CIMA CIMAPRA17-BA2-1-ENG BA2 – Fundamentals of Management Accounting (2017 SYLLABUS) (Online) Online Training
CIMA CIMAPRA17-BA2-1-ENG Online Training
The questions for CIMAPRA17-BA2-1-ENG were last updated at Apr 24,2025.
- Exam Code: CIMAPRA17-BA2-1-ENG
- Exam Name: BA2 - Fundamentals of Management Accounting (2017 SYLLABUS) (Online)
- Certification Provider: CIMA
- Latest update: Apr 24,2025
In the process account, the accounting treatment of the value of the abnormal loss is:
- A . Credit Process account Debit Abnormal Loss account
- B . Debit Process account Credit Abnormal Loss account
- C . Credit Process account Debit Normal Loss account
- D . Debit Process account Credit Normal Loss account
A company can increase its margin of safety by which of the following independent actions?
(a) Increasing sales and production
(b) Raising the selling price per unit
(c) Raising the variable cost per unit
(d) Lowering fixed costs
- A . (a) and (b) only
- B . (a), (b) and (c) only
- C . (a), (b) and (d) only
- D . (a), (c) and (d) only
CORRECT TEXT
Refer to the Exhibit.

A company operates a batch costing system.
Production overhead costs are absorbed into the cost of batches using a direct labour hour rate. Other overhead costs are absorbed at a rate of 20% of total production cost. The company adds a mark-up of 10% to total cost in order to derive its selling prices.
Budgeted production overheads for the period are $44,000 and the budgeted level of activity is 8,800 direct labour hours.
The following data are available for batch number 309:
The required selling price per unit (to two decimal places) is:
Within a relevant range of output, the variable cost per unit of output will:
- A . Increase as output increases
- B . Reduce as output increases
- C . Remain constant as output increases
- D . Be impossible to tell without further information
In investment appraisal, the internal rate of return is
- A . the target rate of return for all investment proposals
- B . the rate at which a project’s cash inflows is equal to its cash outflows
- C . the rate at which the present value of a project’s cash inflows is zero
- D . the rate at which the present value of a project’s cash inflows is equal to the present value of its cash outflows
Prime cost is:
- A . Total product cost minus overheads
- B . The material cost of the product
- C . The cost of operating a cost centre
- D . All costs incurred in making a product
CORRECT TEXT
Refer to the exhibit.
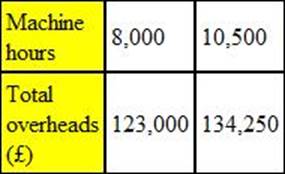
The following data relates to two activity levels of a department. Overhead absorption is on the basis of machine hours.
The variable overhead rate per hour is £4.50. The amount of fixed overhead, to the nearest £000, is:
CORRECT TEXT
Refer to the exhibit.
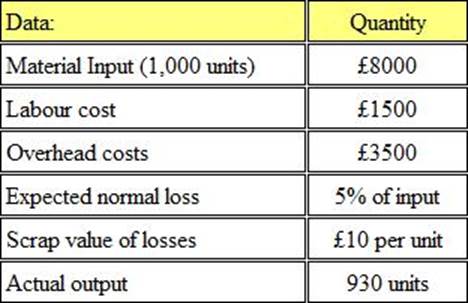
The following information is available for a production process:
The cost per unit of good output is:
Give your answer to 2 decimal places.
Fixed costs can best be described as:
- A . Costs which are difficult to budget accurately
- B . Costs which remain constant, within a relevant range, when activity levels change
- C . Costs which never change
- D . Costs which are uncontrollable
Refer to the exhibit.
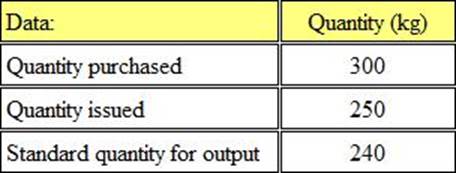
Xell Ltd uses a standard costing system and therefore values all inventory at standard cost.
During period 3 the price paid for material ‘A’ was £6 per kg less than the standard price.
The following information for material ‘A’ relates to period 3:
What was the material price variance for period 3?
- A . £6 Favourable
- B . £60 Favourable
- C . £1500 Favourable
- D . £1800 Favourable
Latest CIMAPRA17-BA2-1-ENG Dumps Valid Version with 392 Q&As
Latest And Valid Q&A | Instant Download | Once Fail, Full Refund

