CFA Institute CFA Level 3 CFA Level 3 Exam Online Training
CFA Institute CFA Level 3 Online Training
The questions for CFA Level 3 were last updated at Mar 07,2025.
- Exam Code: CFA Level 3
- Exam Name: CFA Level 3 Exam
- Certification Provider: CFA Institute
- Latest update: Mar 07,2025
Hilda Olson covers the chemical industry for Bern Securities. Based on conversations with two executives of InterChem, a major producer of synthetic fabrics, she issues a generalized sector report claiming that "according to a survey of industry executives, rayon feedstocks will be in short supply for at least the next 12 months." In addition, Olson recommends Han Chemical, a major producer of rayon, which has routinely reported higher profits than its competitors and should be well positioned to gain further from reduced supply.
In her efforts to learn more about Han Chemical and support her recommendation, Olson scrambles to compile a research report on the firm. She reproduces financial data provided in a research report by Standard & Poor’s (S&P) and the Bank of Korea (BOK), the Korean government’s central bank. She also obtains two research reports from brokerage firms with operations in Korea, and incorporates portions of the text and charts from these reports into her research report.
Olson describes Han Chemical in her research report as "low risk," even though she knows that the operating risk of the chemical industry is above average and that Han has a higher debt-to-equity ratio than its average competitor. She justifies this to her supervisor by saying that since the market for rayon feedstocks is tight, an investment in Han has a very low risk of suffering a loss in the near term. Olson’s supervisor accepts her explanation as valid and the report is issued to the firm’s clients.
Shortly after issuing her research report, Olson visited Han Chemical’s operations in New Jersey. During her conversation with the firm’s vice president of operations, who is also one of Bern’s personal trust clients, she was told in confidence that Han Chemical’s profit margins are higher than its competitors, partly because they routinely discharge untreated chemical waste into the Delaware River in order to reduce production costs. Such action is a direct violation of U.S. environmental laws.
When Olson returns from her trip to New Jersey, Wolfgang Hundt, director of research at Bern Securities, requests a meeting. Hundt has developed a compliance procedure and has provided relevant written information to employees. Every quarter, he issues written reminders regarding the program to Olson and her peers, so when Olson tells Hundt of Han’s chemical dumping, he immediately begins an investigation into the violation.
With regard to the statement concerning rayon feedstocks, Olson has:
- A . not violated CFA Institute Standards.
- B . violated CFA Institute Standards since she has failed to use reasonable judgment in gathering her information.
- C . violated CFA Institute Standards since she is not permitted to project supply and demand conditions in the industry.
Hilda Olson covers the chemical industry for Bern Securities. Based on conversations with two executives of InterChem, a major producer of synthetic fabrics, she issues a generalized sector report claiming that "according to a survey of industry executives, rayon feedstocks will be in short supply for at least the next 12 months." In addition, Olson recommends Han Chemical, a major producer of rayon, which has routinely reported higher profits than its competitors and should be well positioned to gain further from reduced supply.
In her efforts to learn more about Han Chemical and support her recommendation, Olson scrambles to compile a research report on the firm. She reproduces financial data provided in a research report by Standard & Poor’s (S&P) and the Bank of Korea (BOK), the Korean government’s central bank. She also obtains two research reports from brokerage firms with operations in Korea, and incorporates portions of the text and charts from these reports into her research report.
Olson describes Han Chemical in her research report as "low risk," even though she knows that the operating risk of the chemical industry is above average and that Han has a higher debt-to-equity ratio than its average competitor. She justifies this to her supervisor by saying that since the market for rayon feedstocks is tight, an investment in Han has a very low risk of suffering a loss in the near term. Olson’s supervisor accepts her explanation as valid and the report is issued to the firm’s clients.
Shortly after issuing her research report, Olson visited Han Chemical’s operations in New Jersey. During her conversation with the firm’s vice president of operations, who is also one of Bern’s personal trust clients, she was told in confidence that Han Chemical’s profit margins are higher than its competitors, partly because they routinely discharge untreated chemical waste into the Delaware River in order to reduce production costs. Such action is a direct violation of U.S. environmental laws.
When Olson returns from her trip to New Jersey, Wolfgang Hundt, director of research at Bern Securities, requests a meeting. Hundt has developed a compliance procedure and has provided relevant written information to employees. Every quarter, he issues written reminders regarding the program to Olson and her peers, so when Olson tells Hundt of Han’s chemical dumping, he immediately begins an investigation into the violation.
In her report on Han Chemical, Olson has utilized data from S&P and the BOK. With regard to this data,
Olson is allowed to use:
- A . both sources of data, but must acknowledge the sources of the data.
- B . both sources of data, and need not acknowledge the sources of the data.
- C . the S&P data, but not the BOK data, and she must acknowledge the source.
Hilda Olson covers the chemical industry for Bern Securities. Based on conversations with two executives of InterChem, a major producer of synthetic fabrics, she issues a generalized sector report claiming that "according to a survey of industry executives, rayon feedstocks will be in short supply for at least the next 12 months." In addition, Olson recommends Han Chemical, a major producer of rayon, which has routinely reported higher profits than its competitors and should be well positioned to gain further from reduced supply.
In her efforts to learn more about Han Chemical and support her recommendation, Olson scrambles to compile a research report on the firm. She reproduces financial data provided in a research report by Standard & Poor’s (S&P) and the Bank of Korea (BOK), the Korean government’s central bank. She also obtains two research reports from brokerage firms with operations in Korea, and incorporates portions of the text and charts from these reports into her research report.
Olson describes Han Chemical in her research report as "low risk," even though she knows that the operating risk of the chemical industry is above average and that Han has a higher debt-to-equity ratio than its average competitor. She justifies this to her supervisor by saying that since the market for rayon feedstocks is tight, an investment in Han has a very low risk of suffering a loss in the near term. Olson’s supervisor accepts her explanation as valid and the report is issued to the firm’s clients.
Shortly after issuing her research report, Olson visited Han Chemical’s operations in New Jersey. During her conversation with the firm’s vice president of operations, who is also one of Bern’s personal trust clients, she was told in confidence that Han Chemical’s profit margins are higher than its competitors, partly because they routinely discharge untreated chemical waste into the Delaware River in order to reduce production costs. Such action is a direct violation of U.S. environmental laws.
When Olson returns from her trip to New Jersey, Wolfgang Hundt, director of research at Bern Securities, requests a meeting. Hundt has developed a compliance procedure and has provided relevant written information to employees. Every quarter, he issues written reminders regarding the program to Olson and her peers, so when Olson tells Hundt of Han’s chemical dumping, he immediately begins an investigation into the violation.
In her report on Han Chemical, Olson has also utilized two brokerage firms’ reports. With regard to these sources, Olson is:
- A . allowed to use the text and charts, but must acknowledge the sources.
- B . allowed to use the text and charts, and need not acknowledge the sources.
- C . not allowed to use the text and charts from other reports.
Hilda Olson covers the chemical industry for Bern Securities. Based on conversations with two executives of InterChem, a major producer of synthetic fabrics, she issues a generalized sector report claiming that "according to a survey of industry executives, rayon feedstocks will be in short supply for at least the next 12 months." In addition, Olson recommends Han Chemical, a major producer of rayon, which has routinely reported higher profits than its competitors and should be well positioned to gain further from reduced supply.
In her efforts to learn more about Han Chemical and support her recommendation, Olson scrambles to compile a research report on the firm. She reproduces financial data provided in a research report by Standard & Poor’s (S&P) and the Bank of Korea (BOK), the Korean government’s central bank. She also obtains two research reports from brokerage firms with operations in Korea, and incorporates portions of the text and charts from these reports into her research report.
Olson describes Han Chemical in her research report as "low risk," even though she knows that the operating risk of the chemical industry is above average and that Han has a higher debt-to-equity ratio than its average competitor. She justifies this to her supervisor by saying that since the market for rayon feedstocks is tight, an investment in Han has a very low risk of suffering a loss in the near term. Olson’s supervisor accepts her explanation as valid and the report is issued to the firm’s clients.
Shortly after issuing her research report, Olson visited Han Chemical’s operations in New Jersey. During her conversation with the firm’s vice president of operations, who is also one of Bern’s personal trust clients, she was told in confidence that Han Chemical’s profit margins are higher than its competitors, partly because they routinely discharge untreated chemical waste into the Delaware River in order to reduce production costs. Such action is a direct violation of U.S. environmental laws.
When Olson returns from her trip to New Jersey, Wolfgang Hundt, director of research at Bern Securities, requests a meeting. Hundt has developed a compliance procedure and has provided relevant written
information to employees. Every quarter, he issues written reminders regarding the program to Olson and her peers, so when Olson tells Hundt of Han’s chemical dumping, he immediately begins an investigation into the violation.
Olson’s characterization of the risks associated with an investment in Han Chemical is:
- A . acceptable since it is clearly an opinion.
- B . acceptable since it is supported with facts regarding industry supply and demand.
- C . unacceptable since she has not provided enough information for investors to assess Han’s risk.
Hilda Olson covers the chemical industry for Bern Securities. Based on conversations with two executives of InterChem, a major producer of synthetic fabrics, she issues a generalized sector report claiming that "according to a survey of industry executives, rayon feedstocks will be in short supply for at least the next 12 months." In addition, Olson recommends Han Chemical, a major producer of rayon, which has routinely reported higher profits than its competitors and should be well positioned to gain further from reduced supply.
In her efforts to learn more about Han Chemical and support her recommendation, Olson scrambles to compile a research report on the firm. She reproduces financial data provided in a research report by Standard & Poor’s (S&P) and the Bank of Korea (BOK), the Korean government’s central bank. She also obtains two research reports from brokerage firms with operations in Korea, and incorporates portions of the text and charts from these reports into her research report.
Olson describes Han Chemical in her research report as "low risk," even though she knows that the operating risk of the chemical industry is above average and that Han has a higher debt-to-equity ratio than its average competitor. She justifies this to her supervisor by saying that since the market for rayon feedstocks is tight, an investment in Han has a very low risk of suffering a loss in the near term. Olson’s supervisor accepts her explanation as valid and the report is issued to the firm’s clients.
Shortly after issuing her research report, Olson visited Han Chemical’s operations in New Jersey. During her conversation with the firm’s vice president of operations, who is also one of Bern’s personal trust clients, she was told in confidence that Han Chemical’s profit margins are higher than its competitors, partly because they routinely discharge untreated chemical waste into the Delaware River in order to reduce production costs. Such action is a direct violation of U.S. environmental laws.
When Olson returns from her trip to New Jersey, Wolfgang Hundt, director of research at Bern Securities, requests a meeting. Hundt has developed a compliance procedure and has provided relevant written information to employees. Every quarter, he issues written reminders regarding the program to Olson and her peers, so when Olson tells Hundt of Han’s chemical dumping, he immediately begins an investigation into the violation.
With regard to the information Olson received from Han Chemical’s Vice President of Operations, the most appropriate course of action for Olson to take would be to:
- A . not divulge such information in her client research since she now lacks independence and objectivity.
- B . divulge the information to her employer because, even though received in confidence, it involves an illegal act.
- C . divulge the information in her client’s research department in order to demonstrate due diligence in performing her research.
Hilda Olson covers the chemical industry for Bern Securities. Based on conversations with two executives of InterChem, a major producer of synthetic fabrics, she issues a generalized sector report claiming that "according to a survey of industry executives, rayon feedstocks will be in short supply for at least the next 12 months." In addition, Olson recommends Han Chemical, a major producer of rayon, which has routinely reported higher profits than its competitors and should be well positioned to gain further from reduced supply.
In her efforts to learn more about Han Chemical and support her recommendation, Olson scrambles to compile a research report on the firm. She reproduces financial data provided in a research report by Standard & Poor’s (S&P) and the Bank of Korea (BOK), the Korean government’s central bank. She also obtains two research reports from brokerage firms with operations in Korea, and incorporates portions of the text and charts from these reports into her research report.
Olson describes Han Chemical in her research report as "low risk," even though she knows that the operating risk of the chemical industry is above average and that Han has a higher debt-to-equity ratio than its average competitor. She justifies this to her supervisor by saying that since the market for rayon feedstocks is tight, an investment in Han has a very low risk of suffering a loss in the near term. Olson’s supervisor accepts her explanation as valid and the report is issued to the firm’s clients.
Shortly after issuing her research report, Olson visited Han Chemical’s operations in New Jersey. During her conversation with the firm’s vice president of operations, who is also one of Bern’s personal trust clients, she was told in confidence that Han Chemical’s profit margins are higher than its competitors, partly because they routinely discharge untreated chemical waste into the Delaware River in order to reduce production costs. Such action is a direct violation of U.S. environmental laws.
When Olson returns from her trip to New Jersey, Wolfgang Hundt, director of research at Bern Securities, requests a meeting. Hundt has developed a compliance procedure and has provided relevant written information to employees. Every quarter, he issues written reminders regarding the program to Olson and her peers, so when Olson tells Hundt of Han’s chemical dumping, he immediately begins an investigation into the violation.
Olson is concerned that Hundt’s compliance actions as director of the firm’s research department are inconsistent with CFA Institute Standards.
Which of the following properly characterize Hundt’s compliance activities? Hundt’s actions are:
- A . consistent with CFA Institute Standards.
- B . improper with respect to both the investigation procedures and the periodic reminders.
- C . improper regarding the periodic reminders, as these do not constitute regular training.
Dynamic Investment Services (DIS) is a global, full-service investment advisory firm based in the United States. Although the firm provides numerous investment services, DIS specializes in portfolio management for individual and institutional clients and only deals in publicly traded debt, equity, and derivative instruments. Walter Fried, CFA, is a portfolio manager and the director of DIS’s offices in Austria. For several years, Fried has maintained a relationship with a local tax consultant. The consultant provides a DIS marketing brochure with Fried’s contact information to his clients seeking investment advisory services, and in return. Fried manages the consultant’s personal portfolio and informs the consultant of potential tax issues in the referred clients’ portfolios as they occur. Because he cannot personally manage all of the inquiring clients’ assets, Fried generally passes the client information along to one of his employees but never discloses his relationship with the tax accountant. Fried recently forwarded information on the prospective Jones Family Trust account to Beverly Ulster, CFA, one of his newly hired portfolio managers.
Upon receiving the information, Ulster immediately set up a meeting with Terrence Phillips, the trustee of the Jones Family Trust. Ulster began the meeting by explaining DIS’s investment services as detailed in the firm’s approved marketing and public relations literature. Ulster also had Phillips complete a very detailed questionnaire regarding the risk and return objectives, investment constraints, and other information related to the trust beneficiaries, which Phillips is not. While reading the questionnaire, Ulster learned that Phillips heard about DIS’s services through a referral from his tax consultant. Upon further investigation, Ulster discovered the agreement set up between Fried and the tax consultant, which is legal according to Austrian law but was not disclosed by either party Ulster took a break from the meeting to get more details from Fried. With full information on the referral arrangement, Ulster immediately makes full disclosure to the Phillips. Before the meeting with Phillips concluded, Ulster began formalizing the investment policy statement (IPS) for the Jones Family Trust and agreed to Phillips’ request that the IPS should explicitly forbid derivative positions in the Trust portfolio.
A few hours after meeting with the Jones Family Trust representative, Ulster accepted another new referral client, Steven West, from Fried. Following DIS policy, Ulster met with West to address his investment objectives and constraints and explain the firm’s services. During the meeting, Ulster informed West that DIS offers three levels of account status, each with an increasing fee based on the account’s asset value. The first level has the lowest account fees but receives oversubscribed domestic IPO allocations only after the other two levels receive IPO allocations. The second-level clients have the same priority as third-level clients with respect to oversubscribed domestic IPO allocations and receive research with significantly greater detail than first-level clients. Clients who subscribe to the third level of DIS services receive the most detailed research reports and are allowed to participate in both domestic and international IPOs. All clients receive research and recommendations at approximately the same lime. West decided to engage DIS’s services as a second-level client. While signing the enrollment papers, West told Ulster, "If you can give me the kind of performance I am looking for, I may move the rest of my assets to DIS." When Ulster inquired about the other accounts, West would not specify how much or what type of assets he held in other accounts. West also noted that a portion of the existing assets to be transferred to Ulster’s control were private equity investments in small start-up companies, which DIS would need to manage. Ulster assured him that DIS would have no problem managing the private equity investments.
After her meeting with West, Ulster attended a weekly strategy session held by DIS. All managers were required to attend this particular meeting since the focus was on a new strategy designed to reduce portfolio volatility while slightly enhancing return using a combination of futures and options on various asset classes. Intrigued by the idea, Ulster implemented the strategy for all of her clients and achieved positive results for all portfolios. Ulster’s average performance results after one year of using the new strategy are presented in Figure 1. For comparative purposes, performance figures without the new strategy are also presented.
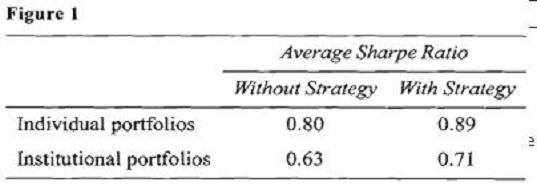
At the latest strategy meeting, DIS economists were extremely pessimistic about emerging market economies and suggested that the firm’s portfolio managers consider selling emerging market securities out of their portfolios and avoid these investments for the next 12 to 15 months. Fried placed a limit order to sell his personal holdings of an emerging market fund at a price 5% higher than the market price at the time. He then began selling his clients’ (all of whom have discretionary accounts with DIS) holdings of the same emerging market fund using market orders. All of his clients’ trade orders were completed just before the price of the fund declined sharply by 13%, causing Fried’s order to remain unfilled.
Did Ulster violate CFA Institute Standards of Professional Conduct by accepting either Phillips or West as new clients?
- A . Standards were violated in accepting both Phillips and West as clients.
- B . There was no violation in accepting Phillips, but there was a violation in accepting West.
- C . There were no Standards violations in accepting either client.
Dynamic Investment Services (DIS) is a global, full-service investment advisory firm based in the United States. Although the firm provides numerous investment services, DIS specializes in portfolio management for individual and institutional clients and only deals in publicly traded debt, equity, and derivative instruments. Walter Fried, CFA, is a portfolio manager and the director of DIS’s offices in Austria. For several years, Fried has maintained a relationship with a local tax consultant. The consultant provides a DIS marketing brochure with Fried’s contact information to his clients seeking investment advisory services, and in return. Fried manages the consultant’s personal portfolio and informs the consultant of potential tax issues in the referred clients’ portfolios as they occur. Because he cannot personally manage all of the inquiring clients’ assets, Fried generally passes the client information along to one of his employees but never discloses his relationship with the tax accountant. Fried recently forwarded information on the prospective Jones Family Trust account to Beverly Ulster, CFA, one of his newly hired portfolio managers.
Upon receiving the information, Ulster immediately set up a meeting with Terrence Phillips, the trustee of the Jones Family Trust. Ulster began the meeting by explaining DIS’s investment services as detailed in the firm’s approved marketing and public relations literature. Ulster also had Phillips complete a very detailed questionnaire regarding the risk and return objectives, investment constraints, and other information related to the trust beneficiaries, which Phillips is not. While reading the questionnaire, Ulster learned that Phillips heard about DIS’s services through a referral from his tax consultant. Upon further investigation, Ulster discovered the agreement set up between Fried and the tax consultant, which is legal according to Austrian law but was not disclosed by either party Ulster took a break from the meeting to get more details from Fried. With full information on the referral arrangement, Ulster immediately makes full disclosure to the Phillips. Before the meeting with Phillips concluded, Ulster began formalizing the investment policy statement (IPS) for the Jones Family Trust and agreed to Phillips’ request that the IPS should explicitly forbid derivative positions in the Trust portfolio.
A few hours after meeting with the Jones Family Trust representative, Ulster accepted another new referral client, Steven West, from Fried. Following DIS policy, Ulster met with West to address his investment objectives and constraints and explain the firm’s services. During the meeting, Ulster informed West that DIS offers three levels of account status, each with an increasing fee based on the account’s asset value. The first level has the lowest account fees but receives oversubscribed domestic IPO allocations only after the other two levels receive IPO allocations. The second-level clients have the same priority as third-level clients with respect to oversubscribed domestic IPO allocations and receive research with significantly greater detail than first-level clients. Clients who subscribe to the third level of DIS services receive the most detailed research reports and are allowed to participate in both domestic and international IPOs. All clients receive research and recommendations at approximately the same lime. West decided to engage
DIS’s services as a second-level client. While signing the enrollment papers, West told Ulster, "If you can give me the kind of performance I am looking for, I may move the rest of my assets to DIS." When Ulster inquired about the other accounts, West would not specify how much or what type of assets he held in other accounts. West also noted that a portion of the existing assets to be transferred to Ulster’s control were private equity investments in small start-up companies, which DIS would need to manage. Ulster assured him that DIS would have no problem managing the private equity investments.
After her meeting with West, Ulster attended a weekly strategy session held by DIS. All managers were required to attend this particular meeting since the focus was on a new strategy designed to reduce portfolio volatility while slightly enhancing return using a combination of futures and options on various asset classes. Intrigued by the idea, Ulster implemented the strategy for all of her clients and achieved positive results for all portfolios. Ulster’s average performance results after one year of using the new strategy are presented in Figure 1. For comparative purposes, performance figures without the new strategy are also presented.
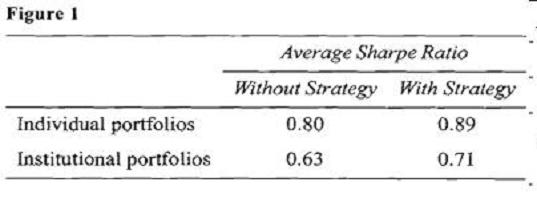
At the latest strategy meeting, DIS economists were extremely pessimistic about emerging market economies and suggested that the firm’s portfolio managers consider selling emerging market securities out of their portfolios and avoid these investments for the next 12 to 15 months. Fried placed a limit order to sell his personal holdings of an emerging market fund at a price 5% higher than the market price at the time. He then began selling his clients’ (all of whom have discretionary accounts with DIS) holdings of the same emerging market fund using market orders. All of his clients’ trade orders were completed just before the price of the fund declined sharply by 13%, causing Fried’s order to remain unfilled.
Does the referral agreement between Fried and the tax consultant violate any CFA Institute Standards of Professional Conduct?
- A . No.
- B . Yes, because client confidentiality is being undermined by the arrangement.
- C . Yes, because it involves non-monetary compensation with no observable cost.
Dynamic Investment Services (DIS) is a global, full-service investment advisory firm based in the United States. Although the firm provides numerous investment services, DIS specializes in portfolio management for individual and institutional clients and only deals in publicly traded debt, equity, and derivative instruments. Walter Fried, CFA, is a portfolio manager and the director of DIS’s offices in Austria. For several years, Fried has maintained a relationship with a local tax consultant. The consultant provides a
DIS marketing brochure with Fried’s contact information to his clients seeking investment advisory services, and in return. Fried manages the consultant’s personal portfolio and informs the consultant of potential tax issues in the referred clients’ portfolios as they occur. Because he cannot personally manage all of the inquiring clients’ assets, Fried generally passes the client information along to one of his employees but never discloses his relationship with the tax accountant. Fried recently forwarded information on the prospective Jones Family Trust account to Beverly Ulster, CFA, one of his newly hired portfolio managers.
Upon receiving the information, Ulster immediately set up a meeting with Terrence Phillips, the trustee of the Jones Family Trust. Ulster began the meeting by explaining DIS’s investment services as detailed in the firm’s approved marketing and public relations literature. Ulster also had Phillips complete a very detailed questionnaire regarding the risk and return objectives, investment constraints, and other information related to the trust beneficiaries, which Phillips is not. While reading the questionnaire, Ulster learned that Phillips heard about DIS’s services through a referral from his tax consultant. Upon further investigation, Ulster discovered the agreement set up between Fried and the tax consultant, which is legal according to Austrian law but was not disclosed by either party Ulster took a break from the meeting to get more details from Fried. With full information on the referral arrangement, Ulster immediately makes full disclosure to the Phillips. Before the meeting with Phillips concluded, Ulster began formalizing the investment policy statement (IPS) for the Jones Family Trust and agreed to Phillips’ request that the IPS should explicitly forbid derivative positions in the Trust portfolio.
A few hours after meeting with the Jones Family Trust representative, Ulster accepted another new referral client, Steven West, from Fried. Following DIS policy, Ulster met with West to address his investment objectives and constraints and explain the firm’s services. During the meeting, Ulster informed West that DIS offers three levels of account status, each with an increasing fee based on the account’s asset value. The first level has the lowest account fees but receives oversubscribed domestic IPO allocations only after the other two levels receive IPO allocations. The second-level clients have the same priority as third-level clients with respect to oversubscribed domestic IPO allocations and receive research with significantly greater detail than first-level clients. Clients who subscribe to the third level of DIS services receive the most detailed research reports and are allowed to participate in both domestic and international IPOs. All clients receive research and recommendations at approximately the same lime. West decided to engage DIS’s services as a second-level client. While signing the enrollment papers, West told Ulster, "If you can give me the kind of performance I am looking for, I may move the rest of my assets to DIS." When Ulster inquired about the other accounts, West would not specify how much or what type of assets he held in other accounts. West also noted that a portion of the existing assets to be transferred to Ulster’s control were private equity investments in small start-up companies, which DIS would need to manage. Ulster assured him that DIS would have no problem managing the private equity investments.
After her meeting with West, Ulster attended a weekly strategy session held by DIS. All managers were required to attend this particular meeting since the focus was on a new strategy designed to reduce portfolio volatility while slightly enhancing return using a combination of futures and options on various asset classes. Intrigued by the idea, Ulster implemented the strategy for all of her clients and achieved positive results for all portfolios. Ulster’s average performance results after one year of using the new strategy are presented in Figure 1. For comparative purposes, performance figures without the new strategy are also presented.
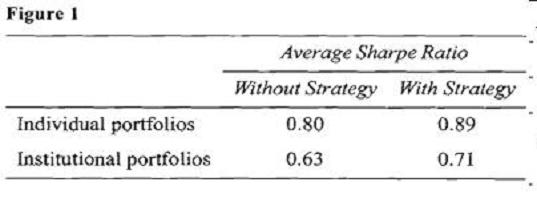
At the latest strategy meeting, DIS economists were extremely pessimistic about emerging market economies and suggested that the firm’s portfolio managers consider selling emerging market securities out of their portfolios and avoid these investments for the next 12 to 15 months. Fried placed a limit order to sell his personal holdings of an emerging market fund at a price 5% higher than the market price at the time. He then began selling his clients’ (all of whom have discretionary accounts with DIS) holdings of the same emerging market fund using market orders. All of his clients’ trade orders were completed just before the price of the fund declined sharply by 13%, causing Fried’s order to remain unfilled.
During her initial meeting with West, did Ulster violate any CFA Institute Standards of Professional Conduct?
- A . Yes.
- B . No, because she developed a detailed investment policy to ensure the suitability of investment choices for the client’s account.
- C . No, because she ensured that all conflicts of interest were disclosed to the client before the investment policy statement was created.
Dynamic Investment Services (DIS) is a global, full-service investment advisory firm based in the United States. Although the firm provides numerous investment services, DIS specializes in portfolio management for individual and institutional clients and only deals in publicly traded debt, equity, and derivative instruments. Walter Fried, CFA, is a portfolio manager and the director of DIS’s offices in Austria. For several years, Fried has maintained a relationship with a local tax consultant. The consultant provides a DIS marketing brochure with Fried’s contact information to his clients seeking investment advisory services, and in return. Fried manages the consultant’s personal portfolio and informs the consultant of potential tax issues in the referred clients’ portfolios as they occur. Because he cannot personally manage all of the inquiring clients’ assets, Fried generally passes the client information along to one of his employees but never discloses his relationship with the tax accountant. Fried recently forwarded information on the prospective Jones Family Trust account to Beverly Ulster, CFA, one of his newly hired portfolio managers.
Upon receiving the information, Ulster immediately set up a meeting with Terrence Phillips, the trustee of the Jones Family Trust. Ulster began the meeting by explaining DIS’s investment services as detailed in the firm’s approved marketing and public relations literature. Ulster also had Phillips complete a very detailed questionnaire regarding the risk and return objectives, investment constraints, and other information related to the trust beneficiaries, which Phillips is not. While reading the questionnaire, Ulster learned that Phillips heard about DIS’s services through a referral from his tax consultant. Upon further investigation, Ulster discovered the agreement set up between Fried and the tax consultant, which is legal according to Austrian law but was not disclosed by either party Ulster took a break from the meeting to get more details from Fried. With full information on the referral arrangement, Ulster immediately makes full disclosure to the Phillips. Before the meeting with Phillips concluded, Ulster began formalizing the investment policy statement (IPS) for the Jones Family Trust and agreed to Phillips’ request that the IPS should explicitly forbid derivative positions in the Trust portfolio.
A few hours after meeting with the Jones Family Trust representative, Ulster accepted another new referral client, Steven West, from Fried. Following DIS policy, Ulster met with West to address his investment objectives and constraints and explain the firm’s services. During the meeting, Ulster informed West that DIS offers three levels of account status, each with an increasing fee based on the account’s asset value. The first level has the lowest account fees but receives oversubscribed domestic IPO allocations only after the other two levels receive IPO allocations. The second-level clients have the same priority as third-level clients with respect to oversubscribed domestic IPO allocations and receive research with significantly greater detail than first-level clients. Clients who subscribe to the third level of DIS services receive the most detailed research reports and are allowed to participate in both domestic and international IPOs. All clients receive research and recommendations at approximately the same lime. West decided to engage DIS’s services as a second-level client. While signing the enrollment papers, West told Ulster, "If you can give me the kind of performance I am looking for, I may move the rest of my assets to DIS." When Ulster inquired about the other accounts, West would not specify how much or what type of assets he held in other accounts. West also noted that a portion of the existing assets to be transferred to Ulster’s control were private equity investments in small start-up companies, which DIS would need to manage. Ulster
assured him that DIS would have no problem managing the private equity investments.
After her meeting with West, Ulster attended a weekly strategy session held by DIS. All managers were required to attend this particular meeting since the focus was on a new strategy designed to reduce portfolio volatility while slightly enhancing return using a combination of futures and options on various asset classes. Intrigued by the idea, Ulster implemented the strategy for all of her clients and achieved positive results for all portfolios. Ulster’s average performance results after one year of using the new strategy are presented in Figure 1. For comparative purposes, performance figures without the new strategy are also presented.
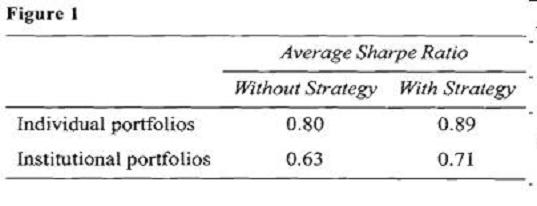
At the latest strategy meeting, DIS economists were extremely pessimistic about emerging market economies and suggested that the firm’s portfolio managers consider selling emerging market securities out of their portfolios and avoid these investments for the next 12 to 15 months. Fried placed a limit order to sell his personal holdings of an emerging market fund at a price 5% higher than the market price at the time. He then began selling his clients’ (all of whom have discretionary accounts with DIS) holdings of the same emerging market fund using market orders. All of his clients’ trade orders were completed just before the price of the fund declined sharply by 13%, causing Fried’s order to remain unfilled.
According to CFA Institute Standards of Professional Conduct, which of the following statements regarding
Ulster’s meeting with West is most accurate? Ulster may:
- A . offer the different service levels and may accept the account without full knowledge of West’s other accounts.
- B . not offer the different service levels but may accept the account without full knowledge of West’s other accounts.
- C . not offer the different service levels and may not accept the account without full knowledge of West’s other accounts.
Latest CFA Level 3 Dumps Valid Version with 362 Q&As
Latest And Valid Q&A | Instant Download | Once Fail, Full Refund

