CIPS L4M1 Scope and Influence of Procurement and Supply Online Training
exams2024-09-20T04:02:17+00:00CIPS L4M1 Online Training
The questions for L4M1 were last updated at Dec 16,2025.
- Exam Code: L4M1
- Exam Name: Scope and Influence of Procurement and Supply
- Certification Provider: CIPS
- Latest update: Dec 16,2025
What is ‘supply chain management’? Outline the drivers, advantages and disadvantages of using this approach within the Procurement Department of an organisation (25 points)
-The question also brings up 2 concepts C supply chain management and tiered supply chains, it would be good to include a definition of both of these.
-Because of the number of things you’ll have to write, you don’t need to go into lots of detail C one paragraph per section will be enough.
Proposed Essay Structure
Intro C what is supply chain management and what is a tiered supply chain P1 C drivers
P2 C advantages P3 C disadvantages
Conclusion C supply chains are complex due to globalisation
Essay Ideas:
-Definition of supply chain management = Making something available in response to a buyer’s requirements. The transformation of goods from raw material into an end product (input > conversion > output)
-Drivers = Cost, Time/ Speed, Reliability, Responsiveness, Transparency, Globalisation
-Advantages = reduced costs by elimination of waste, improved responsiveness to customer requirements, joint-ventures with supply partners leading to innovations, tech sharing, improved communication leads to faster lead times for product development
-Disadvantages = needs considerable investment and internal support, closer relationships may be
risky (IP, loss of control), issues in fairly distributing gains and risks
-(you don’t need to talk about all of these- pick 1 or 2 you feel you know the best and focus on that)
-Example Essay
-Supply Chain Management (SCM) is the arrangement of processes involved in the production and distribution of goods / services – from the origin to the end consumer. In simple terms, it’s taking a raw product and transforming it into an end product that a consumer would purchase. For example taking a potato from a farmer, giving it to a manufacturer to make into chips and sending these to retailers to be sold. SCM relies on close relationships between the parties in the supply chain and adds value to the product at every stage. A Tiered Supply Chain is a specific configuration within SCM that involves multiple levels of suppliers and sub-suppliers. A buyer will work with a small amount of Tier 1 suppliers who will in turn work with their own suppliers. In a tiered system there can be many, many layers of suppliers who all ultimately work towards creating the same product. This essay aims to delve into the drivers, advantages, and disadvantages associated with implementing a complex supply chain, such as the Tiered Supply Chain model.
-The main drivers of using a tiered supply chain are often rooted in the pursuit of efficiency, cost- effectiveness, and flexibility. By consolidating suppliers into distinct tiers, organizations can streamline their management processes, reduce complexity, and enhance overall supply chain performance. Additionally, tiered supply chains are often employed in response to the global nature of modern business, accommodating the need to source materials and components from various regions while maintaining a manageable and responsive supply network.
-One of the advantages of a Tiered Supply Chain is the streamlined management of suppliers. In this model, there are fewer direct suppliers to oversee, simplifying the coordination and communication processes. This can lead to increased efficiency and responsiveness as organizations deal with a smaller, more manageable pool of suppliers. The consolidation of suppliers in a tiered system may also result in potential cost savings and improved collaboration with a select group of trusted partners.
-However, the complexity of a Tiered Supply Chain brings disadvantages. One significant drawback is reduced visibility. As the supply chain extends across multiple tiers, organizations may struggle to have a comprehensive view of the entire process. This lack of visibility can lead to challenges in tracking and responding to potential disruptions. Moreover, ethical risks emerge when companies have limited oversight over lower-tier suppliers, potentially exposing organizations to issues such as labour exploitation, environmental concerns, or violations of ethical standards.
-In conclusion, supply chain management has evolved into a complex discipline due to the forces of globalization and consumer demands for speed and quality. The Tiered Supply Chain model, driven by these factors, presents both advantages and disadvantages. While managing fewer suppliers can enhance efficiency, the trade-off includes diminished visibility and increased ethical risks.
-Organizations must carefully evaluate the specific needs of their operations and weigh the benefits against the challenges when deciding whether to adopt a Tiered Supply Chain. In this intricate landscape, the ability to balance complexity and efficiency becomes paramount for sustained success in the global marketplace.
Tutor Notes
-Definition of supply chain management is from p.5
-Drivers, advantages and disadvantages p.9
This topic used to be much more in depth in the old syllabus and has been drastically simplified in the new study guide. The guide is actually quite light on this topic stating simply that “globalisation and localisation are both drivers of using supply chain tiering”. If you don’t work in manufacturing, or an industry that uses supply chain tiering, this concept may be a bit alien to you and I’d recommend doing a little extra research. The best example of supply chain tiering is in car manufacturing- and that would be a good example to use in an essay. Some additional links for research:
-Supplier Tiers: What’s The Difference Between Tier 1, Tier 2, and Tier 3 | PLANERGY Software
-Sustainable Sourcing – Definition, Examples, Benefits & Best Practices (brightest.io)
-https://youtu.be/fs1rDgBQy1M
Describe the main differences between a traditional procurement approach and supply chain management approach to buying (25 points)
With this type of question you would be expected to discuss 3- 5 differences, giving examples. Example Essay Structure
Introduction C explain what is meant by ‘procurement’ and ‘SCM’ C procurement is the traditional way and is to do with purchasing goods, SCM is the new way which is a more multifaceted way of securing goods and is the result of longer, more complex and more globalised supply chains.
Paragraph 1 C the objectives of each approach (5 Rights vs added value) Paragraph 2 C the approach (reactive buying vs proactive ordering) Paragraph 3 – the way of working (silo working vs cross-functional working) Paragraph 4 C the relationships with suppliers (transactional vs collaborative)
Conclusion C There are many differences between the two approaches, and different companies may favour one over the other depending on their specific circumstances. E.g. small organisations that make low value and low risk purchases may take a traditional procurement approach and large multi- national organisations may require a SRM approach due to the volume of suppliers and com-plexities of the supply chains.
Example essay:
Procurement and Supply Chain Management (SCM) represent two distinct approaches to acquiring goods, reflecting the evolution of purchasing practices. Procurement, the traditional method, in- volves the straightforward purchase of goods. In contrast, SCM is a more intricate approach, born out of longer, more complex, and globalized supply chains. This essay explores the main differences between these two approaches, highlighting their objectives, methods, ways of working, and suppli- er relationships.
In the traditional procurement approach, the focus is on achieving the "5 Rights" C getting the right goods, in the right quantity, at the right quality, for the right price, and at the right time. This en- sures efficiency in the purchasing process. On the other hand, SCM goes beyond these basic objec- tives, aiming to add value to the entire supply chain. This might involve developing strategic rela- tionships with suppliers, ensuring sustainability, and aligning with broader organizational goals. For example, a company employing a traditional procurement approach might emphasize getting the lowest price, while an SCM approach could involve working with suppliers to enhance product in- novation or reduce environmental impact.
Secondly, the traditional procurement approach is often reactive, responding to immediate needs or demands. Companies using this method typically make purchases as required, without a long-term strategy. In contrast, SCM involves proactive ordering, anticipating future needs and trends. For instance, a company employing SCM might engage in demand forecasting, allowing for better plan- ning and inventory management. This proactive approach helps prevent stockouts, reduce costs, and enhance overall supply chain efficiency.
Moreover, traditional procurement often involves silo working, where different departments operate independently. The procurement team may not collaborate closely with other departments like pro- duction or marketing. In SCM, there’s an emphasis on cross-functional working, breaking down de- partmental barriers for a more integrated approach. For example, an SCM team might work closely with production to ensure materials are aligned with manufacturing schedules, fostering efficiency and minimizing disruptions.
Lastly, in traditional procurement, the relationship with suppliers is transactional C focused solely on the exchange of goods for money. Conversely, SCM promotes collaborative relationships, emphasiz- ing long-term partnerships. A company using SCM might work closely with suppliers to improve processes, share information, and jointly address challenges. For instance, an SCM approach might involve collaborating with suppliers to implement just-in-time inventory systems, leading to cost savings and improved responsiveness.
In conclusion, the differences between traditional procurement and SCM are substantial and nu- anced. While a traditional procurement approach may suit smaller organizations with low-value and low-risk purchases, larger multinational companies with complex supply chains often find SCM more suitable. Understanding these differences allows companies to tailor their approach based on their unique circumstances, emphasizing the importance of flexibility and strategic alignment with organizational goals in the ever-evolving landscape of buying and supply chain management.
Tutor Notes
-This question is taken from learning outcome 1.1.1 (p2 onwards). The new study guide has drasti- cally simplified the information on this topic compared to the old syllabus (the table above comes from the old syllabus). This may be good news for students in that you don’t need to know as much, but I do wonder if the study guide gives students enough ‘content’ to write an essay on the subject.
-If a question is to come up from LO 1.1 it would be likely be something like: definitions and dif- ferences between procurement and SCM, difference between a supply chain and a supply network, elements of SCM, or how to add value in the supply chain.
Describe what is meant by the 5 Rights of Procurement (25 points)
This question is worth 25 marks so you can imagine what the mark scheme will look like. There are 5 Rights so there will be 5 points for each Right. Naming the Right will be one point, then you have 4 points for a description and example. You should therefore aim to have 4-5 sentences per Right.
-I would recommend using headings for this type of essay- clearly putting your essay into 5 sections for each right. This makes it easy for the examiner to mark.
Proposed Essay structure
Introduction C what is meant by the 5 Rights
-Price
-Quality
-Quantity
-Time
-Place
-Conclusion C why it’s important, all rights are equally as important Example Essay
Procurement revolves around achieving the delicate balance of acquiring goods and/ or services at the right price, quality, quantity, time, and place. This essay explains why these "Five Rights of Procurement" are important and explains how using this metric can help procurement to make smart choices when they purchase goods or services.
Price:
Firstly, it is important that procurement do not simply seek to find the cheapest option. The First Right is about finding the product/ service at an affordable price that doesn’t compromise on quality. Let’s say a company is buying office furniture. They might go for a supplier that offers a good balance between cost and quality, ensuring they get good value for their money. Considerations here may include Total Cost of Ownership, the Price Iceberg, and Whole Life Costing. The company therefore may seek to get the best price, but in relation to how long the furniture will last. A cheap chair that will break after one year may not be the best price compared to another chair which will last 10 years.
Quality:
The second right, quality, looks at legal compliance and fitness for purpose. Quality adherence aligns with specifications as well as legislation such as the UK Sale of Goods Act 1979. This helps ensure that items meet their commonly intended purpose and maintains satisfactory condition. Buyers deploy both reactive measures like Quality Control and proactive approaches like Quality Assurance to uphold the stipulated quality. This commitment not only ensures legal compliance but also underpins customer satisfaction, brand reputation, and ethical sourcing policies. An example of quality is an organisation buying a washing machine that conforms to ISO standard 97.060 and has a 2-year warrantee.
Quantity:
The third right, quantity, is a strategic consideration about how much of an item to order. It is connected to efficient inventory management. One tool that procurement can use to ensure they order the right quantity of a product is Economic Order Quantity (EOQ) C this serves as a tool for finding the equilibrium between stock-holding costs and avoiding stockouts. Market conditions, supply chain dynamics (e.g. JIT / Lean manufacturing), and organizational policies collectively play a pivotal role in determining the right quantity. For example a confectionary manufacturer will need to order the right number of eggs to make cakes- they will need to consider how many eggs they will need in order to make the cakes, but also take into consideration that they may not need them all at once and that eggs can expire. The use of an MRP system is helpful when determining quantities of products to order.
Time:
Time is about getting things when we need them. In the above example, an egg delivery timing for a confectionary manufacturer will be pivotal to making the cakes on time. Other considerations about time include changing market forces and customer demand. The use of forecasting is therefore extremely useful; particularly if there are peaks in demand for a product, such as toys at Christmas. Moreover, organizations need to avoid bottlenecks and production stoppages, so time (including lead time and delivery time) is an important consideration when making orders.
Place:
Lastly, place is about getting things to the right location. Minimizing environmental impact, reducing risks during transit, and optimizing warehousing practices contribute to achieving the right place.
This is particularly important for perishable items such as food, and for items which require specific storage conditions such as chemicals. This involves good planning in terms of logistics, minimizing any impact on the environment during transport and a consideration for safety.
In conclusion, the Five Rights of Procurement provide a structured framework for organizations to optimize their sourcing practices. All rights are equally as important and it is the relationship between the Rights which is key. While price, quality, quantity, time, and place form the foundation, evolving models acknowledge additional elements like the Right Relationship with the Supplier.
Embracing these principles not only ensures operational efficiency but also promotes sustainability and ethical conduct throughout the procurement process, contributing to long-term success in a globalized and dynamic marketplace.
Tutor Notes
-The 5 Rights is a big topic in CIPS so do learn them off by heart. It’s p. 20 in the study guide.
-The conclusion mentions that additional ‘rights’ are starting to be introduced into the matrix, this is true and isn’t mentioned in this study guide. I believe this starts to come up in Level 5. Just something to be aware of- some people are now talking about other Rights such as finding the right supplier and the right relationship. It’s good to know, but not essential for this essay. Neither is knowing the ISO standard for washing machines C that’s certainly not in the book. You can sprinkle in your own knowledge to essays like this, as it demonstrates you’re able to apply the theory to real life. Why I remember the ISO for washing machines is a different story….
-You could also have mentioned the following topics;
o price C using the right currency and incoterm, aggregation of spend, negotiating prices
o quality C conformance and performance specs
o quantity C fulfilling retail orders, large order quantities leading to discount
o time C additional costs of a stockout, impact on relationships and reputation
o place C additional costs if delivery fails
-This is the type of question you can easily over-write. It’s a huge topic and you could easily spend too long on it and not have enough time to answer other questions. So be careful with your timings. You don’t need to mention everything above.
Another way this type of question can come up is as a scenario. E.g. XYZ is a manufacturer of cakes and needs to order eggs. Discuss how XYZ can ensure the 5 Rights of Procurement when ordering Eggs.
Explain what is meant by added value (5 points). Describe 4 ways the Procurement Department can add value for their organisation (20 points)
-Definition of added value: the economic enhancement given to products or services before offering them to customers. Examples may include a product which has additional features at no additional cost to the customer or the provision of an extended warrantee.
-Description of four of the following with examples and s: providing better customer service levels, risk management, cost control and reduction, relationship management, reputation management, innovation, use of technology, streamlining processes, improving specifications, increasing sustainability, improving quality, ordering processes such as bulk ordering, inventory management, improving the product from the customer’s perspective (e.g. packaging, exclusivity), sustainability, convenience, market development.
Example essay:
Added value in procurement refers to the enhancement or improvement in the economic worth, quality, or utility of products or services before they are offered to customers or end-users. In the context of procurement, the goal is to go beyond simply obtaining goods or services at the lowest cost. Instead, procurement aims to contribute additional value to the organization through various means. This essay explores the concept of added value and outlines four ways the Procurement Department can contribute to organizational improvement.
Improving Specifications
Procurement can add value firstly by ensuring all critical items are procured against a specification, and secondly by improving and regularly updating those specifications. For example, the procurement department might be responsible for procuring light-bulbs for an office. Having an effective specification for this purchase (lightbulbs must meet X safety standard and Y environmental standard) would result in less maverick buying for the organisation and the procurement of a better- quality product. Furthermore, regularly updating specifications ensures that purchases are made against current safety standards and regulations (e.g. the use of low-energy lightbulbs). If procurement don’t update specifications, then there is a risk that items are bought that don’t meet the correct standards. Added value in this regard could also therefore be considered the removal of risks of procuring the wrong item.
Stream-lining Processes
Procurement can add value by stream-lining processes such as requisitions and POs. This reduces the time it takes to procure an item, thus saving the company money. Another process that could be streamlined is the re-ordering process of regularly bought items. This could be automated when the stock levels reach a certain level. For example if an organisation requires its staff to wear PPE, an automatic request could be made once there are only 50 face masks left.
Managing Supplier Relationships
Having strong, positive relationships with suppliers is a source of added value as it means suppliers value you as a buyer and are therefore more likely to help in situations which are adversely affecting business. For example, if a manufacturer puts an order in for 300 items with their supplier but then realises that they have made an error in the amount, if there is a strong relationship, the supplier may allow the buyer to amend the order after the fact. If there is a poor relationship, the supplier may not be as flexible. The flexibility in the supply chain is therefore a source of added value.
Improving Quality / Innovation
This involves adding value from the customer’s perspective. E.g. a customer may choose to purchase a phone that has a longer battery life than others. Procurement’s role in this may be in completing a Value Engineering exercise or procuring higher quality components or materials at the same price in order to achieve this additional feature.
In conclusion, the Procurement Department plays a crucial role in organizational success by adding value through improved specifications, streamlined processes, strong supplier relationships, and a focus on quality and innovation. These strategies contribute to enhanced efficiency, reduced risks, and increased customer satisfaction, making procurement an essential function for organizational excellence.
Tutor Notes
-The question asks specifically to name 4 ways of adding value. You therefore won’t get any additional points if you talk about 5 or 6, even though it may be tempting. Instead, focus your response on providing more information on the 4 you have chosen and bulking out your answer with examples. This demonstrates to the examiner that you fully understand the topic AND that you can apply the theory to real situations.
-You could use real-life examples from your own organisation/ experience or you could give a hypothetical situation such as a cake manufacturer. You could talk through how the procurement department at the cake manufacturer can add value by doing the four things in your essay: by amending the specification so the cakes are more tasty, by streamlining the process for ordering flour, by managing the relationship with the company that fixes the machines when they break down, and by introducing innovation such as using an e-procurement system to source raw materials and the benefits that these will bring to the organisation.
-Added value is part of the syllabus for Learning Outcome 1.2 starting from p.19 but I’m gonna be honest, I think the new study guide is a bit crap on this part of the syllabus. The section starts talking about the 5 rights of procurement and I think that makes things very confusing for students. The 5 rights and added value are linked subjects, but they’re not the same. Getting the rights right, CAN lead to sources of added value, but added value is value that is IN ADDITION to what is expected. So, when you have a question on added value, focus on stuff that’s listed under 1.1.4 ‘other sources of added value’ on p.35 rather than talking about the 5 rights of procurement. My list at the top is more exhaustive than the one in the study guide.
-If you’re looking to be really clever you can quote Michael Porter on ‘what is added value?’. Michael Porter looks at this from a customer perspective – ‘added value’ refers to the addition of greater value (either by reducing the cost to produce it, or by adding something that customers are willing to pay more for). These could be; marketing / design, customer service, maintenance, delivery etc. This comes up at Level 5 / 6.
Bob is a procurement manager at ABC Ltd. He has been asked to ensure all future purchases achieve ‘value for money’ for the organisation. What is meant by ‘value for money’? (5 points). Describe 4 techniques that Bob could use to achieve this (20 points)
2) 4 techniques Bob can use to achieve VFM: this is the bulk of your essay. Each of the 4 will be worth 5 points, so remember to give a thorough and example. Pick 4 from the list below: complete a value analysis to eliminate non-essential features, minimise variety/ consolidate demand, avoid over specification, pro-active sourcing, whole life costing methodologies, eliminate / reduce inventory, use electronic systems, international sourcing, sustainability / environmental policies, currency/ exchange rate considerations, negotiating good payment terms, packaging, warrantees.
Example Essay:
"Value for money" (VFM) is a concept that refers to obtaining the best possible return on investment or benefits relative to the cost incurred. It involves assessing whether the goods, services, or activities provided offer an optimal balance between their cost and the quality, benefits, or outcomes they deliver. Value for money is not solely about choosing the cheapest option; instead, it considers the overall efficiency, effectiveness, and long-term value derived from an expenditure. For Bob, the Procurement Manager at ABC Ltd there are four key ways that he can achieve this for all future purchases.
Value Engineering
This is looking at the components of a product and evaluating the value of each component individually. You can then eliminate any components that do not add value to the end product. To do this Bob would choose a product to review and determine whether any parts of this can be omitted (thus saving the company money) or could be replaced by components that are of a higher quality at the same price (thus providing added value to the customer). For example, Bob could complete a Value Engineering exercise on the new mobile phone prototype ABC plan to release next year. His findings may discover a way to provide a higher quality camera at no additional cost or that some components don’t add value and can be eliminated.
Consolidate demand
Bob can achieve value for money by consolidating demand at ABC ltd. This would mean rather than each individual person/ department ordering what they want when they need it, Bob creates a centralised process for ordering items in bulk for the departments to share. For example, if each department require stationary to be ordered, Bob can consolidate this demand and create one big order each quarter. This will likely result in cost savings for ABC as suppliers often offer discounts for large orders. Moreover, consolidating demand will allow for saving in time (one person does the task once, rather than lots of people doing the same task and duplicating work).
International sourcing
Bob may find there is value for money in changing suppliers and looking at international sourcing. Often other countries outside of the UK can offer the same products at a lower cost. An example of this is manufactured goods from Chin
a. By looking at international supply chains, Bob may be able to make cost-savings for ABC. He should be sure that when using this technique there is no compromise on quality.
Whole Life Costing methodology
This is a technique Bob can use for procuring capital expenditure items for ABC. This involves looking at the costs of the item throughout its lifecycle and not just the initial purchase price. For example, if Bob needs to buy a new delivery truck he should consider not only the price of the truck, but also the costs of insurance for the truck, how expensive it is to buy replacement parts such as tyres and the cost of disposing of the truck once it reaches the end of its life. By considering these factors Bob will ensure that he buys the truck that represents the best value for money long term.
In conclusion Bob should ensure he uses these four techniques for all items he and his team procures in the future. This will ensure ABC Ltd are always achieving value for money, and thus remain competitive in the marketplace.
Tutor Notes
-This case study is really short, and the ones you’ll receive in the exam are often longer and give you more guidance on what they’re expecting you to write. With case study questions, you have to make your entire answer about Bob. So don’t bring in examples from your own experience, rather, focus on giving examples for Bob.
-A good rule of thumb for case study questions is make sure you reference the case study once per paragraph.
-Value for Money is a really broad topic and you can pretty much argue anything that procurement does is helping to achieve value for money. There’s a large table of stuff that’s considered VFM on
p.38 but that table isn’t exhaustive. So feel free to come up with your own ideas for this type of essay.
Some additional tidbits of information on VFM:
-The ‘academic’ definition of Value for Money is ‘the optimum combination of whole life cost and the quality necessary to meet the customer’s requirement’
-Value for Money is an important strategic objective for most organisations but particularly in the public sector. This is because the public sector is financed by public money (taxes), so they must demonstrate that the organisation is using this money wisely. This might be an interesting fact to put into an essay on VFM.
-Value can often be hard to quantify, particularly in the service industry. E.g. in customer service it can be difficult to quantify the value of having knowledgeable and polite employees delivering the service.
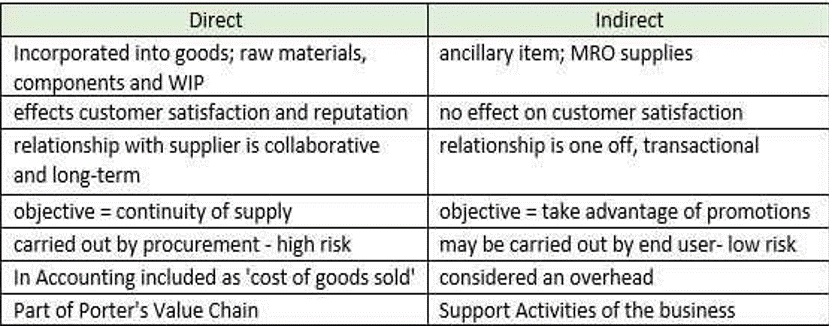
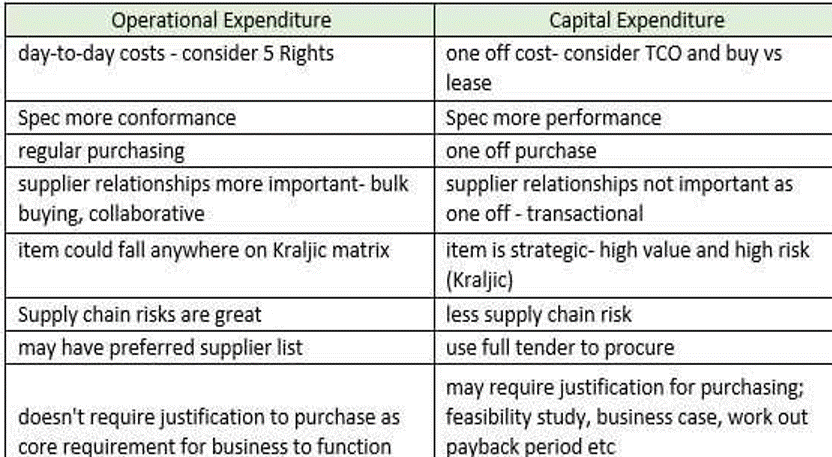
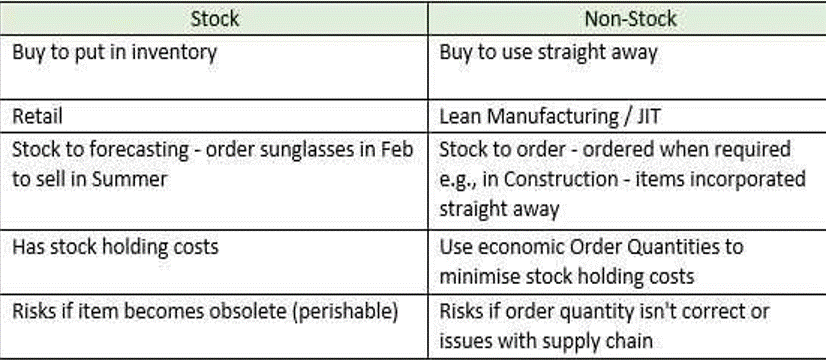
Explain, with examples, the three different ways one can categorise procurement spend: direct vs indirect, capital expenditure vs operational expenditure and stock vs non-stock items. (25 points)
Essay Plan :
Remember to include examples for each of the six categories of spend. This is specifically asked for in the question so it’s important to include as many examples as you can. To do this you could take an example organisation such as a cake manufacturer and explain which of their purchases would fall into each category and why.
Introduction C explain why procurement categorises spend
-Direct C these are items that are incorporated into the final goods (the cakes) so would include raw materials such as flour, eggs, sugar etc
-Indirect C these are items that the company needs, but don’t go into the end product. For example, cleaning products and MRO supplies for the machines
-Capital Expenditure- these are large one-off purchases, such as buying a new piece of equipment such as a giant oven to cook the cakes.
-Operational Expenditure C these are purchases that are required to ensure the business can function day-to-day. They may include PPE for the workers in the factory and cleaning equipment
-Stock items C these are items procured in advance and held in inventory until they are needed. In a cake manufacturing factory this could be PPE for staff such as hairnets and gloves. The organisation will buy these in bulk and keep them in a stock cupboard, using these as and when they are required
-Non- stock items – items that are not stored and used right away. An example would be eggs- these will need to be put directly into the cakes as they would go off if bought in advance.
Conclusion C the categories are not mutually exclusive C an item can be direct and operational, or indirect and stock. Different companies may use different systems to classify items of spend.
Example Introduction and Conclusion Introduction
Procurement categorizes spend to efficiently manage resources and make strategic decisions. Three primary ways of categorizing procurement spend include distinguishing between direct and indirect spend, classifying expenditures as capital or operational, and categorizing items as stock or non- stock. These distinctions aid organizations in optimizing their procurement strategies for better resource allocation.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, categorizing procurement spend into direct vs. indirect, capital vs. operational, and stock vs. non-stock items is essential for strategic resource management. While these categories provide a structured framework, they are not mutually exclusive, as an item can fall into multiple categories. For example, an item may be both direct and operational or indirect and stock. The flexibility of these categories allows organizations to tailor their procurement strategies based on their specific needs, ensuring efficient resource allocation and effective supply chain management. Different companies may adopt varying categorization approaches depending on their industry, size, and operational requirements.
Tutor notes:
-Because you’ve got 6 categories of spend to talk about you’re only going to need 3-4 sentences for each. Providing you’ve said the category, explained what it is and given one example, you’ll absolutely fly through this type of question
-You could also mention that it is useful to use categories of spend as this helps with budgeting. Different categories may also have different processes to follow for procuring the item (this could form part of your introduction or conclusion).
This subject is LO 1.3.2 it’s quite spread out in the text book but the main info is on p.49
Note- different companies/ industries classify items of spend differently. Particularly packaging and salaries. Some say they’re direct costs and some say they’re indirect costs. Honestly, it’s a hotly debated subject and I don’t think there is a right or wrong. I’d just avoid those two examples if you can and stick to ones that aren’t as contentious like eggs and PPE.
Describe the main characteristics of, and differences between, procuring goods, services and construction works (25 points)
2-3 characteristics of each, and 3 differences for a good score.
– Characteristics of goods: tangible, homogeneous, items tend not to perish quickly, can be stored
– Characteristics of services: intangible, heterogenous, inseparable (produced and consumed at the same time), no transfer of ownership, perish upon use (i.e. cannot be stored)
– Characteristics of construction work: project-based procurement, includes procuring both goods and services, complex procurement which has its own set of regulations (CDM2015).
– Differences between these
1)goods are not usually outsourced and services can be.
2)Complexity of the supply chain (goods and construction may have a complex supply chains, but service contracts usually only involve 2 parties).
3)Timescales C construction work has a designated timescale but procurement of goods could be a one off or long-term contract, services is usually a long-term contract.
Example Essay Introduction:
Procurement is a multifaceted field, and understanding the nuances between procuring goods,services, and construction works is pivotal for effective management. This essay explores the main characteristics that differentiate these categories.
Tangible / Intangible:
Goods are tangible items that can be physically seen and touched. For instance, raw materials like wheat and sugar in a manufacturing organization are tangible goods. On the other hand, services are intangible―though the results can be observed, the service itself cannot be touched. An example is a cleaning contract for a factory; while the effects of the cleaning are visible, the service itself remains intangible. Construction is usually a mixture of tangible and intangible procurement; the tangible is the construction materials such as bricks and windows, and the intangible aspect is the labour to complete the project.
Heterogeneous / Homogeneous:
Goods are generally homogeneous, meaning they are always the same. For example, steel purchased for manufacturing purposes will always be the same. In contrast, services are heterogeneous, varying each time they are rendered. Customer service, for instance, is inherently different each time due to the dynamic nature of customer interactions. Construction could be either heterogeneous or homogeneous depending on the project C is it a one off unique building, or is it a large housing estate of same-build properties?
Transfer of Ownership:
When goods are procured, there is a transfer of ownership. The product becomes the property of the buyer upon delivery and payment. In contrast, services do not involve a transfer of ownership as there is no physical entity to transfer. In construction the transfer of ownership is extremely complex and varies depending on the project. Usually the buyer will retain ownership of the land throughout the project, but on some occasions the construction company may take ownership for insurance purposes.
Storable (Separable/ Inseparable):
Goods are storable, allowing for purchase on one day and use on another. For example a factory can buy in plastic to be used to manufacture toys and this is stored in inventory until the time comes to make the toys. However, services are consumed at the point of purchase, making them inseparable. The service is bought and utilized simultaneously. Services cannot be stored. This is the same for construction.
Ability to Outsource:
Goods are rarely outsourced, as they are typically purchased directly from suppliers. Services, on the other hand, can be easily outsourced―examples include outsourcing finance, cleaning, or security services. Construction works are commonly outsourced, with external companies hired to execute projects.
Complexity of the Supply Chain:
Service contracts often involve a simple two-party relationship between the buyer and the supplier. Goods and construction, however, may have complex supply chains. For example, procuring a pen involves a supply chain with various steps, including the raw material supplier, manufacturer, and possibly a wholesaler. Construction works often feature a tiered supply chain with subcontractors playing crucial roles.
Construction as a Hybrid:
Construction procurement represents a hybrid, incorporating elements of both goods and services. It involves hiring a service, such as a bricklayer for laying bricks, while also procuring the tangible goods―bricks. Separating goods from services in construction is challenging, as they are often intertwined, and both aspects are paid for simultaneously.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, distinguishing between the procurement of goods, services, and construction works is essential for effective supply chain management. The tangible or intangible nature, heterogeneity, transfer of ownership, storability, outsourcing potential, and supply chain complexities offer a comprehensive framework for understanding the unique characteristics of each category.
Recognizing these distinctions empowers organizations to tailor their procurement strategies to the specific challenges and dynamics associated with goods, services, and construction works.
Tutor Notes
-What a characteristic is can also be a difference. So for example you can say tangible is a characteristic of goods but tangibility is also the main difference between goods and services. So don’t worry too much about which order to write stuff in, or doing clear sections for this type of essay. It all comes out in the wash.
-Other differences in procuring these include:
-Costs: procuring goods such as stationary for an office will be low-cost so may not require approval, but a service contract may require management sign off. Procuring construction projects tend to be huge sums of money
-Where the budget comes from: goods and services may be operational expenditure and construction works capital expenditure.
-The level of risk involved in the procurement: goods tends to be quite low risk and construction high risk.
-Types of contract involved: procuring goods may be very simple and just require a PO, services is more complex so may require a formal contract or Deed of Appointment. Construction projects will require a contract due to the high value and high risk of the purchase
-Legislation C Goods = Sale of Goods Act, Construction – CDM Regulations 2015. Construction is much more heavily regulated than services or goods. Note CDM regulations isn’t part of CIPS. It’s occasionally referenced in various modules but you don’t have to really know what it is. Just know it’s the main legislation governing the construction indust
Provide a definition of a stakeholder (5 points) and describe 3 categories of stakeholders (20 points).
Definition of Stakeholder- someone who has a ‘stake’ or interest in the company. A person or organisation who influences and can be influenced by the company.
Categories of stakeholders:
1)Internal Stakeholders- these people work inside the company e.g. employees, managers etc
2)Connected- these people work with the company e.g. suppliers, mortgage lenders
3)External Stakeholders C these people are outside of the company e.g. the government, professional bodies, the local community.
Example Essay:
A stakeholder is an individual, group, or entity that has a vested interest or concern in the activities, decisions, or outcomes of an organization or project. Stakeholders are those who can be affected by or can affect the organization, and they play a crucial role in influencing its success, sustainability, and reputation. Understanding and managing stakeholder relationships is a fundamental aspect of effective organizational governance and decision-making and there are several different types of stakeholders.
Firstly, internal stakeholders are those individuals or groups directly connected to the daily operations and management of the organization. Internal stakeholders are key to success and are arguably more vested in the company succeeding. They may depend on the company for their income / livelihood. Anyone who contributes to the company’s internal functions can be considered an internal stakeholder for example:
This category includes
1)Employees: With a direct influence on the organization’s success, employees are critical internal stakeholders. Their engagement, satisfaction, and productivity impact the overall performance.
2)Management and Executives: The leadership team has a significant influence on the organization’s strategic direction and decision-making. Their decisions can shape the company’s future.Secondly, connected stakeholders are those individuals or groups whose interests are tied to the organization but may not be directly involved in its day-to-day operations. Connected stakeholders work alongside the organisation and often have a contractual relationship with the organisation. For example, banks, mortgage lenders, and suppliers. These stakeholders have an interest in the business succeeding, but not as much as internal stakeholders. It is important to keep these stakeholders satisfied as the organisation does depend on them to some extent. For example, it is important that the organisation has a good relationship with their bank / mortgage provider/ supplier as failing to pay what they owe may result in the stakeholders taking legal action against the organisation.
This category includes:
1)Shareholders/Investors: Holding financial stakes in the organization, shareholders seek a return on their investment and have a vested interest in the company’s financial performance.
2)Suppliers and Partners: External entities providing goods, services, or collaboration. Their relationship with the organization impacts the quality and efficiency of its operations.
Lastly external stakeholders are entities outside the organization that can influence or be influenced by its actions. This category includes anyone who is affected by the company but who does not contribute to internal operations. They have less power to influence decisions than internal and connected stakeholders. External stakeholders include the government, professional bodies, pressure groups and the local community. They have quite diverse objectives and have varying ability to influence the organisation. For example, the government may be able to influence the organisation by passing legislation that regulates the industry but they do not have the power to get involved in the day-to-day affairs of the company. Pressure groups may have varying degrees of success in influencing the organisation depending on the subject matter. This category includes:
1)Customers: With a direct impact on the organization’s revenue, customers are vital external stakeholders. Their satisfaction and loyalty are crucial for the company’s success.
2)Government and Regulatory Bodies: External entities overseeing industry regulations. Compliance with these regulations is crucial for the organization’s reputation and legal standing.
In conclusion, stakeholders are diverse entities with a vested interest in an organization’s activities.
The three categories―internal, connected and external ―encompass various groups that significantly influence and are influenced by the organization. Recognizing and addressing the needs and concerns of stakeholders are vital for sustainable and responsible business practices.
Tutor Notes
-The above essay is pretty short and to the point and would pass. If you want to beef out the essay you can include some of the following information for a higher score:
-Stakeholders can be harmed by, or benefit from the organisation (can affect and be affected by the organisation). For example a stakeholder can be harmed if the organisation becomes involved in illegal or immoral practices- e.g. the local community can suffer if the organisation begins to pollute the local rivers. The local community can also benefit from the organisation through increased employment levels.
-CSR argues organisations should respect the rights of stakeholder groups
-Stakeholders are important because they may have direct or indirect influence on decisions
-The public sector has a wider and more complex range of stakeholders as they’re managed on behalf of society as a whole. They’re more likely to take a rage of stakeholder views into account when making decisions. However, these stakeholders are less powerful C i.e. they can’t threaten market sanctions, to withdraw funding, or to quit the business etc.
-The essay doesn’t specifically ask you to Map Stakeholders, but you could throw in a cheeky mention of Mendelow’s Stakeholder Matrix, perhaps in the conclusion. Don’t spend time describing it though- you won’t get more than 1 point for mentioning it. You’d be better off spending your time giving lots and lots of examples of different types of stakeholders.
-Study guide p. 58
What is meant by Stakeholder Mapping? Describe a tool that can be used by a Procurement Professional to map the stakeholders at their organisation (25 points)
-Describe a Stakeholder mapping tool C the most common tool is Mendelow’s Stakeholder Matrix so I would recommend using this one. It is explained in detail in the study guide. However, the question is open so you could choose to describe another tool such as Edgar’s Stakeholder Position Analysis if you so wished. You wouldn’t be wrong choosing this, but honestly, I’d just go for Mendelow. You can’t go wrong with Mendelow. Because the Matrix has 4 sections you can imagine you’d get 5 points for the definition of stakeholder mapping, and 5 points for each of the quadrants of the matrix.
Essay Plan:
Introduction – The reason why stakeholder mapping is important is because interests and expectations of stakeholder groups will be different and possibly conflicting. Mapping this allows an organisation to see the variety and decide on an appropriate management style for each stakeholder group.
Paragraph 1 – Mendelow’s Power / Interest Matrix maps stakeholders based on their influencing power and the strength of their motivation to use that power. It uses a 2×2 grid and defines power as high or low and interest and high or low. It then provides four strategies for managing the stakeholders based on which quadrant of the grid the stakeholder falls into. These 4 categories are: Paragraph 2 – Keep satisfied C high power but low interest. If the stakeholder becomes dissatisfied or concerned their interest may peak. Examples include regulatory bodies, shareholders, senior management. The best approach is to keep them up to date so they are informed of what is going on, but do not burden them with information they do not need.
Paragraph 3 – Manage Closely C AKA Key players C includes major customers, key suppliers, partners, senior management. These stakeholders need to know everything that is going on and approve of what is going on. The recommended strategy is early involvement and participation, and integrating their goals with yours. This group requires regular communication and meetings. You should take their opinions on board.
Paragraph 4- Monitor C minimum effort required C this is the low priority group as they have low power and low interest. Includes small volume suppliers and other organisational functions with no direct interest in your activities. This group does not need to receive regular communication.
Paragraph 5 – Keep informed – high interest, but low power. If they’re not kept in the loop and understand the need for decisions, they may lobby together to protect their interest if they feel threatened. Employee groups, suppliers and community groups may be in this category. This group should receive regular communication.
Conclusion – Mendelow created the matrix in 1991 and it is still used today. It is a popular management tool due to its simplicity. It’s important to notes that stakeholders can move through the matrix- it isn’t stagnant. For example, at the beginning of a project a manager in another department may be classed as ‘low priority’ because they are seen to have no interest and no power in the project. However, as the project progresses the manager may become interested. They will then transfer into the keep informed category. Therefore, the matrix should be redone regularly throughout the lifetime of a project to capture any movements. The matrix should also be redone for each individual project C it cannot be assumed that a stakeholder who had interest in one project would be interested in another.
Tutor Notes
-The above essay plan is basically the entire essay, I got carried away. The only thing you’d need to add into that is an example of a stakeholder for each of the sections! (e.g. the CEO is high power, but low interest stakeholder for the procurement department. He/ She doesn’t care about the day to day operations but should be kept informed of any big news). For your examples you could use your own place of work.
-At level 4 you don’t have to analyse the model, you just have to be able to memorise it and repeat it. Mendelow comes up again at Level 5 and 6 in a bit more detail. If you want to score super bonus points you could mention in your conclusion that the main disadvantage of Mendelow’s Matrix is that it doesn’t take into consideration the stakeholder’s position on the project C whether they’re for it or against it. Therefore, it doesn’t provide the full picture or provide much help on how to manage stakeholders. E.g. two stakeholders might both be in ‘manage closely’ section, but one is for the project and the other against C they’d need to be handled very differently!
Sarah has recently been hired as the new Head of Procurement at Alpha Ltd, a manufacturer of small electronics such as hairdryers and alarm clocks. Alpha Ltd has a large factory based in Birmingham where many of the products are manufactured. One of the large pieces of machinery in the factory has recently broken and Sarah has been charged with replacing it as quickly as possible. Sarah is considering using the Whole Life Costing approach to this procurement. What is meant by Whole Life Costing? (5 points). Discuss 5 factors that Sarah should consider when buying new machinery (20 points).
-I’d use clear headings with numbers for this one. It asks you for a definition and 5 factors. Number them. Makes it easy for you to write and easy for the examiner to mark.
-Don’t go over 5 C you won’t get any extra points for this. So spend your time giving examples and explaining the 5 well, rather than naming more than 5.
Example Essay
As the new Head of Procurement at Alpha Ltd, Sarah faces the urgent task of replacing a critical piece of machinery in the company’s Birmingham factory. Recognizing the complexity of the decision, Sarah contemplates utilizing the Whole Life Costing approach to ensure a comprehensive evaluation that goes beyond initial expenses. This essay explores the concept of Whole Life Costing and delves into five essential factors Sarah should consider when procuring new machinery.
Definition:
Whole Life Costing (WLC) is a procurement approach that considers the total cost associated with an asset throughout its entire lifecycle. Unlike traditional procurement methods that focus primarily on the initial purchase price, WLC evaluates all costs incurred from acquisition to disposal. This includes operational, maintenance, and disposal costs, providing a holistic perspective on the true financial impact of an asset over time.
Factors to Consider in Machinery Procurement
1)Initial Purchase Price:
While WLC looks beyond the initial cost, the purchase price remains a critical factor. Sarah should balance the upfront expense with the long-term costs to ensure the initial investment aligns with the overall financial strategy.
2)Operational Costs:
Sarah needs to analyze the ongoing operational costs associated with the new machinery. This includes energy consumption, routine maintenance, and potential repair expenses. Opting for energy-efficient and reliable equipment can contribute to substantial operational savings over the machine’s lifespan, even though this may result in a higher up-front purchase price
3)Training and Integration:
The cost of training employees to operate and maintain the new machinery is a significant consideration. Sarah should assess how easily the equipment integrates into existing workflows and whether additional training programs are required, impacting both immediate and long-term costs.
4)Downtime and Productivity:
Evaluating the potential downtime and its impact on productivity is crucial. Sarah should assess the reliability and historical performance of the machinery to gauge its potential contribution to sustained production levels and minimized disruptions, impacting the overall operational efficiency.
5)Technology Upgrades and Adaptability:
Sarah should consider the machinery’s adaptability to technological advancements and potential upgrades. Investing in equipment that allows for seamless integration with future technologies ensures that Alpha Ltd remains competitive and resilient in a rapidly evolving industry landscape.
In conclusion, adopting a Whole Life Costing approach empowers Sarah to make informed decisions that align with Alpha Ltd’s strategic goals. By considering factors beyond the initial purchase price, such as operational costs, training, downtime, and technology adaptability, Sarah ensures that the replacement machinery not only meets immediate production needs but proves to be a cost- effective and efficient asset throughout its entire lifecycle. The WLC approach safeguards against unforeseen financial burdens, fostering sustainable and informed procurement practices in the dynamic manufacturing environment.
Tutor Notes
-Whole Life Costing is on p.28
-Total Life Cycle Costs, Total Cost of Ownership and Life Cycle Costs are all practically the same thing. The book says they’re slightly different, but don’t get yourself bogged down in trying to remember the differences. Honestly, in the real world, people use this language interchangeably.
-Other factors you could have chosen to talk about include commissioning costs and disposal costs
-Don’t worry if you feel CIPS breezed
Latest L4M1 Dumps Valid Version with 40 Q&As
Latest And Valid Q&A | Instant Download | Once Fail, Full Refund

