Based on this information, which model would have the HIGHEST recall with respect to the fraudulent class?
A company wants to classify user behavior as either fraudulent or normal. Based on internal research, a Machine Learning Specialist would like to build a binary classifier based on two features: age of account and transaction month.
The class distribution for these features is illustrated in the figure provided.
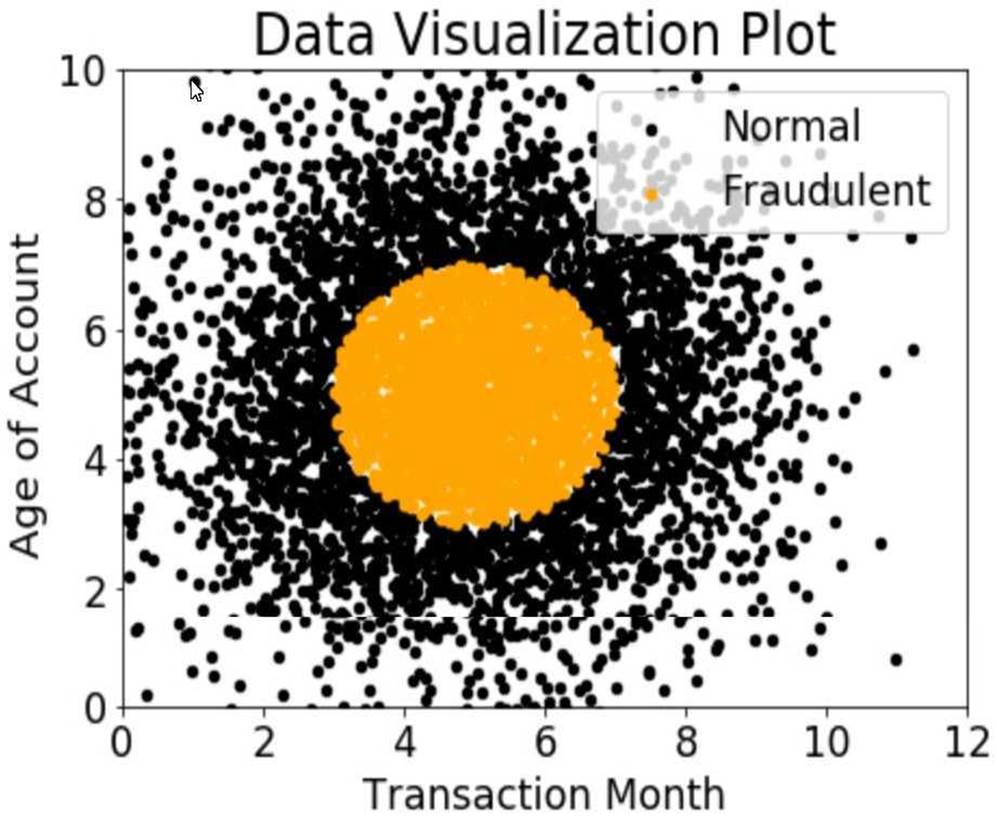
Based on this information, which model would have the HIGHEST recall with respect to the fraudulent class?
A . Decision tree
B . Linear support vector machine (SVM)
C . Naive Bayesian classifier
D . Single Perceptron with sigmoidal activation function
Answer: A
Explanation:
Based on the figure provided, a decision tree would have the highest recall with respect to the fraudulent class. Recall is a model evaluation metric that measures the proportion of actual positive instances that are correctly classified by the model. Recall is calculated as follows: Recall = True Positives / (True Positives + False Negatives)
A decision tree is a type of machine learning model that can perform classification tasks by splitting the data into smaller and purer subsets based on a series of rules or conditions. A decision tree can handle both linear and non-linear data, and can capture complex patterns and interactions among the features. A decision tree can also be easily visualized and interpreted1
In this case, the data is not linearly separable, and has a clear pattern of seasonality. The fraudulent class forms a large circle in the center of the plot, while the normal class is scattered around the edges. A decision tree can use the transaction month and the age of account as the splitting criteria, and create a circular boundary that separates the fraudulent class from the normal class. A decision tree can achieve a high recall for the fraudulent class, as it can correctly identify most of the black dots as positive instances, and minimize the number of false negatives. A decision tree can also adjust the depth and complexity of the tree to balance the trade-off between recall and precision23 The other options are not valid or suitable for achieving a high recall for the fraudulent class. A linear support vector machine (SVM) is a type of machine learning model that can perform classification tasks by finding a linear hyperplane that maximizes the margin between the classes. A linear SVM can handle linearly separable data, but not non-linear data. A linear SVM cannot capture the circular pattern of the fraudulent class, and may misclassify many of the black dots as negative instances, resulting in a low recall4 A naive Bayesian classifier is a type of machine learning model that can perform classification tasks by applying the Bayes’ theorem and assuming conditional independence among the features. A naive Bayesian classifier can handle both linear and non-linear data, and can incorporate prior knowledge and probabilities into the model. However, a naive Bayesian classifier may not perform well when the features are correlated or dependent, as in this case. A naive Bayesian classifier may not capture the circular pattern of the fraudulent class, and may misclassify many of the black dots as negative instances, resulting in a low recall5 A single perceptron with sigmoidal activation function is a type of machine learning model that can perform classification tasks by applying a weighted linear combination of the features and a non-linear activation function. A single perceptron with sigmoidal activation function can handle linearly separable data, but not non-linear data. A single perceptron with sigmoidal activation function cannot capture the circular pattern of the fraudulent class, and may misclassify many of the black dots as negative instances, resulting in a low recall.
Latest MLS-C01 Dumps Valid Version with 104 Q&As
Latest And Valid Q&A | Instant Download | Once Fail, Full Refund

