruder’s attempts.
Samuel wants to completely block hackers brute force attempts on his network.
What are the alternatives to defending against possible brute-force password attacks on his site?
- A . Enforce a password policy and use account lockouts after three wrong logon attempts even though this might lock out legit users
- B . Enable the IDS to monitor the intrusion attempts and alert you by e-mail about the IP address of the intruder so that you can block them at the Firewall manually
- C . Enforce complex password policy on your network so that passwords are more difficult to brute force
- D . You cannot completely block the intruders attempt if they constantly switch proxies
What type of port scan is shown below?

- A . Idle Scan
- B . FIN Scan
- C . XMAS Scan
- D . Windows Scan
Attackers target HINFO record types stored on a DNS server to enumerate information. These are information records and potential source for reconnaissance. A network administrator has the option of entering host information specifically the CPU type and operating system when creating a new DNS record. An attacker can extract this type of information easily from a DNS server.
Which of the following commands extracts the HINFO record?
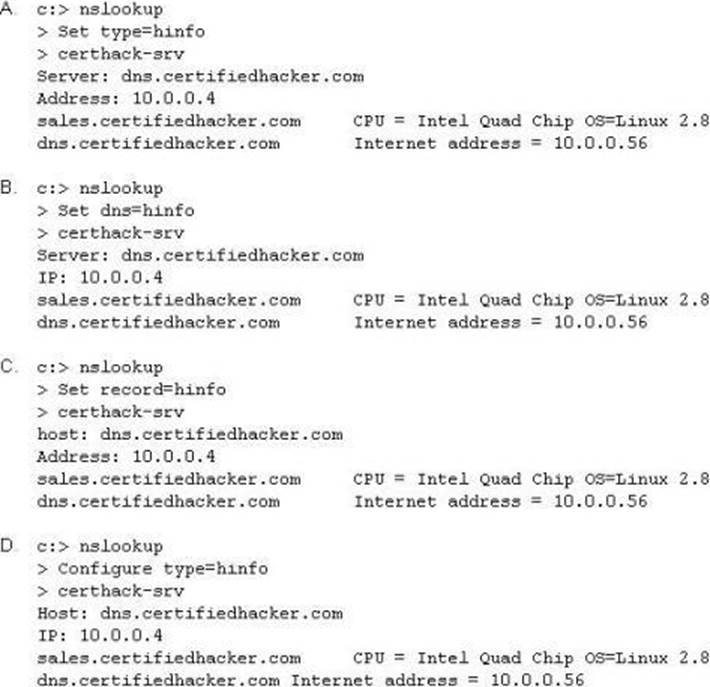
- A . Option A
- B . Option B
- C . Option C
- D . Option D
Latest CEH-001 Dumps Valid Version with 878 Q&As
Latest And Valid Q&A | Instant Download | Once Fail, Full Refund

