CIMA CIMAPRA17-BA2-1-ENG BA2 – Fundamentals of Management Accounting (2017 SYLLABUS) (Online) Online Training
CIMA CIMAPRA17-BA2-1-ENG Online Training
The questions for CIMAPRA17-BA2-1-ENG were last updated at Dec 20,2025.
- Exam Code: CIMAPRA17-BA2-1-ENG
- Exam Name: BA2 - Fundamentals of Management Accounting (2017 SYLLABUS) (Online)
- Certification Provider: CIMA
- Latest update: Dec 20,2025
An increase in the selling price per unit, will cause the point at which the line plotted on a profit/volume (PV) graph intersects the horizontal axis to:
- A . Move to the left
- B . Move to the right
- C . Double
- D . Stay where it is
A company currently allows a discount of 20% to customers who pay at the time of purchase.
If 30% of customers pay immediately, the extra sales needed in July to increase the cash receipts in that month by £6,000 are:
- A . £7500
- B . £20000
- C . £25000
- D . £30000
Refer to the exhibit.
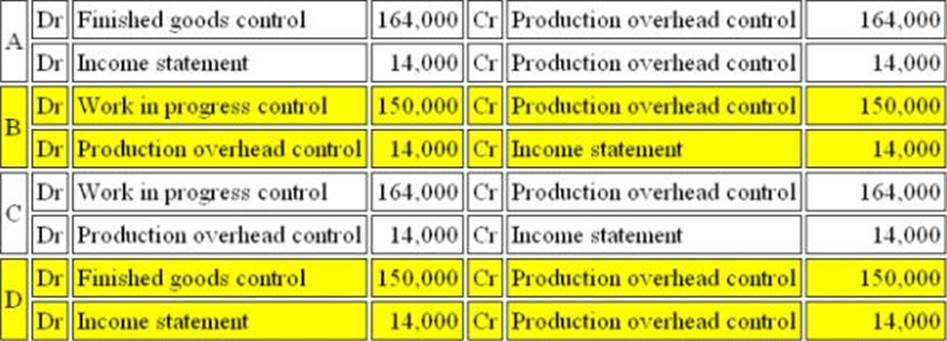
WS operates an integrated accounting system.
Transactions relating to production overheads for the month of May were as follows:
Indirect Material costs were $15,000
Indirect Labour Costs were $45,000
Production overheads of $58,000 were incurred during the period.
Depreciation of factory machinery amounted to $32,000.
Overheads costs absorbed by production using a standard absorption rate was $164,000 for the period.
What are the correct entries to record the absorption of production overheads for the period?
The correct set of entries to record the absorption of production overheads for the period is:
- A . A
- B . B
- C . C
- D . D
Refer to the exhibit.

SP, a manufacturing company, uses a standard costing system.
The standard variable production overhead cost is based on the following budgeted figures for the year:
During the month of September, 5,300 actual hours were worked and 5,600 standard hours of output were produced. Total variable production overhead costs in September were $8,600.
What was the total variable production overhead variance in September?
- A . $200 adverse
- B . $650 adverse
- C . $650 favourable
- D . $200 favourable
PQR Manufacturing Ltd. has £3,000,000 of fixed costs for the forthcoming period. The company produces a single product ‘X’, which has a selling price of £75 per unit and total cost of £50.
75% of the total cost represents variable costs.
What are the break-even units?
- A . 80,000
- B . 240,000
- C . 120,000
- D . 40,000
Eton Ltd. operates a manufacturing process that produces product A.
Information for this process last month is as follows:
(a) Opening work in progress – 2,500 kg valued at £2,000 for direct material and £1,500 for labour and overheads.
(b) Materials input – 25,000 kg at £2.10 per kg.
(c) Labour – £10,000
(d) Overheads – £5,000
(e) Output during the month – 20,000 kg.
(f) There were 7,500 units of closing work in progress which was complete as to materials and 30% complete as to conversion.
(g) Normal loss for the month was 3% of input and all losses have a scrap value of £1 per kg.
What was the average cost per kg of finished output during the month?
- A . £1.73
- B . £2.72
- C . £2.78
- D . £2.80
Refer to the Exhibit.
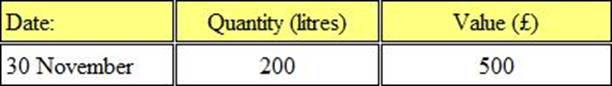
Fabex Ltd manufactures a household detergent called "Clear".
The standard data for one of the chemicals used in production (chemical XTC) is as follows:
(a) 50 litres used per 100 litres of ‘Clear’ produced
(b) Budgeted monthly production is 1000 litres of ‘Clear’.
The closing inventory of chemical XTC for November valued at standard price was as follows:
Actual results for the period during December were as follows:
(a) 500 litres of chemical XTC was purchased for £1300.
(b) 550 litres of chemical XTC was used.
(c) 900 litres of ‘Clear’ was produced.
It is company policy to extract the material price variance at the time of purchase.
What is the total direct material price variance (to the nearest whole number)?
- A . £50 adverse
- B . £50 favourable
- C . £55 adverse
- D . £55 favourable
In the process account, the accounting treatment of the value of the abnormal gain is:
- A . Credit Process account Debit Abnormal Gain account
- B . Debit Process account Credit Abnormal Gain account
- C . Credit Process account Debit Normal Loss account
- D . Debit Process account Credit Normal Loss account
CORRECT TEXT
Each unit of product GM requires 4 labour hours to be produced. 25% of the units will be completed during overtime hours.
Sales of 24,000 units are planned and finished goods inventory is budgeted to rise by 2,000 units.
If the wage rate is £6 per hour and the overtime premium is 50%, what is the budgeted labour cost?
Refer to the exhibit.
![]()
T operates a process costing system. Data is available for Process A for the month of July.
Inputs for the month:
Normal losses are 15% of input and can be sold for $6 per kg. Actual output was 2,600 kg.
There is no opening or closing work in progress for the period.
What is the value of the output from the process in the month?
- A . $49,291
- B . $46,538
- C . $43,784
- D . $45,120
Latest CIMAPRA17-BA2-1-ENG Dumps Valid Version with 392 Q&As
Latest And Valid Q&A | Instant Download | Once Fail, Full Refund

